
Top ▲

Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| class A G protein-coupled receptor | ||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 7 | 419 | 11p15.5 | DRD4 | dopamine receptor D4 | 74 |
| Mouse | 7 | 387 | 7 86.6 cM | Drd4 | dopamine receptor D4 | 41 |
| Rat | 7 | 387 | 1q41 | Drd4 | dopamine receptor D4 | 17 |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| d(2C) dopamine receptor | dopamine receptor 4 | D4R |
Database Links  |
|
| Specialist databases | |
| GPCRdb | drd4_human (Hs), drd4_mouse (Mm), drd4_rat (Rn) |
| Other databases | |
| Alphafold | P21917 (Hs), P51436 (Mm), P30729 (Rn) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL219 (Hs), CHEMBL2574 (Mm), CHEMBL3361 (Rn) |
| DrugBank Target | P21917 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000069696 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000025496 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000017927 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 1815 (Hs), 13491 (Mm), 25432 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000069696 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:1815 (Hs), mmu:13491 (Mm), rno:25432 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 126452 (Hs) |
| Pharos | P21917 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_000797 (Hs), NM_007878 (Mm), NM_012944 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_000788 (Hs), NP_031904 (Mm), NP_037076 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | P21917 (Hs), P51436 (Mm), P30729 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | DRD4 (Hs) |
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
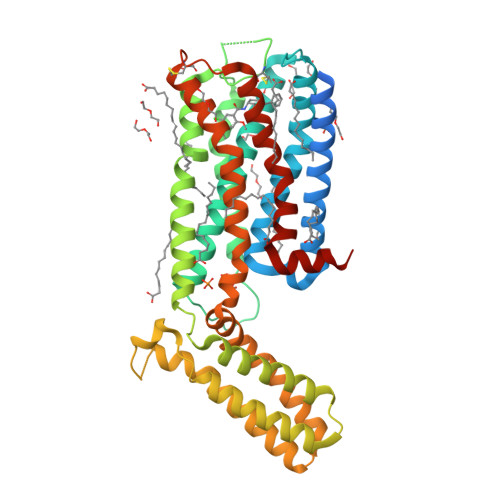
|
|
||||||||||||
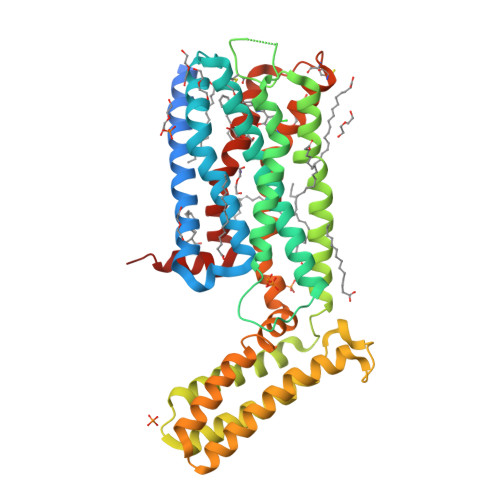
|
|
||||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| dopamine |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific agonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific antagonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immuno Process Associations | ||
|
Primary Transduction Mechanisms 
|
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gi/Go family | Adenylyl cyclase inhibition |
| References: 45 | |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Expression Datasets  |
|
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Biologically Significant Variants 
|
||||||||
|
| General Comments |
|
Human and primate receptors have a variable number (2-10) of imperfect 48 bp repeats in exon 3 [31,75]. This leads to a highly variable length and amino acid composition of the putative third cytoplasmic loop, apparently not associated with any marked variation in pharmacology. In humans the D4.2, D4.4 and D4.7 variants are the predominant variants [55]. Most D4 receptor-antagonists display agonistic activities in some heterologous expression systems [18-19]. |
1. Al Hussainy R, Verbeek J, van der Born D, Braker AH, Leysen JE, Knol RJ, Booij J, Herscheid JK. (2011) Design, synthesis, radiolabeling, and in vitro and in vivo evaluation of bridgehead iodinated analogues of N-{2-[4-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl]ethyl}-N-(pyridin-2-yl)cyclohexanecarboxamide (WAY-100635) as potential SPECT ligands for the 5-HT1A receptor. J Med Chem, 54 (10): 3480-91. [PMID:21520940]
