
Top ▲

GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| class A G protein-coupled receptor | ||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 7 | 488 | 5p13.1 | PTGER4 | prostaglandin E receptor 4 | 7,13 |
| Mouse | 7 | 513 | 15 1.99 cM | Ptger4 | prostaglandin E receptor 4 (subtype EP4) | 50 |
| Rat | 7 | 488 | 2q16 | Ptger4 | prostaglandin E receptor 4 | 19,120 |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
|
| EP2 [7,13,45,50,120] | PGE receptor EP4 subtype | prostanoid EP4 receptor | |
Database Links  |
|
| Specialist databases | |
| GPCRdb | pe2r4_human (Hs), pe2r4_mouse (Mm), pe2r4_rat (Rn) |
| Other databases | |
| Alphafold | P35408 (Hs), P32240 (Mm), P43114 (Rn) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL1836 (Hs), CHEMBL2489 (Mm), CHEMBL4086 (Rn) |
| DrugBank Target | P35408 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000171522 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000039942 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000013240 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 5734 (Hs), 19219 (Mm), 84023 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000171522 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:5734 (Hs), mmu:19219 (Mm), rno:84023 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 601586 (Hs) |
| Pharos | P35408 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_000958 (Hs), NM_008965 (Mm), NM_032076 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_000949 (Hs), NP_032991 (Mm), NP_114465 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | P35408 (Hs), P32240 (Mm), P43114 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | PTGER4 (Hs) |
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
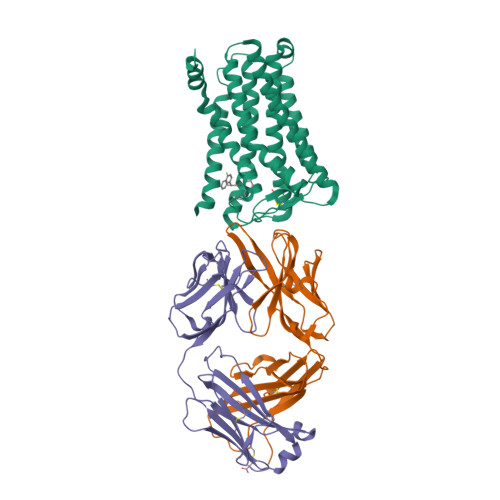
|
|
||||||||||||
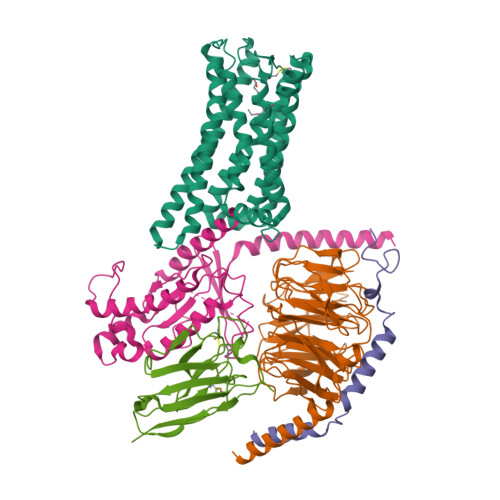
|
|
||||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| PGD2 |
| PGE1 |
| PGE2 |
| PGF2α |
| PGI2 |
| Comments: PGE2 is the principal endogenous agonist |
| Potency order of endogenous ligands |
| PGE2 = PGE1 > PGF2α, PGI2 > PGD2, thromboxane A2 |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific agonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ONO-AE1-329, TCS-2510 and L-902688 are useful selective EP4 agonists. Analogues with optimized EP2 / EP4 agonism have been recently developed [62]. ONO-4232, a selective EP4 agonist is in Phase I clinical trials in acute heart failure [137]. A conjugate of an EP4a agonist that reverses osteopenia in a rat model [77] should not be confused with the L-161,982 (EP4A) antagonist in the table below. Chemistry of EP4 agonist conjugates in disclosed in Arns et al. (2012) [8]. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific antagonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The archetypal EP4 antagonist AH-23848 has been superseded by more potent and selective agents: CJ-023423, GW-627368, L-161982, ONO-AE3-208. The NH group in antagonists containing an acyl-sulphonamido moiety (e.g. GW-627368) is acidic. The EP4 antagonist grapiprant is approved for the treatment of pain and inflammation in osteoarthritis in dogs [114]. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allosteric Modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | Click column headers to sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immunopharmacology Comments |
| The EP4 prostanoid receptor is one of four receptor subtypes for prostaglandin PGE2. The anti- and pro-inflammatory (and non-inflammatory) activities of this receptor are reviewed in [148]. Foudi et al. (2012) [37] review the presence and role of EP1-4 receptors in human inflammation and immune cells. The PGE2/EP4 receptor axis appears to act as an amplifier of cytokine (like IL-6) activity and induces the differentiation and expansion of inflammatory T-helper (Th) lymphocytes. Results from several mouse models indicate that the PGE2/EP4 receptor axis is important in regulating the inflammatory response across a range of tissues [30,32,116,126,146]. PGE2, acting via EP2 and EP4 receptors in synovial tissue appears to contribute to the progression of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in a rat model [143]. Blocking EP4 and EP2 using their antagonists or genetically modified animals prevents inflammation in CNS, gut and skin in animal models for multiple sclerosis, colitis, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis and contact hypersensitivity [32,73,80,116,144]. EP4 antagonists with anti-inflammatory action are discussed in [59]. CR6086 is an example of a EP4 antagonist that is in clinical development for RA. The EP4 receptor is discussed in this review of immuno-oncology [2].The roles of PGE2 in chronic immune-mediated inflammation is reviewed here [145]. |
