1. Briscoe CP, Peat AJ, McKeown SC, Corbett DF, Goetz AS, Littleton TR, McCoy DC, Kenakin TP, Andrews JL, Ammala C et al.. (2006) Pharmacological regulation of insulin secretion in MIN6 cells through the fatty acid receptor GPR40: identification of agonist and antagonist small molecules.
Br J Pharmacol, 148 (5): 619-28.
[PMID:16702987]
2. Briscoe CP, Tadayyon M, Andrews JL, Benson WG, Chambers JK, Eilert MM, Ellis C, Elshourbagy NA, Goetz AS, Minnick DT et al.. (2003) The orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR40 is activated by medium and long chain fatty acids.
J Biol Chem, 278 (13): 11303-11.
[PMID:12496284]
3. Chen Y, Ren Q, Zhou Z, Deng L, Hu L, Zhang L, Li Z. (2020) HWL-088, a new potent free fatty acid receptor 1 (FFAR1) agonist, improves glucolipid metabolism and acts additively with metformin in ob/ob diabetic mice.
Br J Pharmacol, 177 (10): 2286-2302.
[PMID:31971610]
4. Christiansen E, Due-Hansen ME, Urban C, Grundmann M, Schröder R, Hudson BD, Milligan G, Cawthorne MA, Kostenis E, Kassack MU et al.. (2012) Free fatty acid receptor 1 (FFA1/GPR40) agonists: mesylpropoxy appendage lowers lipophilicity and improves ADME properties.
J Med Chem, 55 (14): 6624-8.
[PMID:22724451]
5. Christiansen E, Hansen SV, Urban C, Hudson BD, Wargent ET, Grundmann M, Jenkins L, Zaibi M, Stocker CJ, Ullrich S et al.. (2013) Discovery of TUG-770: A Highly Potent Free Fatty Acid Receptor 1 (FFA1/GPR40) Agonist for Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes.
ACS Med Chem Lett, 4 (5): 441-445.
[PMID:23687558]
6. Christiansen E, Hudson BD, Hansen AH, Milligan G, Ulven T. (2016) Development and Characterization of a Potent Free Fatty Acid Receptor 1 (FFA1) Fluorescent Tracer.
J Med Chem, 59 (10): 4849-58.
[PMID:27074625]
7. Christiansen E, Urban C, Merten N, Liebscher K, Karlsen KK, Hamacher A, Spinrath A, Bond AD, Drewke C, Ullrich S et al.. (2008) Discovery of potent and selective agonists for the free fatty acid receptor 1 (FFA(1)/GPR40), a potential target for the treatment of type II diabetes.
J Med Chem, 51 (22): 7061-4.
[PMID:18947221]
8. Feng DD, Luo Z, Roh SG, Hernandez M, Tawadros N, Keating DJ, Chen C. (2006) Reduction in voltage-gated K+ currents in primary cultured rat pancreatic beta-cells by linoleic acids.
Endocrinology, 147: 674-682.
[PMID:16254037]
9. Flodgren E, Olde B, Meidute-Abaraviciene S, Winzell MS, Ahrén B, Salehi A. (2007) GPR40 is expressed in glucagon producing cells and affects glucagon secretion.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 354 (1): 240-5.
[PMID:17214971]
10. Gagnon L, Leduc M, Thibodeau JF, Zhang MZ, Grouix B, Sarra-Bournet F, Gagnon W, Hince K, Tremblay M, Geerts L et al.. (2018) A Newly Discovered Antifibrotic Pathway Regulated by Two Fatty Acid Receptors: GPR40 and GPR84.
Am J Pathol, 188 (5): 1132-1148.
[PMID:29454750]
11. Garrido DM, Corbett DF, Dwornik KA, Goetz AS, Littleton TR, McKeown SC, Mills WY, Smalley Jr TL, Briscoe CP, Peat AJ. (2006) Synthesis and activity of small molecule GPR40 agonists.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 16 (7): 1840-5.
[PMID:16439116]
12. Hardy S, St-Onge GG, Joly E, Langelier Y, Prentki M. (2005) Oleate promotes the proliferation of breast cancer cells via the G protein-coupled receptor GPR40.
J Biol Chem, 280 (14): 13285-91.
[PMID:15695516]
13. Itoh Y, Kawamata Y, Harada M, Kobayashi M, Fujii R, Fukusumi S, Ogi K, Hosoya M, Tanaka Y, Uejima H et al.. (2003) Free fatty acids regulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells through GPR40.
Nature, 422 (6928): 173-6.
[PMID:12629551]
14. Kaku K, Enya K, Nakaya R, Ohira T, Matsuno R. (2015) Efficacy and safety of fasiglifam (TAK-875), a G protein-coupled receptor 40 agonist, in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled by diet and exercise: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial.
Diabetes Obes Metab, 17 (7): 675-81.
[PMID:25787200]
15. Kotarsky K, Nilsson NE, Flodgren E, Owman C, Olde B. (2003) A human cell surface receptor activated by free fatty acids and thiazolidinedione drugs.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 301 (2): 406-10.
[PMID:12565875]
16. Lin DC, Guo Q, Luo J, Zhang J, Nguyen K, Chen M, Tran T, Dransfield PJ, Brown SP, Houze J et al.. (2012) Identification and pharmacological characterization of multiple allosteric binding sites on the free fatty acid 1 receptor.