2. Asghari V, Sanyal S, Buchwaldt S, Paterson A, Jovanovic V, Van Tol HH. (1995) Modulation of intracellular cyclic AMP levels by different human dopamine D4 receptor variants. J Neurochem, 65 (3): 1157-65. [PMID:7643093]
3. Auerbach SS, DrugMatrix® and ToxFX® Coordinator National Toxicology Program. National Toxicology Program: Dept of Health and Human Services. Accessed on 02/05/2014. Modified on 02/05/2014. DrugMatrix, https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/drugmatrix/index.html
4. Bek MJ, Wang X, Asico LD, Jones JE, Zheng S, Li X, Eisner GM, Grandy DK, Carey RM, Soares-da-Silva P et al.. (2006) Angiotensin-II type 1 receptor-mediated hypertension in D4 dopamine receptor-deficient mice. Hypertension, 47 (2): 288-95. [PMID:16380537]
5. Bergman J, Roof RA, Furman CA, Conroy JL, Mello NK, Sibley DR, Skolnick P. (2013) Modification of cocaine self-administration by buspirone (buspar®): potential involvement of D3 and D4 dopamine receptors. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol, 16 (2): 445-58. [PMID:22827916]
6. Berry CB, Bubser M, Jones CK, Hayes JP, Wepy JA, Locuson CW, Daniels JS, Lindsley CW, Hopkins CR. (2014) Discovery and Characterization of ML398, a Potent and Selective Antagonist of the D4 Receptor with in Vivo Activity. ACS Med Chem Lett, 5 (9): 1060-4. [PMID:25221667]
7. Burstein ES, Ma J, Wong S, Gao Y, Pham E, Knapp AE, Nash NR, Olsson R, Davis RE, Hacksell U et al.. (2005) Intrinsic efficacy of antipsychotics at human D2, D3, and D4 dopamine receptors: identification of the clozapine metabolite N-desmethylclozapine as a D2/D3 partial agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 315 (3): 1278-87. [PMID:16135699]
8. Chemel BR, Roth BL, Armbruster B, Watts VJ, Nichols DE. (2006) WAY-100635 is a potent dopamine D4 receptor agonist. Psychopharmacology (Berl.), 188 (2): 244-51. [PMID:16915381]
9. Chen K, Deng K, Wang X, Wang Z, Zheng S, Ren H, He D, Han Y, Asico LD, Jose PA et al.. (2015) Activation of D4 dopamine receptor decreases angiotensin II type 1 receptor expression in rat renal proximal tubule cells. Hypertension, 65 (1): 153-60. [PMID:25368031]
10. Chio CL, Drong RF, Riley DT, Gill GS, Slightom JL, Huff RM. (1994) D4 dopamine receptor-mediated signaling events determined in transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem, 269 (16): 11813-9. [PMID:7512953]
11. Cohen AI, Todd RD, Harmon S, O'Malley KL. (1992) Photoreceptors of mouse retinas possess D4 receptors coupled to adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 89 (24): 12093-7. [PMID:1334557]
12. Collins GT, Butler P, Wayman C, Ratcliffe S, Gupta P, Oberhofer G, Caine SB. (2012) Lack of abuse potential in a highly selective dopamine D3 agonist, PF-592,379, in drug self-administration and drug discrimination in rats. Behav Pharmacol, 23 (3): 280-91. [PMID:22470105]
13. Dulawa SC, Grandy DK, Low MJ, Paulus MP, Geyer MA. (1999) Dopamine D4 receptor-knock-out mice exhibit reduced exploration of novel stimuli. J Neurosci, 19 (21): 9550-6. [PMID:10531457]
14. Durcan MJ, Rigdon GC, Norman MH, Morgan PF. (1995) Is clozapine selective for the dopamine D4 receptor?. Life Sci, 57 (18): PL275-83. [PMID:7475902]
15. El-Faddagh M, Laucht M, Maras A, Vöhringer L, Schmidt MH. (2004) Association of dopamine D4 receptor (DRD4) gene with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in a high-risk community sample: a longitudinal study from birth to 11 years of age. J Neural Transm (Vienna), 111 (7): 883-9. [PMID:15206004]