Primary Transduction Mechanisms 
|
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gs family | Adenylyl cyclase stimulation |
| References: 97 | |
Secondary Transduction Mechanisms  |
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gi/Go family | Other - See Comments |
| Comments: A second EP4 signaling pathway is PI3K dependent via G protein Gi activation. | |
| References: 40,42,115,118 | |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Expression Datasets  |
|
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression Comments | ||||||||||
| Deletion of this single gene has been reported to create a mouse model of patent ductus arteriosus, a congenital heart disorder where the ductus arteriosus fails to close spontaneously in neonates (see OMIM:607411) [99]. | ||||||||||
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Biologically Significant Variants 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
| General Comments |
|
The recombinant EP4 receptor was originally identified as EP2 [13,50]. The EP2 and EP4 receptors are thought to mediate most of the hemodynamic responses to PGE2 in the female but not the male mouse [10]. |
1. Abramovitz M, Adam M, Boie Y, Carrière M, Denis D, Godbout C, Lamontagne S, Rochette C, Sawyer N, Tremblay NM et al.. (2000) The utilization of recombinant prostanoid receptors to determine the affinities and selectivities of prostaglandins and related analogs. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1483 (2): 285-93. [PMID:10634944]
2. Adams JL, Smothers J, Srinivasan R, Hoos A. (2015) Big opportunities for small molecules in immuno-oncology. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 14 (9): 603-22. [PMID:26228631]
3. Akhter MP, Cullen DM, Pan LC. (2006) Bone biomechanical properties in EP4 knockout mice. Calcif Tissue Int, 78 (6): 357-62. [PMID:16830205]
4. Albu DI, Wang Z, Huang KC, Wu J, Twine N, Leacu S, Ingersoll C, Parent L, Lee W, Liu D et al.. (2017) EP4 Antagonism by E7046 diminishes Myeloid immunosuppression and synergizes with Treg-reducing IL-2-Diphtheria toxin fusion protein in restoring anti-tumor immunity. Oncoimmunology, 6 (8): e1338239. [PMID:28920002]
5. Amano H, Hayashi I, Endo H, Kitasato H, Yamashina S, Maruyama T, Kobayashi M, Satoh K, Narita M, Sugimoto Y et al.. (2003) Host prostaglandin E(2)-EP3 signaling regulates tumor-associated angiogenesis and tumor growth. J Exp Med, 197 (2): 221-32. [PMID:12538661]
6. Amaradhi R, Banik A, Mohammed S, Patro V, Rojas A, Wang W, Motati DR, Dingledine R, Ganesh T. (2020) Potent, Selective, Water Soluble, Brain-Permeable EP2 Receptor Antagonist for Use in Central Nervous System Disease Models. J Med Chem, 63 (3): 1032-1050. [PMID:31904232]
7. An S, Yang J, Xia M, Goetzl EJ. (1993) Cloning and expression of the EP2 subtype of human receptors for prostaglandin E2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 197 (1): 263-70. [PMID:8250933]
8. Arns S, Gibe R, Moreau A, Monzur Morshed M, Young RN. (2012) Design and synthesis of novel bone-targeting dual-action pro-drugs for the treatment and reversal of osteoporosis. Bioorg Med Chem, 20 (6): 2131-40. [PMID:22341574]
9. Attur M, Al-Mussawir HE, Patel J, Kitay A, Dave M, Palmer G, Pillinger MH, Abramson SB. (2008) Prostaglandin E2 exerts catabolic effects in osteoarthritis cartilage: evidence for signaling via the EP4 receptor. J Immunol, 181 (7): 5082-8. [PMID:18802112]
10. Audoly LP, Tilley SL, Goulet J, Key M, Nguyen M, Stock JL, McNeish JD, Koller BH, Coffman TM. (1999) Identification of specific EP receptors responsible for the hemodynamic effects of PGE2. Am J Physiol, 277 (3): H924-30. [PMID:10484412]
11. Bäurle S, Nagel J, Peters O, Bräuer N, Ter Laak A, Preusse C, Rottmann A, Heldmann D, Bothe U, Blume T et al.. (2019) Identification of a Benzimidazolecarboxylic Acid Derivative (BAY 1316957) as a Potent and Selective Human Prostaglandin E2 Receptor Subtype 4 (hEP4-R) Antagonist for the Treatment of Endometriosis. J Med Chem, 62 (5): 2541-2563. [PMID:30707023]
