
Top ▲

Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 2 | 528 | 12q13.12 | ASIC1 | acid sensing ion channel subunit 1 | |
| Mouse | 2 | 526 | 15 F1 | Asic1 | acid-sensing ion channel 1 | |
| Rat | 2 | 526 | 7q36 | Asic1 | acid sensing ion channel subunit 1 | |
Database Links  |
|
| Alphafold | P78348 (Hs), Q6NXK8 (Mm), P55926 (Rn) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL1628477 (Hs), CHEMBL3232694 (Mm), CHEMBL3562170 (Rn) |
| DrugBank Target | P78348 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000110881 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000023017 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000059765 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 41 (Hs), 11419 (Mm), 79123 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000110881 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:41 (Hs), mmu:11419 (Mm), rno:79123 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 602866 (Hs) |
| Pharos | P78348 (Hs) |
| UniProtKB | P78348 (Hs), Q6NXK8 (Mm), P55926 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | ASIC1 (Hs) |
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||
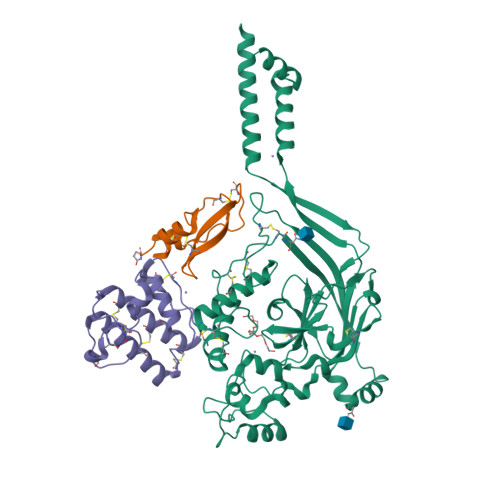
|
|
||||||||||
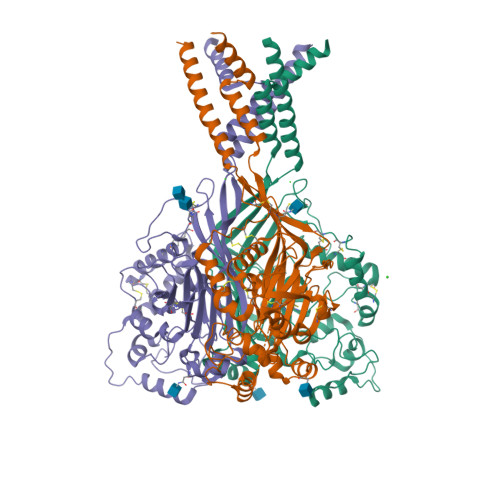
|
|
||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| H+ |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Activators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | Click column headers to sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Channel Blockers | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific channel blocker tables | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other Binding Ligands | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | Click column headers to sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immunopharmacology Comments |
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are direct inhibitors of ASIC currents (reviewed in [3]). Inflammatory conditions and particular pro-inflammatory mediators such as arachidonic acid induce overexpression of ASIC-encoding genes and enhance ASIC currents [7,16,21]. The sustained current component mediated by ASIC3 is potentiated by hypertonic solutions in a manner that is synergistic with the effect of arachidonic acid [7]. |
1. Baconguis I, Bohlen CJ, Goehring A, Julius D, Gouaux E. (2014) X-ray structure of acid-sensing ion channel 1-snake toxin complex reveals open state of a Na(+)-selective channel. Cell, 156 (4): 717-29. [PMID:24507937]
2. Baron A, Diochot S, Salinas M, Deval E, Noël J, Lingueglia E. (2013) Venom toxins in the exploration of molecular, physiological and pathophysiological functions of acid-sensing ion channels. Toxicon, 75: 187-204. [PMID:23624383]
3. Baron A, Lingueglia E. (2015) Pharmacology of acid-sensing ion channels - Physiological and therapeutical perspectives. Neuropharmacology, 94: 19-35. [PMID:25613302]
4. Brunner FS, Anaya-Rojas JM, Matthews B, Eizaguirre C. (2017) Experimental evidence that parasites drive eco-evolutionary feedbacks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 114 (14): 3678-3683. [PMID:28320947]
5. Buta A, Maximyuk O, Kovalskyy D, Sukach V, Vovk M, Ievglevskyi O, Isaeva E, Isaev D, Savotchenko A, Krishtal O. (2015) Novel Potent Orthosteric Antagonist of ASIC1a Prevents NMDAR-Dependent LTP Induction. J Med Chem, 58 (11): 4449-61. [PMID:25974655]
6. Chu XP, Wemmie JA, Wang WZ, Zhu XM, Saugstad JA, Price MP, Simon RP, Xiong ZG. (2004) Subunit-dependent high-affinity zinc inhibition of acid-sensing ion channels. J Neurosci, 24 (40): 8678-89. [PMID:15470133]
7. Deval E, Noël J, Lay N, Alloui A, Diochot S, Friend V, Jodar M, Lazdunski M, Lingueglia E. (2008) ASIC3, a sensor of acidic and primary inflammatory pain. EMBO J, 27 (22): 3047-55. [PMID:18923424]
8. Diochot S, Baron A, Salinas M, Douguet D, Scarzello S, Dabert-Gay AS, Debayle D, Friend V, Alloui A, Lazdunski M et al.. (2012) Black mamba venom peptides target acid-sensing ion channels to abolish pain. Nature, 490 (7421): 552-5. [PMID:23034652]