16. Falzone TL, Gelman DM, Young JI, Grandy DK, Low MJ, Rubinstein M. (2002) Absence of dopamine D4 receptors results in enhanced reactivity to unconditioned, but not conditioned, fear. Eur J Neurosci, 15 (1): 158-64. [PMID:11860516]
17. Fishburn CS, Carmon S, Fuchs S. (1995) Molecular cloning and characterisation of the gene encoding the murine D4 dopamine receptor. FEBS Lett, 361: 215-219. [PMID:7698326]
18. Gazi L, Bobirnac I, Danzeisen M, Schüpbach E, Bruinvels AT, Geisse S, Sommer B, Hoyer D, Tricklebank M, Schoeffter P. (1998) The agonist activities of the putative antipsychotic agents, L-745,870 and U-101958 in HEK293 cells expressing the human dopamine D4.4 receptor. Br J Pharmacol, 124 (5): 889-96. [PMID:9692773]
19. Gazi L, Bobirnac I, Danzeisen M, Schüpbach E, Langenegger D, Sommer B, Hoyer D, Tricklebank M, Schoeffter P. (1999) Receptor density as a factor governing the efficacy of the dopamine D4 receptor ligands, L-745,870 and U-101958 at human recombinant D4.4 receptors expressed in CHO cells. Br J Pharmacol, 128 (3): 613-20. [PMID:10516640]
20. Gazi L, Schoeffter P, Nunn C, Croskery K, Hoyer D, Feuerbach D. (2000) Cloning, expression, functional coupling and pharmacological characterization of the rat dopamine D4 receptor. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol, 361 (5): 555-64. [PMID:10832611]
21. Glavin GB, Hall AM. (1994) Clozapine, a dopamine DA4 receptor antagonist, reduces gastric acid secretion and stress-induced gastric mucosal injury. Life Sci, 54 (16): PL261-4. [PMID:8152334]
22. Grady DL, Thanos PK, Corrada MM, Barnett Jr JC, Ciobanu V, Shustarovich D, Napoli A, Moyzis AG, Grandy D, Rubinstein M et al.. (2013) DRD4 genotype predicts longevity in mouse and human. J Neurosci, 33 (1): 286-91. [PMID:23283341]
23. Graziane NM, Yuen EY, Yan Z. (2009) Dopamine D4 Receptors Regulate GABAA Receptor Trafficking via an Actin/Cofilin/Myosin-dependent Mechanism. J Biol Chem, 284 (13): 8329-36. [PMID:19179335]
24. Hidaka K, Matsumoto M, Tada S, Tasaki Y, Yamaguchi T. (1995) Differential effects of [3H]nemonapride and [3H]spiperone binding on human dopamine D4 receptors. Neurosci Lett, 186 (2-3): 145-8. [PMID:7777184]
25. Kim JS, Bailey MJ, Weller JL, Sugden D, Rath MF, Møller M, Klein DC. (2010) Thyroid hormone and adrenergic signaling interact to control pineal expression of the dopamine receptor D4 gene (Drd4). Mol Cell Endocrinol, 314 (1): 128-35. [PMID:19482058]
26. Kortagere S, Gmeiner P, Weinstein H, Schetz JA. (2004) Certain 1,4-disubstituted aromatic piperidines and piperazines with extreme selectivity for the dopamine D4 receptor interact with a common receptor microdomain. Mol Pharmacol, 66 (6): 1491-9. [PMID:15448188]
27. Kroeze WK, Sassano MF, Huang XP, Lansu K, McCorvy JD, Giguère PM, Sciaky N, Roth BL. (2015) PRESTO-Tango as an open-source resource for interrogation of the druggable human GPCRome. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 22 (5): 362-9. [PMID:25895059]
28. Kulagowski JJ, Broughton HB, Curtis NR, Mawer IM, Ridgill MP, Baker R, Emms F, Freedman SB, Marwood R, Patel S et al.. (1996) 3-((4-(4-Chlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-methyl)-1H-pyrrolo-2,3-b-pyridine: an antagonist with high affinity and selectivity for the human dopamine D4 receptor. J Med Chem, 39 (10): 1941-2. [PMID:8642550]