12. Barrett SD, Holt MC, Kramer JB, Germain B, Ho CS, Ciske FL, Kornilov A, Colombo JM, Uzieblo A, O'Malley JP et al.. (2019) Difluoromethylene at the γ-Lactam α-Position Improves 11-Deoxy-8-aza-PGE1 Series EP4 Receptor Binding and Activity: 11-Deoxy-10,10-difluoro-8-aza-PGE1 Analog (KMN-159) as a Potent EP4 Agonist. J Med Chem, 62 (9): 4731-4741. [PMID:30964292]
13. Bastien L, Sawyer N, Grygorczyk R, Metters KM, Adam M. (1994) Cloning, functional expression, and characterization of the human prostaglandin E2 receptor EP2 subtype. J Biol Chem, 269 (16): 11873-7. [PMID:8163486]
14. Baxter GS, Clayton JK, Coleman RA, Marshall K, Sangha R, Senior J. (1995) Characterization of the prostanoid receptors mediating constriction and relaxation of human isolated uterine artery. Br J Pharmacol, 116 (1): 1692-6. [PMID:8564239]
15. Belley A, Chadee K. (1999) Prostaglandin E(2) stimulates rat and human colonic mucin exocytosis via the EP(4) receptor. Gastroenterology, 117 (6): 1352-62. [PMID:10579976]
16. Benyahia C, Gomez I, Kanyinda L, Boukais K, Danel C, Leséche G, Longrois D, Norel X. (2012) PGE(2) receptor (EP(4)) agonists: potent dilators of human bronchi and future asthma therapy?. Pulm Pharmacol Ther, 25 (1): 115-8. [PMID:22244823]
17. Biswas S, Bhattacherjee P, Paterson CA, Tilley SL, Koller BH. (2006) Ocular inflammatory responses in the EP2 and EP4 receptor knockout mice. Ocul Immunol Inflamm, 14 (3): 157-63. [PMID:16766399]
18. Blouin M, Han Y, Burch J, Farand J, Mellon C, Gaudreault M, Wrona M, Lévesque JF, Denis D, Mathieu MC et al.. (2010) The discovery of 4-{1-[({2,5-dimethyl-4-[4-(trifluoromethyl)benzyl]-3-thienyl}carbonyl)amino]cyclopropyl}benzoic acid (MK-2894), a potent and selective prostaglandin E2 subtype 4 receptor antagonist. J Med Chem, 53 (5): 2227-38. [PMID:20163116]
19. Boie Y, Stocco R, Sawyer N, Slipetz DM, Ungrin MD, Neuschäfer-Rube F, Püschel GP, Metters KM, Abramovitz M. (1997) Molecular cloning and characterization of the four rat prostaglandin E2 prostanoid receptor subtypes. Eur J Pharmacol, 340 (2-3): 227-41. [PMID:9537820]
20. Breyer MD, Davis L, Jacobson HR, Breyer RM. (1996) Differential localization of prostaglandin E receptor subtypes in human kidney. Am J Physiol, 270 (5 Pt 2): F912-8. [PMID:8928854]
21. Buckley J, Birrell MA, Maher SA, Nials AT, Clarke DL, Belvisi MG. (2011) EP4 receptor as a new target for bronchodilator therapy. Thorax, 66 (12): 1029-35. [PMID:21606476]
22. Cao RY, St Amand T, Li X, Yoon SH, Wang CP, Song H, Maruyama T, Brown PM, Zelt DT, Funk CD. (2012) Prostaglandin receptor EP4 in abdominal aortic aneurysms. Am J Pathol, 181 (1): 313-21. [PMID:22595380]
23. Caselli G, Bonazzi A, Lanza M, Ferrari F, Maggioni D, Ferioli C, Giambelli R, Comi E, Zerbi S, Perrella M et al.. (2018) Pharmacological characterisation of CR6086, a potent prostaglandin E2receptor 4 antagonist, as a new potential disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug. Arthritis Res Ther, 20 (1): 39. [PMID:29490676]
24. Chen Q, Muramoto K, Masaaki N, Ding Y, Yang H, Mackey M, Li W, Inoue Y, Ackermann K, Shirota H et al.. (2010) A novel antagonist of the prostaglandin E(2) EP(4) receptor inhibits Th1 differentiation and Th17 expansion and is orally active in arthritis models. Br J Pharmacol, 160 (2): 292-310. [PMID:20423341]
25. Cipollone F, Fazia ML, Iezzi A, Cuccurullo C, De Cesare D, Ucchino S, Spigonardo F, Marchetti A, Buttitta F, Paloscia L et al.. (2005) Association between prostaglandin E receptor subtype EP4 overexpression and unstable phenotype in atherosclerotic plaques in human. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 25 (9): 1925-31. [PMID:16020747]
26. Clark P, Rowland SE, Denis D, Mathieu MC, Stocco R, Poirier H, Burch J, Han Y, Audoly L, Therien AG et al.. (2008) MF498 [N-{[4-(5,9-Diethoxy-6-oxo-6,8-dihydro-7H-pyrrolo[3,4-g]quinolin-7-yl)-3-methylbenzyl]sulfonyl}-2-(2-methoxyphenyl)acetamide], a selective E prostanoid receptor 4 antagonist, relieves joint inflammation and pain in rodent models of rheumatoid and osteoarthritis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 325 (2): 425-34. [PMID:18287210]
