
Top ▲

Gene and Protein Information  |
|||||||
| Species | TM | P Loops | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 3 | 1 | 883 | 4q32.1 | GRIA2 | glutamate ionotropic receptor AMPA type subunit 2 | 43,63 |
| Mouse | 3 | 1 | 883 | 3 E3 | Gria2 | glutamate receptor, ionotropic, AMPA2 (alpha 2) | 55 |
| Rat | 3 | 1 | 883 | 2q33 | Gria2 | glutamate ionotropic receptor AMPA type subunit 2 | 6,32,47,60 |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| GluR2 | GluRB | HBGR2 | AMPA-selective glutamate receptor 2 | glutamate receptor |
Database Links  |
|
| Alphafold | P42262 (Hs), P23819 (Mm), P19491 (Rn) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL4016 (Hs), CHEMBL2096617 (Mm), CHEMBL3503 (Rn) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000120251 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000033981 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000054204 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 2891 (Hs), 14800 (Mm), 29627 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000120251 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:2891 (Hs), mmu:14800 (Mm), rno:29627 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 138247 (Hs) |
| Pharos | P42262 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_001083619 (Hs), NM_000826 (Hs), NM_013540 (Mm), NM_001083806 (Mm), NM_001039195 (Mm), NM_017261 (Rn), NM_001083811 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_000817 (Hs), NP_001077088 (Hs), NP_001077275 (Mm), NP_038568 (Mm), NP_001034284 (Mm), NP_001077280 (Rn), NP_058957 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | P42262 (Hs), P23819 (Mm), P19491 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | GRIA2 (Hs) |
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
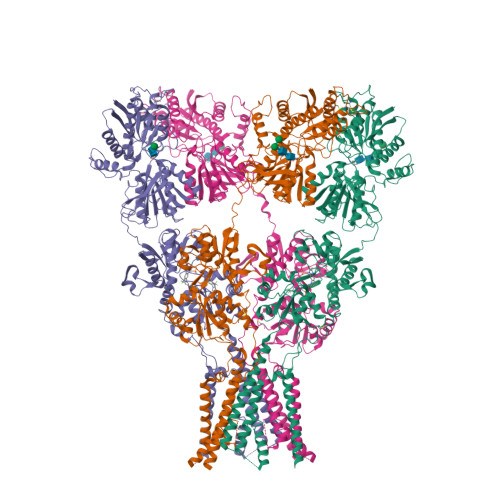
|
|
||||||||||||
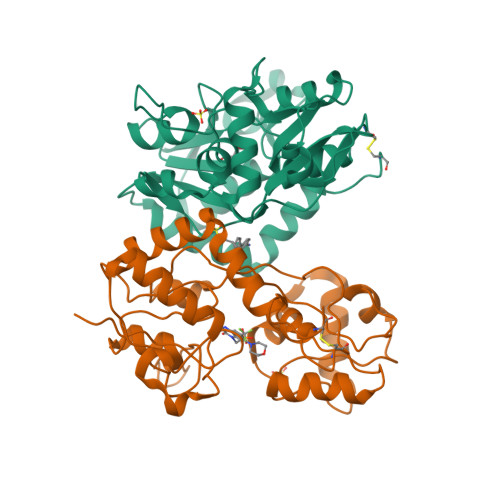
|
|
||||||||||||
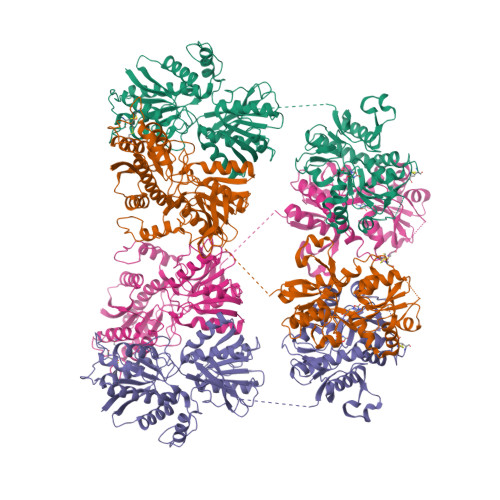
|
|
||||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| L-glutamic acid |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific antagonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Channel Blockers | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Channel Blocker Comments | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GluA2 is also blocked by intracellular polyamines. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allosteric Modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allosteric Modulator Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Piracetam and aniracetam are examples of pyrrolidinones. Cyclothiazide, S18986, and IDRA-21 are examples of benzothiadiazides. CX516 and CX546 are examples of benzylpiperidines. LY392098, LY404187 and LY503430 are examples of biarylpropylsulfonamides. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immuno Process Associations | ||
|
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
Biologically Significant Variants 
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
| Biologically Significant Variant Comments | ||||||||||||||