29. Lahti RA, Evans DL, Stratman NC, Figur LM. (1993) Dopamine D4 versus D2 receptor selectivity of dopamine receptor antagonists: possible therapeutic implications. Eur J Pharmacol, 236 (3): 483-6. [PMID:8102973]
30. Lanau F, Zenner MT, Civelli O, Hartman DS. (1997) Epinephrine and norepinephrine act as potent agonists at the recombinant human dopamine D4 receptor. J Neurochem, 68 (2): 804-12. [PMID:9003072]
31. Livak KJ, Rogers J, Lichter JB. (1995) Variability of dopamine D4 receptor (DRD4) gene sequence within and among nonhuman primate species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 92 (2): 427-31. [PMID:7831304]
32. McAllister G, Knowles MR, Ward-Booth SM, Sinclair HA, Patel S, Marwood R, Emms F, Patel S, Smith A, Seabrook GR et al.. (1995) Functional coupling of human D2, D3, and D4 dopamine receptors in HEK293 cells. J Recept Signal Transduct Res, 15 (1-4): 267-81. [PMID:8903944]
33. Meade JA, Free RB, Miller NR, Chun LS, Doyle TB, Moritz AE, Conroy JL, Watts VJ, Sibley DR. (2015) (-)-Stepholidine is a potent pan-dopamine receptor antagonist of both G protein- and β-arrestin-mediated signaling. Psychopharmacology (Berl.), 232 (5): 917-30. [PMID:25231919]
34. Meador-Woodruff JH, Damask SP, Wang J, Haroutunian V, Davis KL, Watson SJ. (1996) Dopamine receptor mRNA expression in human striatum and neocortex. Neuropsychopharmacology, 15 (1): 17-29. [PMID:8797188]
35. Mei YA, Griffon N, Buquet C, Martres MP, Vaudry H, Schwartz JC, Sokoloff P, Cazin L. (1995) Activation of dopamine D4 receptor inhibits an L-type calcium current in cerebellar granule cells. Neuroscience, 68 (1): 107-16. [PMID:7477916]
36. Millan MJ, Maiofiss L, Cussac D, Audinot V, Boutin JA, Newman-Tancredi A. (2002) Differential actions of antiparkinson agents at multiple classes of monoaminergic receptor. I. A multivariate analysis of the binding profiles of 14 drugs at 21 native and cloned human receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 303 (2): 791-804. [PMID:12388666]
37. Moreland RB, Patel M, Hsieh GC, Wetter JM, Marsh K, Brioni JD. (2005) A-412997 is a selective dopamine D4 receptor agonist in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav, 82 (1): 140-7. [PMID:16153699]
38. Mulcrone J, Kerwin RW. (1997) The regional pattern of D4 gene expression in human brain. Neurosci Lett, 234 (2-3): 147-50. [PMID:9364519]
39. Nakane M, Cowart MD, Hsieh GC, Miller L, Uchic ME, Chang R, Terranova MA, Donnelly-Roberts DL, Namovic MT, Miller TR et al.. (2005) 2-[4-(3,4-Dimethylphenyl)piperazin-1-ylmethyl]-1H benzoimidazole (A-381393), a selective dopamine D4 receptor antagonist. Neuropharmacology, 49 (1): 112-21. [PMID:15992586]
40. Nir I, Harrison JM, Haque R, Low MJ, Grandy DK, Rubinstein M, Iuvone PM. (2002) Dysfunctional light-evoked regulation of cAMP in photoreceptors and abnormal retinal adaptation in mice lacking dopamine D4 receptors. J Neurosci, 22 (6): 2063-73. [PMID:11896146]
41. O'Malley KL, Harmon S, Tang L, Todd RD. (1992) The rat dopamine D4 receptor: sequence, gene structure, and demonstration of expression in the cardiovascular system. New Biol, 4 (2): 137-46. [PMID:1554689]