27. Davis TL, Sharif NA. (2000) Pharmacological characterization of [(3)H]-prostaglandin E(2) binding to the cloned human EP(4) prostanoid receptor. Br J Pharmacol, 130: 1919-1926. [PMID:10952683]
28. Diamond JM, Akimova T, Kazi A, Shah RJ, Cantu E, Feng R, Levine MH, Kawut SM, Meyer NJ, Lee JC et al.. (2014) Genetic variation in the prostaglandin E2 pathway is associated with primary graft dysfunction. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 189 (5): 567-75. [PMID:24467603]
29. Ding M, Kinoshita Y, Kishi K, Nakata H, Hassan S, Kawanami C, Sugimoto Y, Katsuyama M, Negishi M, Narumiya S et al.. (1997) Distribution of prostaglandin E receptors in the rat gastrointestinal tract. Prostaglandins, 53 (3): 199-216. [PMID:9206801]
30. Duffin R, O'Connor RA, Crittenden S, Forster T, Yu C, Zheng X, Smyth D, Robb CT, Rossi F, Skouras C et al.. (2016) Prostaglandin E₂ constrains systemic inflammation through an innate lymphoid cell-IL-22 axis. Science, 351 (6279): 1333-8. [PMID:26989254]
31. El-Nefiawy N, Abdel-Hakim K, Kanayama N, Terao T. (2005) Role of prostaglandin E2 receptor subtypes in ovarian follicle growth in the rat in vivo. Correlation with interleukin-8 and neutrophils. Histol Histopathol, 20 (3): 825-31. [PMID:15944932]
32. Esaki Y, Li Y, Sakata D, Yao C, Segi-Nishida E, Matsuoka T, Fukuda K, Narumiya S. (2010) Dual roles of PGE2-EP4 signaling in mouse experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 107 (27): 12233-8. [PMID:20566843]
33. Facemire CS, Nguyen M, Jania L, Beierwaltes WH, Kim HS, Koller BH, Coffman TM. (2011) A major role for the EP4 receptor in regulation of renin. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 301 (5): F1035-41. [PMID:21835766]
34. Feehan KT, Bridgewater HE, Stenkiewicz-Witeska J, De Maeyer RPH, Ferguson J, Mack M, Brown J, Ercoli G, Mawer CM, Akbar AN et al.. (2024) Post-resolution macrophages shape long-term tissue immunity and integrity in a mouse model of pneumococcal pneumonia. Nat Commun, 15 (1): 4326. [PMID:38773113]
35. Feng C, Beller EM, Bagga S, Boyce JA. (2006) Human mast cells express multiple EP receptors for prostaglandin E2 that differentially modulate activation responses. Blood, 107 (8): 3243-50. [PMID:16357326]
36. Fennekohl A, Sugimoto Y, Segi E, Maruyama T, Ichikawa A, Püschel GP. (2002) Contribution of the two Gs-coupled PGE2-receptors EP2-receptor and EP4-receptor to the inhibition by PGE2 of the LPS-induced TNFalpha-formation in Kupffer cells from EP2-or EP4-receptor-deficient mice. Pivotal role for the EP4-receptor in wild type Kupffer cells. J Hepatol, 36 (3): 328-34. [PMID:11867175]
37. Foudi N, Gomez I, Benyahia C, Longrois D, Norel X. (2012) Prostaglandin E2 receptor subtypes in human blood and vascular cells. Eur J Pharmacol, 695 (1-3): 1-6. [PMID:22964467]
38. Foudi N, Kotelevets L, Gomez I, Louedec L, Longrois D, Chastre E, Norel X. (2011) Differential reactivity of human mammary artery and saphenous vein to prostaglandin E(2) : implication for cardiovascular grafts. Br J Pharmacol, 163 (4): 826-34. [PMID:21323896]
39. Foudi N, Kotelevets L, Louedec L, Leséche G, Henin D, Chastre E, Norel X. (2008) Vasorelaxation induced by prostaglandin E2 in human pulmonary vein: role of the EP4 receptor subtype. Br J Pharmacol, 154 (8): 1631-9. [PMID:18516068]
40. Fujino H, Salvi S, Regan JW. (2005) Differential regulation of phosphorylation of the cAMP response element-binding protein after activation of EP2 and EP4 prostanoid receptors by prostaglandin E2. Mol Pharmacol, 68 (1): 251-9. [PMID:15855407]
41. Fujino H, West KA, Regan JW. (2002) Phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 and stimulation of T-cell factor signaling following activation of EP2 and EP4 prostanoid receptors by prostaglandin E2. J Biol Chem, 277 (4): 2614-9. [PMID:11706038]
42. Fujino H, Xu W, Regan JW. (2003) Prostaglandin E2 induced functional expression of early growth response factor-1 by EP4, but not EP2, prostanoid receptors via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinases. J Biol Chem, 278 (14): 12151-6. [PMID:12566441]
43. Ganesh T, Jiang J, Shashidharamurthy R, Dingledine R. (2013) Discovery and characterization of carbamothioylacrylamides as EP2 selective antagonists. ACS Med Chem Lett, 4 (7): 616-621. [PMID:23914286]