| Structure: a GluA2 subunit consists of 1 extracellular N-terminal domain, 1 ligand binding domain (S1 (a domain of the N-terminal region) + S2 (a domain of the extracellular loop between M3 and M4)), 3 membrane-spanning domains (M1, M3, M4), 1 cytoplasmic re-entrant loop (M2) and 1 C-terminal intracellular domain. GluA2 exists as several splice variants: 2 C-terminal splice variants: a minor one with a long C-terminal domain (GluA2L) and the predominant variant with a short C-terminal domain. GluA2 exists as alternatively spliced ‘flip’ and ‘flop’ isoforms which differ with respect to a cassette of 35 amino acids in the extracellular loop between M3 and M4 [32,60]. Tetrameric receptors assembled from the ‘flip’ isoform enter the desensitized state more slowly, and recover more quickly, than those formed from the ‘flop’ isoform [34,46,60]. In addition, RNA editing by adenosine deaminase type 2 (CAG->CIG), which occurs in virtually all GluA2 subunits, changes residue 607 within the channel pore from glutamine to arginine (at the ‘Q/R site’) [61]. GluA1, GluA3 and GluA4 are not subject to this form of editing and thus retain glutamine at the Q/R site. AMPA receptors that lack edited GluA2 subunits are (i) of relatively high single channel conductance [5]; (ii) permeable to Ca2+ [11,26], (iii) blocked by intracellular polyamines, causing inward rectification at depolarized potentials and (iv) blocked by extracellular argiotoxin and Joro spider toxins [27]. Q/R editing also influences the oligomerisation and trafficking of GluA2 subunits [23]. RNA editing (AGA->IGA) also occurs at a codon for arginine (unedited), or glycine (edited) at a locus with the extracellular loop that immediately precedes the alternatively spliced ‘flip’ and ‘flop’ modules. Edited channels recover from desensitization at a faster rate than those that are unedited [39]. GluA2 may express with long, or short, C-termini as a consequence of alternative splicing, the short form is predominant in mouse brain [35]. |
| General Comments |
| For general reviews please see:[3,28] |
1. Aicher SA, Sharma S, Mitchell JL. (2002) Co-localization of AMPA receptor subunits in the nucleus of the solitary tract in the rat. Brain Res, 958 (2): 454-8. [PMID:12470884]
2. Antal M, Fukazawa Y, Eördögh M, Muszil D, Molnár E, Itakura M, Takahashi M, Shigemoto R. (2008) Numbers, densities, and colocalization of AMPA- and NMDA-type glutamate receptors at individual synapses in the superficial spinal dorsal horn of rats. J Neurosci, 28 (39): 9692-701. [PMID:18815255]
3. Bassani S, Valnegri P, Beretta F, Passafaro M. (2009) The GLUR2 subunit of AMPA receptors: synaptic role. Neuroscience, 158 (1): 55-61. [PMID:18977416]
4. Beneyto M, Kristiansen LV, Oni-Orisan A, McCullumsmith RE, Meador-Woodruff JH. (2007) Abnormal glutamate receptor expression in the medial temporal lobe in schizophrenia and mood disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology, 32 (9): 1888-902. [PMID:17299517]
5. Bochet P, Audinat E, Lambolez B, Crépel F, Rossier J, Iino M, Tsuzuki K, Ozawa S. (1994) Subunit composition at the single-cell level explains functional properties of a glutamate-gated channel. Neuron, 12 (2): 383-8. [PMID:7509161]