42. Patel MV, Kolasa T, Mortell K, Matulenko MA, Hakeem AA, Rohde JJ, Nelson SL, Cowart MD, Nakane M, Miller LN et al.. (2006) Discovery of 3-methyl-N-(1-oxy-3',4',5',6'-tetrahydro-2'H-[2,4'-bipyridine]-1'-ylmethyl)benzamide (ABT-670), an orally bioavailable dopamine D4 agonist for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. J Med Chem, 49 (25): 7450-65. [PMID:17149874]
43. Patel S, Freedman S, Chapman KL, Emms F, Fletcher AE, Knowles M, Marwood R, Mcallister G, Myers J, Curtis N et al.. (1997) Biological profile of L-745,870, a selective antagonist with high affinity for the dopamine D4 receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 283 (2): 636-47. [PMID:9353380]
44. Patel S, Patel S, Marwood R, Emms F, Marston D, Leeson PD, Curtis NR, Kulagowski JJ, Freedman SB. (1996) Identification and pharmacological characterization of [125I]L-750,667, a novel radioligand for the dopamine D4 receptor. Mol Pharmacol, 50 (6): 1658-64. [PMID:8967990]
45. Pilla M, Perachon S, Sautel F, Garrido F, Mann A, Wermuth CG, Schwartz JC, Everitt BJ, Sokoloff P. (1999) Selective inhibition of cocaine-seeking behaviour by a partial dopamine D3 receptor agonist. Nature, 400 (6742): 371-5. [PMID:10432116]
46. Pillai G, Brown NA, McAllister G, Milligan G, Seabrook GR. (1998) Human D2 and D4 dopamine receptors couple through betagamma G-protein subunits to inwardly rectifying K+ channels (GIRK1) in a Xenopus oocyte expression system: selective antagonism by L-741,626 and L-745,870 respectively. Neuropharmacology, 37: 983-987. [PMID:9833627]
47. Primus RJ, Thurkauf A, Xu J, Yevich E, McInerney S, Shaw K, Tallman JF, Gallagher DW. (1997) II. Localization and characterization of dopamine D4 binding sites in rat and human brain by use of the novel, D4 receptor-selective ligand [3H]NGD 94-1. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 282 (2): 1020-7. [PMID:9262371]
48. Ricci A, Mignini F, Tomassoni D, Amenta F. (2006) Dopamine receptor subtypes in the human pulmonary arterial tree. Auton Autacoid Pharmacol, 26 (4): 361-9. [PMID:16968475]
49. Rivera A, Peñafiel A, Megías M, Agnati LF, López-Téllez JF, Gago B, Gutiérrez A, de la Calle A, Fuxe K. (2008) Cellular localization and distribution of dopamine D(4) receptors in the rat cerebral cortex and their relationship with the cortical dopaminergic and noradrenergic nerve terminal networks. Neuroscience, 155 (3): 997-1010. [PMID:18620029]
50. Rivera A, Trías S, Peñafiel A, Angel Narváez J, Díaz-Cabiale Z, Moratalla R, de la Calle A. (2003) Expression of D4 dopamine receptors in striatonigral and striatopallidal neurons in the rat striatum. Brain Res, 989 (1): 35-41. [PMID:14519509]
51. Rowley M, Broughton HB, Collins I, Baker R, Emms F, Marwood R, Patel S, Patel S, Ragan CI, Freedman SB et al.. (1996) 5-(4-Chlorophenyl)-4-methyl-3-(1-(2-phenylethyl)piperidin-4-yl)isoxazole: a potent, selective antagonist at human cloned dopamine D4 receptors. J Med Chem, 39 (10): 1943-5. [PMID:8642551]
52. Rubinstein M, Phillips TJ, Bunzow JR, Falzone TL, Dziewczapolski G, Zhang G, Fang Y, Larson JL, McDougall JA, Chester JA, Saez C, Pugsley TA, Gershanik O, Low MJ, Grandy DK. (1997) Mice lacking dopamine D4 receptors are supersensitive to ethanol, cocaine, and methamphetamine. Cell, 90: 991-1001. [PMID:9323127]