44. Glas J, Seiderer J, Czamara D, Pasciuto G, Diegelmann J, Wetzke M, Olszak T, Wolf C, Müller-Myhsok B, Balschun T et al.. (2012) PTGER4 expression-modulating polymorphisms in the 5p13.1 region predispose to Crohn's disease and affect NF-κB and XBP1 binding sites. PLoS One, 7 (12): e52873. [PMID:23300802]
45. Grygorczyk R, Abramovitz M, Boie Y, Bastien L, Adam M. (1995) Detection of adenylate cyclase-coupled receptors in Xenopus oocytes by coexpression with cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. Anal Biochem, 227: 27-31. [PMID:7545356]
46. Hamaguchi K, Yamamoto N, Nakagawa T, Furuyashiki T, Narumiya S, Ito J. (2012) Role of PGE-type receptor 4 in auditory function and noise-induced hearing loss in mice. Neuropharmacology, 62 (4): 1841-7. [PMID:22198478]
47. Hattori R, Shimizu S, Majima Y, Shimizu T. (2008) EP4 agonist inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced mucus secretion in airway epithelial cells. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 117 (1): 51-8. [PMID:18254372]
48. Hattori R, Shimizu S, Majima Y, Shimizu T. (2009) Prostaglandin E2 receptor EP2, EP3, and EP4 agonists inhibit antigen-induced mucus hypersecretion in the nasal epithelium of sensitized rats. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 118 (7): 536-41. [PMID:19708495]
49. Hishikari K, Suzuki J, Ogawa M, Isobe K, Takahashi T, Onishi M, Takayama K, Isobe M. (2009) Pharmacological activation of the prostaglandin E2 receptor EP4 improves cardiac function after myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res, 81 (1): 123-32. [PMID:18805784]
50. Honda A, Sugimoto Y, Namba T, Watabe A, Irie A, Negishi M, Narumiya S, Ichikawa A. (1993) Cloning and expression of a cDNA for mouse prostaglandin E receptor EP2 subtype. J Biol Chem, 268 (11): 7759-62. [PMID:8385118]
51. Hong DS, Parikh A, Shapiro GI, Varga A, Naing A, Meric-Bernstam F, Ataman Ö, Reyderman L, Binder TA, Ren M et al.. (2020) First-in-human phase I study of immunomodulatory E7046, an antagonist of PGE2-receptor E-type 4 (EP4), in patients with advanced cancers. J Immunother Cancer, 8 (1). [PMID:32554609]
52. Hristovska AM, Rasmussen LE, Hansen PB, Nielsen SS, Nüsing RM, Narumiya S, Vanhoutte P, Skøtt O, Jensen BL. (2007) Prostaglandin E2 induces vascular relaxation by E-prostanoid 4 receptor-mediated activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Hypertension, 50 (3): 525-30. [PMID:17635857]
53. Inazumi T, Yamada K, Shirata N, Sato H, Taketomi Y, Morita K, Hohjoh H, Tsuchiya S, Oniki K, Watanabe T et al.. (2020) Prostaglandin E2-EP4 Axis Promotes Lipolysis and Fibrosis in Adipose Tissue Leading to Ectopic Fat Deposition and Insulin Resistance. Cell Rep, 33 (2): 108265. [PMID:33053354]
54. International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium, Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2, Sawcer S, Hellenthal G, Pirinen M, Spencer CC, Patsopoulos NA, Moutsianas L, Dilthey A, Su Z et al.. (2011) Genetic risk and a primary role for cell-mediated immune mechanisms in multiple sclerosis. Nature, 476 (7359): 214-9. [PMID:21833088]
55. Iyú D, Glenn JR, White AE, Johnson AJ, Fox SC, Heptinstall S. (2010) The role of prostanoid receptors in mediating the effects of PGE(2) on human platelet function. Platelets, 21 (5): 329-42. [PMID:20433310]
56. Jain S, Chakraborty G, Raja R, Kale S, Kundu GC. (2008) Prostaglandin E2 regulates tumor angiogenesis in prostate cancer. Cancer Res, 68 (19): 7750-9. [PMID:18829529]
57. Jensen BL, Mann B, Skøtt O, Kurtz A. (1999) Differential regulation of renal prostaglandin receptor mRNAs by dietary salt intake in the rat. Kidney Int, 56 (2): 528-37. [PMID:10432392]
58. Jones CL, Li T, Cowley EA. (2012) The prostaglandin E₂ type 4 receptor participates in the response to acute oxidant stress in airway epithelial cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 341 (2): 552-63. [PMID:22362924]
59. Jones RL, Giembycz MA, Woodward DF. (2009) Prostanoid receptor antagonists: development strategies and therapeutic applications. Br J Pharmacol, 158 (1): 104-45. [PMID:19624532]
60. Kabashima K, Saji T, Murata T, Nagamachi M, Matsuoka T, Segi E, Tsuboi K, Sugimoto Y, Kobayashi T, Miyachi Y et al.. (2002) The prostaglandin receptor EP4 suppresses colitis, mucosal damage and CD4 cell activation in the gut. J Clin Invest, 109 (7): 883-93. [PMID:11927615]