9. Dubé GR, Lehto SG, Breese NM, Baker SJ, Wang X, Matulenko MA, Honoré P, Stewart AO, Moreland RB, Brioni JD. (2005) Electrophysiological and in vivo characterization of A-317567, a novel blocker of acid sensing ion channels. Pain, 117 (1-2): 88-96. [PMID:16061325]
10. Er SY, Cristofori-Armstrong B, Escoubas P, Rash LD. (2017) Discovery and molecular interaction studies of a highly stable, tarantula peptide modulator of acid-sensing ion channel 1. Neuropharmacology, 127: 185-195. [PMID:28327374]
11. Escoubas P, De Weille JR, Lecoq A, Diochot S, Waldmann R, Champigny G, Moinier D, Ménez A, Lazdunski M. (2000) Isolation of a tarantula toxin specific for a class of proton-gated Na+ channels. J Biol Chem, 275 (33): 25116-21. [PMID:10829030]
12. Krauson AJ, Rooney JG, Carattino MD. (2018) Molecular basis of inhibition of acid sensing ion channel 1A by diminazene. PLoS One, 13 (5): e0196894. [PMID:29782492]
13. Lee JYP, Saez NJ, Cristofori-Armstrong B, Anangi R, King GF, Smith MT, Rash LD. (2018) Inhibition of acid-sensing ion channels by diminazene and APETx2 evoke partial and highly variable antihyperalgesia in a rat model of inflammatory pain. Br J Pharmacol, 175 (12): 2204-2218. [PMID:29134638]
14. Liu Y, Ma J, DesJarlais RL, Hagan R, Rech J, Lin D, Liu C, Miller R, Schoellerman J, Luo J et al.. (2021) Molecular mechanism and structural basis of small-molecule modulation of the gating of acid-sensing ion channel 1. Commun Biol, 4 (1): 174. [PMID:33564124]
15. Lynagh T, Romero-Rojo JL, Lund C, Pless SA. (2017) Molecular Basis for Allosteric Inhibition of Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1a by Ibuprofen. J Med Chem, 60 (19): 8192-8200. [PMID:28949138]
16. Mamet J, Baron A, Lazdunski M, Voilley N. (2002) Proinflammatory mediators, stimulators of sensory neuron excitability via the expression of acid-sensing ion channels. J Neurosci, 22 (24): 10662-70. [PMID:12486159]
17. Munro G, Christensen JK, Erichsen HK, Dyhring T, Demnitz J, Dam E, Ahring PK. (2016) NS383 Selectively Inhibits Acid-Sensing Ion Channels Containing 1a and 3 Subunits to Reverse Inflammatory and Neuropathic Hyperalgesia in Rats. CNS Neurosci Ther, 22 (2): 135-45. [PMID:26663905]
18. Qiang M, Dong X, Zha Z, Zuo XK, Song XL, Zhao L, Yuan C, Huang C, Tao P, Hu Q et al.. (2018) Selection of an ASIC1a-blocking combinatorial antibody that protects cells from ischemic death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 115 (32): E7469-E7477. [PMID:30042215]
19. Salinas M, Rash LD, Baron A, Lambeau G, Escoubas P, Lazdunski M. (2006) The receptor site of the spider toxin PcTx1 on the proton-gated cation channel ASIC1a. J Physiol, 570 (Pt 2): 339-54. [PMID:16284080]
20. Schmidt A, Rossetti G, Joussen S, Gründer S. (2017) Diminazene Is a Slow Pore Blocker of Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1a (ASIC1a). Mol Pharmacol, 92 (6): 665-675. [PMID:29025967]
21. Smith ES, Cadiou H, McNaughton PA. (2007) Arachidonic acid potentiates acid-sensing ion channels in rat sensory neurons by a direct action. Neuroscience, 145 (2): 686-98. [PMID:17258862]
22. Ugawa S, Ishida Y, Ueda T, Inoue K, Nagao M, Shimada S. (2007) Nafamostat mesilate reversibly blocks acid-sensing ion channel currents. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 363 (1): 203-8. [PMID:17826743]
23. Voilley N, de Weille J, Mamet J, Lazdunski M. (2001) Nonsteroid anti-inflammatory drugs inhibit both the activity and the inflammation-induced expression of acid-sensing ion channels in nociceptors. J Neurosci, 21 (20): 8026-33. [PMID:11588175]
24. Waldmann R, Champigny G, Bassilana F, Heurteaux C, Lazdunski M. (1997) A proton-gated cation channel involved in acid-sensing. Nature, 386 (6621): 173-7. [PMID:9062189]
25. Wang W, Duan B, Xu H, Xu L, Xu TL. (2006) Calcium-permeable acid-sensing ion channel is a molecular target of the neurotoxic metal ion lead. J Biol Chem, 281 (5): 2497-505. [PMID:16319075]
26. Yoder N, Yoshioka C, Gouaux E. (2018) Gating mechanisms of acid-sensing ion channels. Nature, 555 (7696): 397-401. [PMID:29513651]