53. Schetz JA, Benjamin PS, Sibley DR. (2000) Nonconserved residues in the second transmembrane-spanning domain of the D(4) dopamine receptor are molecular determinants of D(4)-selective pharmacology. Mol Pharmacol, 57 (1): 144-52. [PMID:10617689]
54. Schlachter SK, Poel TJ, Lawson CF, Dinh DM, Lajiness ME, Romero AG, Rees SA, Duncan JN, Smith MW. (1997) Substituted 4-aminopiperidines having high in vitro affinity and selectivity for the cloned human dopamine D4 receptor. Eur J Pharmacol, 322 (2-3): 283-6. [PMID:9098699]
55. Schoots O, Van Tol HH. (2003) The human dopamine D4 receptor repeat sequences modulate expression. Pharmacogenomics J, 3 (6): 343-8. [PMID:14581929]
56. Schotte A, Janssen PF, Gommeren W, Luyten WH, Van Gompel P, Lesage AS, De Loore K, Leysen JE. (1996) Risperidone compared with new and reference antipsychotic drugs: in vitro and in vivo receptor binding. Psychopharmacology (Berl.), 124 (1-2): 57-73. [PMID:8935801]
57. Seeman P. (2001) Antipsychotic drugs, dopamine receptors, and schizophrenia. Clinical Neuroscience Research, 1 (1-2): 53-60. DOI: 10.1016/S1566-2772(00)00007-4
58. Seeman P, Corbett R, Van Tol HH. (1997) Atypical neuroleptics have low affinity for dopamine D2 receptors or are selective for D4 receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology, 16 (2): 93-110; discussion 111-35. [PMID:9015795]
59. Seeman P, Guan HC, Van Tol HH, Niznik HB. (1993) Low density of dopamine D4 receptors in Parkinson's, schizophrenia, and control brain striata. Synapse, 14: 247-253. [PMID:8248849]
60. Seeman P, Tallerico T. (1998) Antipsychotic drugs which elicit little or no parkinsonism bind more loosely than dopamine to brain D2 receptors, yet occupy high levels of these receptors. Mol Psychiatry, 3 (2): 123-34. [PMID:9577836]
61. Shahid M, Walker GB, Zorn SH, Wong EH. (2009) Asenapine: a novel psychopharmacologic agent with a unique human receptor signature. J Psychopharmacol (Oxford), 23 (1): 65-73. [PMID:18308814]
62. Shih YH, Chung FZ, Pugsley TA. (1997) Cloning, expression and characterization of a human dopamine D4.2 receptor (CHO K1 cells) and various D4.2/D2L chimeras (COS-7 cells). Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry, 21 (1): 153-67. [PMID:9075264]
63. Shin Y, Kumar U, Patel Y, Patel SC, Sidhu A. (2003) Differential expression of D2-like dopamine receptors in the kidney of the spontaneously hypertensive rat. J Hypertens, 21 (1): 199-207. [PMID:12544452]
64. Skaaning Jensen B, Levavi-Sivan B, Fishburn CS, Fuchs S. (1997) Functional expression of the murine D2, D3, and D4 dopamine receptors in Xenopus laevis oocytes. FEBS Lett, 420: 191-195. [PMID:9459308]
65. Sun D, Wilborn TW, Schafer JA. (1998) Dopamine D4 receptor isoform mRNA and protein are expressed in the rat cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol, 275 (5): F742-51. [PMID:9815131]
66. Sunohara GA, Roberts W, Malone M, Schachar RJ, Tannock R, Basile VS, Wigal T, Wigal SB, Schuck S, Moriarty J, Swanson JM, Kennedy JL, Barr CL. (2000) Linkage of the dopamine D4 receptor gene and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry, 39: 1537-1542. [PMID:11128331]
67. Suzuki T, Kobayashi K, Nagatsu T. (1995) Genomic structure and tissue distribution of the mouse dopamine D4 receptor. Neurosci Lett, 199: 69-72. [PMID:8584230]