61. Kabashima K, Sakata D, Nagamachi M, Miyachi Y, Inaba K, Narumiya S. (2003) Prostaglandin E2-EP4 signaling initiates skin immune responses by promoting migration and maturation of Langerhans cells. Nat Med, 9 (6): 744-9. [PMID:12740571]
62. Kambe T, Maruyama T, Nakano M, Nakai Y, Yoshida T, Matsunaga N, Oida H, Konaka A, Maruyama T, Nakai H et al.. (2012) Discovery of a novel EP2/EP4 dual agonist with high subtype-selectivity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 22 (1): 396-401. [PMID:22119471]
63. Kataoka H, Sakanaka M, Semma M, Yamamoto T, Hirota S, Tanaka S, Ichikawa A. (2008) PGE2-receptor subtype EP4-dependent adherence of mastocytoma P-815 cells to matrix components in subcutaneous tissues overlaying inside surface of air pouch cavity in CDF1 mouse. Inflamm Res, 57 (8): 362-6. [PMID:18787774]
64. Kato S, Aihara E, Yoshii K, Takeuchi K. (2005) Dual action of prostaglandin E2 on gastric acid secretion through different EP-receptor subtypes in the rat. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 289 (1): G64-9. [PMID:15961884]
65. Kiriyama M, Ushikubi F, Kobayashi T, Hirata M, Sugimoto Y, Narumiya S. (1997) Ligand binding specificities of the eight types and subtypes of the mouse prostanoid receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Br J Pharmacol, 122 (2): 217-24. [PMID:9313928]
66. Komuro M, Kamiyama M, Furuya Y, Takihana Y, Araki I, Takeda M. (2006) Gene and protein expression profiles of prostaglandin E2 receptor subtypes in the human corpus cavernosum. Int J Impot Res, 18 (3): 275-81. [PMID:16239896]
67. Konya V, Philipose S, Bálint Z, Olschewski A, Marsche G, Sturm EM, Schicho R, Peskar BA, Schuligoi R, Heinemann A. (2011) Interaction of eosinophils with endothelial cells is modulated by prostaglandin EP4 receptors. Eur J Immunol, 41 (8): 2379-89. [PMID:21681739]
68. Kunikata T, Araki H, Takeeda M, Kato S, Takeuchi K. (2001) Prostaglandin E prevents indomethacin-induced gastric and intestinal damage through different EP receptor subtypes. J Physiol Paris, 95 (1-6): 157-63. [PMID:11595431]
69. Kunikata T, Tanaka A, Miyazawa T, Kato S, Takeuchi K. (2002) 16,16-Dimethyl prostaglandin E2 inhibits indomethacin-induced small intestinal lesions through EP3 and EP4 receptors. Dig Dis Sci, 47 (4): 894-904. [PMID:11991626]
70. Kuwano K, Hashino A, Asaki T, Hamamoto T, Yamada T, Okubo K, Kuwabara K. (2007) 2-[4-[(5,6-diphenylpyrazin-2-yl)(isopropyl)amino]butoxy]-N-(methylsulfonyl)acetamide (NS-304), an orally available and long-acting prostacyclin receptor agonist prodrug. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 322 (3): 1181-8. [PMID:17545310]
71. Leduc M, Breton B, Galés C, Le Gouill C, Bouvier M, Chemtob S, Heveker N. (2009) Functional selectivity of natural and synthetic prostaglandin EP4 receptor ligands. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 331 (1): 297-307. [PMID:19584306]
72. Leduc M, Hou X, Hamel D, Sanchez M, Quiniou C, Honoré JC, Roy O, Madaan A, Lubell W, Varma DR et al.. (2013) Restoration of renal function by a novel prostaglandin EP4 receptor-derived peptide in models of acute renal failure. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol, 304 (1): R10-22. [PMID:23152113]
73. Lee J, Aoki T, Thumkeo D, Siriwach R, Yao C, Narumiya S. (2019) T cell-intrinsic prostaglandin E2-EP2/EP4 signaling is critical in pathogenic TH17 cell-driven inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 143 (2): 631-643. [PMID:29935220]
74. Li M, Healy DR, Li Y, Simmons HA, Crawford DT, Ke HZ, Pan LC, Brown TA, Thompson DD. (2005) Osteopenia and impaired fracture healing in aged EP4 receptor knockout mice. Bone, 37 (1): 46-54. [PMID:15869929]
75. Liang X, Lin L, Woodling NS, Wang Q, Anacker C, Pan T, Merchant M, Andreasson K. (2011) Signaling via the prostaglandin E₂ receptor EP4 exerts neuronal and vascular protection in a mouse model of cerebral ischemia. J Clin Invest, 121 (11): 4362-71. [PMID:21965326]
76. Libioulle C, Louis E, Hansoul S, Sandor C, Farnir F, Franchimont D, Vermeire S, Dewit O, de Vos M, Dixon A et al.. (2007) Novel Crohn disease locus identified by genome-wide association maps to a gene desert on 5p13.1 and modulates expression of PTGER4. PLoS Genet, 3 (4): e58. [PMID:17447842]