6. Boulter J, Hollmann M, O'Shea-Greenfield A, Hartley M, Deneris E, Maron C, Heinemann S. (1990) Molecular cloning and functional expression of glutamate receptor subunit genes. Science, 249 (4972): 1033-7. [PMID:2168579]
7. Brand-Schieber E, Lowery SL, Werner P. (2004) Select ionotropic glutamate AMPA/kainate receptors are expressed at the astrocyte-vessel interface. Brain Res, 1007 (1-2): 178-82. [PMID:15064149]
8. Brand-Schieber E, Werner P. (2003) (+/-)-Alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid and kainate receptor subunit expression in mouse versus rat spinal cord white matter: similarities in astrocytes but differences in oligodendrocytes. Neurosci Lett, 345 (2): 126-30. [PMID:12821187]
9. Brand-Schieber E, Werner P. (2003) AMPA/kainate receptors in mouse spinal cord cell-specific display of receptor subunits by oligodendrocytes and astrocytes and at the nodes of Ranvier. Glia, 42 (1): 12-24. [PMID:12594733]
10. Brusa R, Zimmermann F, Koh DS, Feldmeyer D, Gass P, Seeburg PH, Sprengel R. (1995) Early-onset epilepsy and postnatal lethality associated with an editing-deficient GluR-B allele in mice. Science, 270 (5242): 1677-80. [PMID:7502080]
11. Burnashev N, Monyer H, Seeburg PH, Sakmann B. (1992) Divalent ion permeability of AMPA receptor channels is dominated by the edited form of a single subunit. Neuron, 8 (1): 189-98. [PMID:1370372]
12. Caicedo A, Zucchi B, Pereira E, Roper SD. (2004) Rat gustatory neurons in the geniculate ganglion express glutamate receptor subunits. Chem Senses, 29 (6): 463-71. [PMID:15269118]
13. Chen LW, Tse YC, Li C, Guan ZL, Lai CH, Yung KK, Shum DK, Chan YS. (2006) Differential expression of NMDA and AMPA/KA receptor subunits in the inferior olive of postnatal rats. Brain Res, 1067 (1): 103-14. [PMID:16376317]
14. Chun YH, Frank D, Lee JS, Zhang Y, Auh QS, Ro JY. (2008) Peripheral AMPA receptors contribute to muscle nociception and c-fos activation. Neurosci Res, 62 (2): 97-104. [PMID:18655811]
15. Corbett EK, Saha S, Deuchars J, McWilliam PN, Batten TF. (2003) Ionotropic glutamate receptor subunit immunoreactivity of vagal preganglionic neurones projecting to the rat heart. Auton Neurosci, 105 (2): 105-17. [PMID:12798207]
16. Deng YP, Xie JP, Wang HB, Lei WL, Chen Q, Reiner A. (2007) Differential localization of the GluR1 and GluR2 subunits of the AMPA-type glutamate receptor among striatal neuron types in rats. J Chem Neuroanat, 33 (4): 167-92. [PMID:17446041]
17. Dijk F, Kamphuis W. (2004) Ischemia-induced alterations of AMPA-type glutamate receptor subunit. Expression patterns in the rat retina--an immunocytochemical study. Brain Res, 997 (2): 207-21. [PMID:14706873]
18. Douyard J, Shen L, Huganir RL, Rubio ME. (2007) Differential neuronal and glial expression of GluR1 AMPA receptor subunit and the scaffolding proteins SAP97 and 4.1N during rat cerebellar development. J Comp Neurol, 502 (1): 141-56. [PMID:17335044]
19. Dracheva S, Byne W, Chin B, Haroutunian V. (2008) Ionotropic glutamate receptor mRNA expression in the human thalamus: absence of change in schizophrenia. Brain Res, 1214: 23-34. [PMID:18462708]
20. Dracheva S, McGurk SR, Haroutunian V. (2005) mRNA expression of AMPA receptors and AMPA receptor binding proteins in the cerebral cortex of elderly schizophrenics. J Neurosci Res, 79 (6): 868-78. [PMID:15696539]