Mol Pharmacol, 82 (5): 843-59.
[PMID:22859723]
17. Ma D, Tao B, Warashina S, Kotani S, Lu L, Kaplamadzhiev DB, Mori Y, Tonchev AB, Yamashima T. (2007) Expression of free fatty acid receptor GPR40 in the central nervous system of adult monkeys.
Neurosci Res, 58 (4): 394-401.
[PMID:17583366]
18. McKeown SC, Corbett DF, Goetz AS, Littleton TR, Bigham E, Briscoe CP, Peat AJ, Watson SP, Hickey DM. (2007) Solid phase synthesis and SAR of small molecule agonists for the GPR40 receptor.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 17 (6): 1584-9.
[PMID:17240142]
19. Negoro N, Sasaki S, Mikami S, Ito M, Suzuki M, Tsujihata Y, Ito R, Harada A, Takeuchi K, Suzuki N et al.. (2010) Discovery of TAK-875: A Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable GPR40 Agonist.
ACS Med Chem Lett, 1 (6): 290-4.
[PMID:24900210]
20. Ogawa T, Hirose H, Miyashita K, Saito I, Saruta T. (2005) GPR40 gene Arg211His polymorphism may contribute to the variation of insulin secretory capacity in Japanese men.
Metab Clin Exp, 54 (3): 296-9.
[PMID:15736105]
21. Sawzdargo M, George SR, Nguyen T, Xu S, Kolakowski LF, O'Dowd BF. (1997) A cluster of four novel human G protein-coupled receptor genes occurring in close proximity to CD22 gene on chromosome 19q13.1.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 239 (2): 543-7.
[PMID:9344866]
22. Song F, Lu S, Gunnet J, Xu JZ, Wines P, Proost J, Liang Y, Baumann C, Lenhard J, Murray WV et al.. (2007) Synthesis and biological evaluation of 3-aryl-3-(4-phenoxy)-propionic acid as a novel series of G protein-coupled receptor 40 agonists.
J Med Chem, 50 (12): 2807-17.
[PMID:17500511]
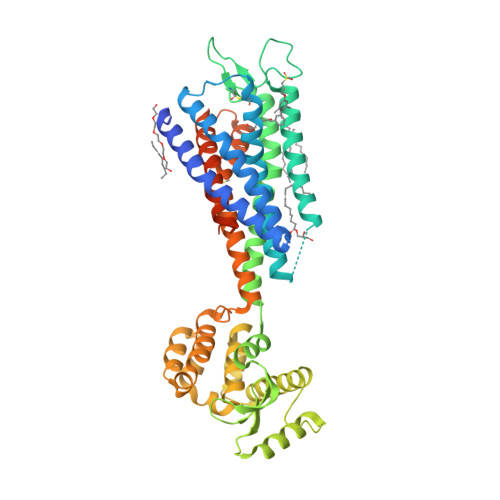
23. Srivastava A, Yano J, Hirozane Y, Kefala G, Gruswitz F, Snell G, Lane W, Ivetac A, Aertgeerts K, Nguyen J et al.. (2014) High-resolution structure of the human GPR40 receptor bound to allosteric agonist TAK-875.
Nature, 513 (7516): 124-7.
[PMID:25043059]
24. Steneberg P, Rubins N, Bartoov-Shifman R, Walker MD, Edlund H. (2005) The FFA receptor GPR40 links hyperinsulinemia, hepatic steatosis, and impaired glucose homeostasis in mouse.
Cell Metab, 1 (4): 245-58.
[PMID:16054069]
25. Stoddart LA, Brown AJ, Milligan G. (2007) Uncovering the pharmacology of the G protein-coupled receptor GPR40: high apparent constitutive activity in guanosine 5'-O-(3-[35S]thio)triphosphate binding studies reflects binding of an endogenous agonist.
Mol Pharmacol, 71 (4): 994-1005.
[PMID:17200419]
26. Sum CS, Tikhonova IG, Neumann S, Engel S, Raaka BM, Costanzi S, Gershengorn MC. (2007) Identification of residues important for agonist recognition and activation in GPR40.
J Biol Chem, 282 (40): 29248-55.
[PMID:17699519]
27. Tan CP, Feng Y, Zhou YP, Eiermann GJ, Petrov A, Zhou C, Lin S, Salituro G, Meinke P, Mosley R et al.. (2008) Selective small-molecule agonists of G protein-coupled receptor 40 promote glucose-dependent insulin secretion and reduce blood glucose in mice.
Diabetes, 57 (8): 2211-9.
[PMID:18477808]
28. Tikhonova IG, Sum CS, Neumann S, Thomas CJ, Raaka BM, Costanzi S, Gershengorn MC. (2007) Bidirectional, iterative approach to the structural delineation of the functional "chemoprint" in GPR40 for agonist recognition.
J Med Chem, 50 (13): 2981-9.
[PMID:17552505]
29. Tsujihata Y, Ito R, Suzuki M, Harada A, Negoro N, Yasuma T, Momose Y, Takeuchi K. (2011) TAK-875, an orally available G protein-coupled receptor 40/free fatty acid receptor 1 agonist, enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion and improves both postprandial and fasting hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetic rats.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 339 (1): 228-37.
[PMID:21752941]