77. Liu CC, Hu S, Chen G, Georgiou J, Arns S, Kumar NS, Young RN, Grynpas MD. (2015) Novel EP4 receptor agonist-bisphosphonate conjugate drug (C1) promotes bone formation and improves vertebral mechanical properties in the ovariectomized rat model of postmenopausal bone loss. J Bone Miner Res, 30 (4): 670-80. [PMID:25284325]
78. Luschnig-Schratl P, Sturm EM, Konya V, Philipose S, Marsche G, Fröhlich E, Samberger C, Lang-Loidolt D, Gattenlöhner S, Lippe IT et al.. (2011) EP4 receptor stimulation down-regulates human eosinophil function. Cell Mol Life Sci, 68 (21): 3573-87. [PMID:21365278]
79. Machwate M, Harada S, Leu CT, Seedor G, Labelle M, Gallant M, Hutchins S, Lachance N, Sawyer N, Slipetz D et al.. (2001) Prostaglandin receptor EP(4) mediates the bone anabolic effects of PGE(2). Mol Pharmacol, 60 (1): 36-41. [PMID:11408598]
80. Maseda D, Banerjee A, Johnson EM, Washington MK, Kim H, Lau KS, Crofford LJ. (2018) mPGES-1-Mediated Production of PGE2 and EP4 Receptor Sensing Regulate T Cell Colonic Inflammation. Front Immunol, 9: 2954. [PMID:30619314]
81. Masuko K, Murata M, Yudoh K, Shimizu H, Beppu M, Nakamura H, Kato T. (2010) Prostaglandin E2 regulates the expression of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF/CCN2) in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes via the EP4 receptor. BMC Res Notes, 3: 5. [PMID:20205862]
82. Matesanz F, González-Pérez A, Lucas M, Sanna S, Gayán J, Urcelay E, Zara I, Pitzalis M, Cavanillas ML, Arroyo R et al.. (2012) Genome-wide association study of multiple sclerosis confirms a novel locus at 5p13.1. PLoS One, 7 (5): e36140. [PMID:22570697]
83. Maubach KA, Davis RJ, Clark DE, Fenton G, Lockey PM, Clark KL, Oxford AW, Hagan RM, Routledge C, Coleman RA. (2009) BGC20-1531, a novel, potent and selective prostanoid EP receptor antagonist: a putative new treatment for migraine headache. Br J Pharmacol, 156 (2): 316-27. [PMID:19154437]
84. McCoy JM, Wicks JR, Audoly LP. (2002) The role of prostaglandin E2 receptors in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest, 110 (5): 651-8. [PMID:12208866]
85. Mitomi H, Yamada H, Ito H, Nozaki Shibata T, Yamasaki Y, Nomoto S, Kusaba A, Yamashita H, Ozaki S. (2013) Hypoxia-induced endogenous prostaglandin E2 negatively regulates hypoxia-enhanced aberrant overgrowth of rheumatoid synovial tissue. Mod Rheumatol, 23 (6): 1069-75. [PMID:23183906]
86. Miyamoto M, Ito H, Mukai S, Kobayashi T, Yamamoto H, Kobayashi M, Maruyama T, Akiyama H, Nakamura T. (2003) Simultaneous stimulation of EP2 and EP4 is essential to the effect of prostaglandin E2 in chondrocyte differentiation. Osteoarthr Cartil, 11 (9): 644-52. [PMID:12954235]
87. Miyaura C, Inada M, Suzawa T, Sugimoto Y, Ushikubi F, Ichikawa A, Narumiya S, Suda T. (2000) Impaired bone resorption to prostaglandin E2 in prostaglandin E receptor EP4-knockout mice. J Biol Chem, 275 (26): 19819-23. [PMID:10749873]
88. Morath R, Klein T, Seyberth HW, Nüsing RM. (1999) Immunolocalization of the four prostaglandin E2 receptor proteins EP1, EP2, EP3, and EP4 in human kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol, 10 (9): 1851-60. [PMID:10477136]
89. Murase A, Okumura T, Sakakibara A, Tonai-Kachi H, Nakao K, Takada J. (2008) Effect of prostanoid EP4 receptor antagonist, CJ-042,794, in rat models of pain and inflammation. Eur J Pharmacol, 580 (1-2): 116-21. [PMID:18031725]
90. Murase A, Taniguchi Y, Tonai-Kachi H, Nakao K, Takada J. (2008) In vitro pharmacological characterization of CJ-042794, a novel, potent, and selective prostaglandin EP(4) receptor antagonist. Life Sci, 82 (3-4): 226-32. [PMID:18155068]
91. Murn J, Alibert O, Wu N, Tendil S, Gidrol X. (2008) Prostaglandin E2 regulates B cell proliferation through a candidate tumor suppressor, Ptger4. J Exp Med, 205 (13): 3091-103. [PMID:19075289]
92. Mutoh M, Watanabe K, Kitamura T, Shoji Y, Takahashi M, Kawamori T, Tani K, Kobayashi M, Maruyama T, Kobayashi K et al.. (2002) Involvement of prostaglandin E receptor subtype EP(4) in colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Res, 62 (1): 28-32. [PMID:11782353]
93. Myren M, Baun M, Ploug KB, Jansen-Olesen I, Olesen J, Gupta S. (2010) Functional and molecular characterization of prostaglandin E2 dilatory receptors in the rat craniovascular system in relevance to migraine. Cephalalgia, 30 (9): 1110-22. [PMID:20713561]