21. Fujiyama F, Kuramoto E, Okamoto K, Hioki H, Furuta T, Zhou L, Nomura S, Kaneko T. (2004) Presynaptic localization of an AMPA-type glutamate receptor in corticostriatal and thalamostriatal axon terminals. Eur J Neurosci, 20 (12): 3322-30. [PMID:15610164]
22. Fux CM, Krug M, Dityatev A, Schuster T, Schachner M. (2003) NCAM180 and glutamate receptor subtypes in potentiated spine synapses: an immunogold electron microscopic study. Mol Cell Neurosci, 24 (4): 939-50. [PMID:14697660]
23. Greger IH, Khatri L, Kong X, Ziff EB. (2003) AMPA receptor tetramerization is mediated by Q/R editing. Neuron, 40 (4): 763-74. [PMID:14622580]
24. Gryder DS, Castaneda DC, Rogawski MA. (2005) Evidence for low GluR2 AMPA receptor subunit expression at synapses in the rat basolateral amygdala. J Neurochem, 94 (6): 1728-38. [PMID:16045445]
25. Horning MS, Kwon B, Blakemore LJ, Spencer CM, Goltz M, Houpt TA, Trombley PQ. (2004) Alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate receptor subunit expression in rat olfactory bulb. Neurosci Lett, 372 (3): 230-4. [PMID:15542246]
26. Hume RI, Dingledine R, Heinemann SF. (1991) Identification of a site in glutamate receptor subunits that controls calcium permeability. Science, 253 (5023): 1028-31. [PMID:1653450]
27. Iino M, Koike M, Isa T, Ozawa S. (1996) Voltage-dependent blockage of Ca(2+)-permeable AMPA receptors by joro spider toxin in cultured rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol (Lond.), 496 ( Pt 2): 431-7. [PMID:8910227]
28. Isaac JT, Ashby M, McBain CJ. (2007) The role of the GluR2 subunit in AMPA receptor function and synaptic plasticity. Neuron, 54 (6): 859-71. [PMID:17582328]
29. Kamphuis W, Klooster J, Dijk F. (2003) Expression of AMPA-type glutamate receptor subunit (GluR2) in ON-bipolar neurons in the rat retina. J Comp Neurol, 455 (2): 172-86. [PMID:12454983]
30. Kaur C, Sivakumar V, Ling EA. (2005) Expression of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) and alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate (AMPA) GluR2/3 receptors in the developing rat pineal gland. J Pineal Res, 39 (3): 294-301. [PMID:16150111]
31. Kawahara Y, Kwak S, Sun H, Ito K, Hashida H, Aizawa H, Jeong SY, Kanazawa I. (2003) Human spinal motoneurons express low relative abundance of GluR2 mRNA: an implication for excitotoxicity in ALS. J Neurochem, 85 (3): 680-9. [PMID:12694394]
32. Keinänen K, Wisden W, Sommer B, Werner P, Herb A, Verdoorn TA, Sakmann B, Seeburg PH. (1990) A family of AMPA-selective glutamate receptors. Science, 249 (4968): 556-60. [PMID:2166337]
33. Kim M, Chiego DJ, Bradley RM. (2008) Ionotropic glutamate receptor expression in preganglionic neurons of the rat inferior salivatory nucleus. Auton Neurosci, 138 (1-2): 83-90. [PMID:18096442]
34. Koike M, Tsukada S, Tsuzuki K, Kijima H, Ozawa S. (2000) Regulation of kinetic properties of GluR2 AMPA receptor channels by alternative splicing. J Neurosci, 20 (6): 2166-74. [PMID:10704491]
35. Köhler M, Kornau HC, Seeburg PH. (1994) The organization of the gene for the functionally dominant alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid receptor subunit GluR-B. J Biol Chem, 269 (26): 17367-70. [PMID:7545935]