68. Svingos AL, Periasamy S, Pickel VM. (2000) Presynaptic dopamine D(4) receptor localization in the rat nucleus accumbens shell. Synapse, 36 (3): 222-32. [PMID:10819901]
69. Tallman JF, Primus RJ, Brodbeck R, Cornfield L, Meade R, Woodruff K, Ross P, Thurkauf A, Gallager DW. (1997) I. NGD 94-1: identification of a novel, high-affinity antagonist at the human dopamine D4 receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 282 (2): 1011-9. [PMID:9262370]
70. Tang L, Todd RD, Heller A, O'Malley KL. (1994) Pharmacological and functional characterization of D2, D3 and D4 dopamine receptors in fibroblast and dopaminergic cell lines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 268 (1): 495-502. [PMID:8301592]
71. Thomas TC, Grandy DK, Gerhardt GA, Glaser PE. (2009) Decreased dopamine D4 receptor expression increases extracellular glutamate and alters its regulation in mouse striatum. Neuropsychopharmacology, 34 (2): 436-45. [PMID:18536704]
72. Thomas TC, Kruzich PJ, Joyce BM, Gash CR, Suchland K, Surgener SP, Rutherford EC, Grandy DK, Gerhardt GA, Glaser PE. (2007) Dopamine D4 receptor knockout mice exhibit neurochemical changes consistent with decreased dopamine release. J Neurosci Methods, 166 (2): 306-14. [PMID:17449106]
73. Tice MA, Hashemi T, Taylor LA, Duffy RA, McQuade RD. (1994) Characterization of the binding of SCH 39166 to the five cloned dopamine receptor subtypes. Pharmacol Biochem Behav, 49 (3): 567-71. [PMID:7862709]
74. Van Tol HH, Bunzow JR, Guan HC, Sunahara RK, Seeman P, Niznik HB, Civelli O. (1991) Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D4 receptor with high affinity for the antipsychotic clozapine. Nature, 350 (6319): 610-4. [PMID:1840645]
75. Van Tol HH, Wu CM, Guan HC, Ohara K, Bunzow JR, Civelli O, Kennedy J, Seeman P, Niznik HB, Jovanovic V. (1992) Multiple dopamine D4 receptor variants in the human population. Nature, 358 (6382): 149-52. [PMID:1319557]
76. van Vliet LA, Tepper PG, Dijkstra D, Damsma G, Wikström H, Pugsley TA, Akunne HC, Heffner TG, Glase SA, Wise LD. (1996) Affinity for dopamine D2, D3, and D4 receptors of 2-aminotetralins. Relevance of D2 agonist binding for determination of receptor subtype selectivity. J Med Chem, 39 (21): 4233-7. [PMID:8863800]
77. Wang S, Wacker D, Levit A, Che T, Betz RM, McCorvy JD, Venkatakrishnan AJ, Huang XP, Dror RO, Shoichet BK et al.. (2017) D4 dopamine receptor high-resolution structures enable the discovery of selective agonists. Science, 358 (6361): 381-386. [PMID:29051383]
78. Wedemeyer C, Goutman JD, Avale ME, Franchini LF, Rubinstein M, Calvo DJ. (2007) Functional activation by central monoamines of human dopamine D(4) receptor polymorphic variants coupled to GIRK channels in Xenopus oocytes. Eur J Pharmacol, 562 (3): 165-73. [PMID:17350612]
79. Yuen EY, Zhong P, Yan Z. (2010) Homeostatic regulation of glutamatergic transmission by dopamine D4 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 107 (51): 22308-13. [PMID:21135234]
80. Zarei S, Frieden M, Rubi B, Villemin P, Gauthier BR, Maechler P, Vischer UM. (2006) Dopamine modulates von Willebrand factor secretion in endothelial cells via D2-D4 receptors. J Thromb Haemost, 4 (7): 1588-95. [PMID:16839358]
81. Zhong P, Yan Z. (2016) Distinct Physiological Effects of Dopamine D4 Receptors on Prefrontal Cortical Pyramidal Neurons and Fast-Spiking Interneurons. Cereb Cortex, 26 (1): 180-91. [PMID:25146372]