36. Lachamp P, Balland B, Tell F, Crest M, Kessler JP. (2003) Synaptic localization of the glutamate receptor subunit GluR2 in the rat nucleus tractus solitarii. Eur J Neurosci, 17 (4): 892-6. [PMID:12603280]
37. Linja MJ, Visakorpi T. (2004) Alterations of androgen receptor in prostate cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, 92 (4): 255-64. [PMID:15663988]
38. Liu Q, Wong-Riley MT. (2005) Postnatal developmental expressions of neurotransmitters and receptors in various brain stem nuclei of rats. J Appl Physiol, 98 (4): 1442-57. [PMID:15618314]
39. Lomeli H, Mosbacher J, Melcher T, Höger T, Geiger JR, Kuner T, Monyer H, Higuchi M, Bach A, Seeburg PH. (1994) Control of kinetic properties of AMPA receptor channels by nuclear RNA editing. Science, 266 (5191): 1709-13. [PMID:7992055]
40. Lu CR, Hwang SJ, Phend KD, Rustioni A, Valtschanoff JG. (2002) Primary afferent terminals in spinal cord express presynaptic AMPA receptors. J Neurosci, 22 (21): 9522-9. [PMID:12417676]
41. Lu CR, Willcockson HH, Phend KD, Lucifora S, Darstein M, Valtschanoff JG, Rustioni A. (2005) Ionotropic glutamate receptors are expressed in GABAergic terminals in the rat superficial dorsal horn. J Comp Neurol, 486 (2): 169-78. [PMID:15844209]
42. Martínez L, Nascimento AS, Nunes FM, Phillips K, Aparicio R, Dias SM, Figueira AC, Lin JH, Nguyen P, Apriletti JW, Neves FA, Baxter JD, Webb P, Skaf MS, Polikarpov I. (2009) Gaining ligand selectivity in thyroid hormone receptors via entropy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,. [PMID:19926848]
43. McNamara JO, Eubanks JH, McPherson JD, Wasmuth JJ, Evans GA, Heinemann SF. (1992) Chromosomal localization of human glutamate receptor genes. J Neurosci, 12 (7): 2555-62. [PMID:1319477]
44. Meyerson JR, Kumar J, Chittori S, Rao P, Pierson J, Bartesaghi A, Mayer ML, Subramaniam S. (2014) Structural mechanism of glutamate receptor activation and desensitization. Nature, 514 (7522): 328-34. [PMID:25119039]
45. Miu P, Jarvie KR, Radhakrishnan V, Gates MR, Ogden A, Ornstein PL, Zarrinmayeh H, Ho K, Peters D, Grabell J et al.. (2001) Novel AMPA receptor potentiators LY392098 and LY404187: effects on recombinant human AMPA receptors in vitro. Neuropharmacology, 40 (8): 976-83. [PMID:11406188]
46. Mosbacher J, Schoepfer R, Monyer H, Burnashev N, Seeburg PH, Ruppersberg JP. (1994) A molecular determinant for submillisecond desensitization in glutamate receptors. Science, 266 (5187): 1059-62. [PMID:7973663]
47. Nakanishi N, Shneider NA, Axel R. (1990) A family of glutamate receptor genes: evidence for the formation of heteromultimeric receptors with distinct channel properties. Neuron, 5 (5): 569-81. [PMID:1699567]
48. Peddie CJ, Davies HA, Colyer FM, Stewart MG, Rodríguez JJ. (2008) Colocalisation of serotonin2A receptors with the glutamate receptor subunits NR1 and GluR2 in the dentate gyrus: an ultrastructural study of a modulatory role. Exp Neurol, 211 (2): 561-73. [PMID:18439999]
49. Polgár E, Watanabe M, Hartmann B, Grant SG, Todd AJ. (2008) Expression of AMPA receptor subunits at synapses in laminae I-III of the rodent spinal dorsal horn. Mol Pain, 4: 5. [PMID:18215271]
50. Puyal J, Sage C, Demêmes D, Dechesne CJ. (2002) Distribution of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4 isoazolepropionic acid and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunits in the vestibular and spiral ganglia of the mouse during early development. Brain Res Dev Brain Res, 139 (1): 51-7. [PMID:12414093]
51. Radley JJ, Farb CR, He Y, Janssen WG, Rodrigues SM, Johnson LR, Hof PR, LeDoux JE, Morrison JH. (2007) Distribution of NMDA and AMPA receptor subunits at thalamo-amygdaloid dendritic spines. Brain Res, 1134 (1): 87-94. [PMID:17207780]
52. Ragnarson B, Ornung G, Grant G, Ottersen OP, Ulfhake B. (2003) Glutamate and AMPA receptor immunoreactivity in Ia synapses with motoneurons and neurons of the central cervical nucleus. Exp Brain Res, 149 (4): 447-57. [PMID:12677325]
53. Ritter LM, Vazquez DM, Meador-Woodruff JH. (2002) Ontogeny of ionotropic glutamate receptor subunit expression in the rat hippocampus. Brain Res Dev Brain Res, 139 (2): 227-36. [PMID:12480137]
54. Rubio ME. (2006) Redistribution of synaptic AMPA receptors at glutamatergic synapses in the dorsal cochlear nucleus as an early response to cochlear ablation in rats. Hear Res, 216-217: 154-67. [PMID:16644159]
55. Sakimura K, Bujo H, Kushiya E, Araki K, Yamazaki M, Yamazaki M, Meguro H, Warashina A, Numa S, Mishina M. (1990) Functional expression from cloned cDNAs of glutamate receptor species responsive to kainate and quisqualate. FEBS Lett, 272 (1-2): 73-80. [PMID:1699805]
56. Santiago AR, Hughes JM, Kamphuis W, Schlingemann RO, Ambrósio AF. (2008) Diabetes changes ionotropic glutamate receptor subunit expression level in the human retina. Brain Res, 1198: 153-9. [PMID:18258217]
57. Schauwecker PE. (2003) Differences in ionotropic glutamate receptor subunit expression are not responsible for strain-dependent susceptibility to excitotoxin-induced injury. Brain Res Mol Brain Res, 112 (1-2): 70-81. [PMID:12670704]
58. Semkova I, Huemmeke M, Ho MS, Merkl B, Abari E, Paulsson M, Joussen AM, Plomann M. (2010) Retinal localization of the glutamate receptor GluR2 and GluR2-regulating proteins in diabetic rats. Exp Eye Res, 90 (2): 244-53. [PMID:19878674]
59. Sobolevsky AI, Rosconi MP, Gouaux E. (2009) X-ray structure, symmetry and mechanism of an AMPA-subtype glutamate receptor. Nature, 462 (7274): 745-56. [PMID:19946266]
60. Sommer B, Keinänen K, Verdoorn TA, Wisden W, Burnashev N, Herb A, Köhler M, Takagi T, Sakmann B, Seeburg PH. (1990) Flip and flop: a cell-specific functional switch in glutamate-operated channels of the CNS. Science, 249 (4976): 1580-5. [PMID:1699275]
61. Sommer B, Köhler M, Sprengel R, Seeburg PH. (1991) RNA editing in brain controls a determinant of ion flow in glutamate-gated channels. Cell, 67 (1): 11-9. [PMID:1717158]
62. Sun H, Kawahara Y, Ito K, Kanazawa I, Kwak S. (2005) Expression profile of AMPA receptor subunit mRNA in single adult rat brain and spinal cord neurons in situ. Neurosci Res, 52 (3): 228-34. [PMID:15927724]
63. Sun W, Ferrer-Montiel AV, Schinder AF, McPherson JP, Evans GA, Montal M. (1992) Molecular cloning, chromosomal mapping, and functional expression of human brain glutamate receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 89 (4): 1443-7. [PMID:1311100]
64. Szczesniak AM, Gilbert RW, Mukhida M, Anderson GI. (2005) Mechanical loading modulates glutamate receptor subunit expression in bone. Bone, 37 (1): 63-73. [PMID:15922681]
65. Talos DM, Fishman RE, Park H, Folkerth RD, Follett PL, Volpe JJ, Jensen FE. (2006) Developmental regulation of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionic acid receptor subunit expression in forebrain and relationship to regional susceptibility to hypoxic/ischemic injury. I. Rodent cerebral white matter and cortex. J Comp Neurol, 497 (1): 42-60. [PMID:16680782]
66. Talos DM, Follett PL, Folkerth RD, Fishman RE, Trachtenberg FL, Volpe JJ, Jensen FE. (2006) Developmental regulation of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionic acid receptor subunit expression in forebrain and relationship to regional susceptibility to hypoxic/ischemic injury. II. Human cerebral white matter and cortex. J Comp Neurol, 497 (1): 61-77. [PMID:16680761]
67. Tan PH, Yang LC, Chiang PT, Jang JS, Chung HC, Kuo CH. (2008) Inflammation-induced up-regulation of ionotropic glutamate receptor expression in human skin. Br J Anaesth, 100 (3): 380-4. [PMID:18238837]
68. Todd AJ, Polgár E, Watt C, Bailey ME, Watanabe M. (2009) Neurokinin 1 receptor-expressing projection neurons in laminae III and IV of the rat spinal cord have synaptic AMPA receptors that contain GluR2, GluR3 and GluR4 subunits. Eur J Neurosci, 29 (4): 718-26. [PMID:19200070]
69. Tse YC, Lai CH, Lai SK, Liu JX, Yung KK, Shum DK, Chan YS. (2008) Developmental expression of NMDA and AMPA receptor subunits in vestibular nuclear neurons that encode gravity-related horizontal orientations. J Comp Neurol, 508 (2): 343-64. [PMID:18335497]
70. Wang C, Niu L. (2013) Mechanism of inhibition of the GluA2 AMPA receptor channel opening by talampanel and its enantiomer: the stereochemistry of the 4-methyl group on the diazepine ring of 2,3-benzodiazepine derivatives. ACS Chem Neurosci, 4 (4): 635-44. [PMID:23402301]
71. Wang YQ, Hu HJ, Cao R, Chen LW. (2005) Differential co-localization of neurokinin-3 receptor and NMDA/AMPA receptor subunits in neurons of the substantia nigra of C57/BL mice. Brain Res, 1053 (1-2): 207-12. [PMID:16038885]
72. Willcockson H, Valtschanoff J. (2008) AMPA and NMDA glutamate receptors are found in both peptidergic and non-peptidergic primary afferent neurons in the rat. Cell Tissue Res, 334 (1): 17-23. [PMID:18679721]
73. Yelshanskaya MV, Singh AK, Narangoda C, Williams RSB, Kurnikova MG, Sobolevsky AI. (2022) Structural basis of AMPA receptor inhibition by trans-4-butylcyclohexane carboxylic acid. Br J Pharmacol, 179 (14): 3628-3644. [PMID:32959886]
74. Yoneyama M, Kitayama T, Taniura H, Yoneda Y. (2004) Immunohistochemical detection by immersion fixation with Carnoy solution of particular non-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunits in murine hippocampus. Neurochem Int, 44 (6): 413-22. [PMID:14687606]
75. Zhang JP, Wei LC, Cao R, Chen LW. (2006) Differential co-expression of AMPA receptor subunits in substance P receptor-containing neurons of basal forebrain regions of C57/BL mice. Neurochem Int, 49 (3): 319-26. [PMID:16580093]