94. Nakagawa N, Yuhki K, Kawabe J, Fujino T, Takahata O, Kabara M, Abe K, Kojima F, Kashiwagi H, Hasebe N et al.. (2012) The intrinsic prostaglandin E2-EP4 system of the renal tubular epithelium limits the development of tubulointerstitial fibrosis in mice. Kidney Int, 82 (2): 158-71. [PMID:22513820]
95. Nakao K, Murase A, Ohshiro H, Okumura T, Taniguchi K, Murata Y, Masuda M, Kato T, Okumura Y, Takada J. (2007) CJ-023,423, a novel, potent and selective prostaglandin EP4 receptor antagonist with antihyperalgesic properties. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 322 (2): 686-94. [PMID:17495127]
96. Nataraj C, Thomas DW, Tilley SL, Nguyen MT, Mannon R, Koller BH, Coffman TM. (2001) Receptors for prostaglandin E(2) that regulate cellular immune responses in the mouse. J Clin Invest, 108 (8): 1229-35. [PMID:11602631]
97. Neuschäfer-Rube F, Hänecke K, Blaschke V, Jungermann K, Püschel GP. (1997) The C-terminal domain of the Gs-coupled EP4 receptor confers agonist-dependent coupling control to Gi but no coupling to Gs in a receptor hybrid with the Gi-coupled EP3 receptor. FEBS Lett, 401 (2-3): 185-90. [PMID:9013884]
98. Ngoc PB, Suzuki J, Ogawa M, Hishikari K, Takayama K, Hirata Y, Nagai R, Isobe M. (2011) The anti-inflammatory mechanism of prostaglandin e2 receptor 4 activation in rat experimental autoimmune myocarditis. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol, 57 (3): 365-72. [PMID:21383594]
99. Nguyen M, Camenisch T, Snouwaert JN, Hicks E, Coffman TM, Anderson PA, Malouf NN, Koller BH. (1997) The prostaglandin receptor EP4 triggers remodelling of the cardiovascular system at birth. Nature, 390 (6655): 78-81. [PMID:9363893]
100. Nishitani K, Ito H, Hiramitsu T, Tsutsumi R, Tanida S, Kitaori T, Yoshitomi H, Kobayashi M, Nakamura T. (2010) PGE2 inhibits MMP expression by suppressing MKK4-JNK MAP kinase-c-JUN pathway via EP4 in human articular chondrocytes. J Cell Biochem, 109 (2): 425-33. [PMID:19998410]
101. Noguchi K, Shitashige M, Endo H, Kondo H, Ishikawa I. (2002) Binary regulation of interleukin (IL)-6 production by EP1 and EP2/EP4 subtypes of PGE2 receptors in IL-1beta-stimulated human gingival fibroblasts. J Periodont Res, 37 (1): 29-36. [PMID:11842936]
102. Nojima S, Fujita Y, Kimura KT, Nomura N, Suno R, Morimoto K, Yamamoto M, Noda T, Iwata S, Shigematsu H et al.. (2021) Cryo-EM Structure of the Prostaglandin E Receptor EP4 Coupled to G Protein. Structure, 29 (3): 252-260.e6. [PMID:33264604]
103. Nüsing RM, Treude A, Weissenberger C, Jensen B, Bek M, Wagner C, Narumiya S, Seyberth HW. (2005) Dominant role of prostaglandin E2 EP4 receptor in furosemide-induced salt-losing tubulopathy: a model for hyperprostaglandin E syndrome/antenatal Bartter syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol, 16 (8): 2354-62. [PMID:15976003]
104. Okamoto F, Kajiya H, Fukushima H, Jimi E, Okabe K. (2004) Prostaglandin E2 activates outwardly rectifying Cl(-) channels via a cAMP-dependent pathway and reduces cell motility in rat osteoclasts. Am J Physiol, Cell Physiol, 287 (1): C114-24. [PMID:15044156]
105. Ono K, Akatsu T, Kugai N, Pilbeam CC, Raisz LG. (2003) The effect of deletion of cyclooxygenase-2, prostaglandin receptor EP2, or EP4 in bone marrow cells on osteoclasts induced by mouse mammary cancer cell lines. Bone, 33 (5): 798-804. [PMID:14623055]
106. Owen TA, Patel C, Wei S, Ho CS, Birmingham K, Sanchez S, Chung N, Cahill A, O'Malley JP, Barrett SD et al.. (2020) KMN-159, a novel EP4 receptor selective agonist, stimulates osteoblastic differentiation in cultured whole rat bone marrow. Gene, 748: 144668. [PMID:32334025]
107. Palikhe NS, Sin HJ, Kim SH, Sin HJ, Hwang EK, Ye YM, Park HS. (2012) Genetic variability of prostaglandin E2 receptor subtype EP4 gene in aspirin-intolerant chronic urticaria. J Hum Genet, 57 (8): 494-9. [PMID:22695889]
108. Patankar JV, Müller TM, Kantham S, Acera MG, Mascia F, Scheibe K, Mahapatro M, Heichler C, Yu Y, Li W et al.. (2021) E-type prostanoid receptor 4 drives resolution of intestinal inflammation by blocking epithelial necroptosis. Nat Cell Biol, 23 (7): 796-807. [PMID:34239062]
109. Philipose S, Konya V, Sreckovic I, Marsche G, Lippe IT, Peskar BA, Heinemann A, Schuligoi R. (2010) The prostaglandin E2 receptor EP4 is expressed by human platelets and potently inhibits platelet aggregation and thrombus formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 30 (12): 2416-23. [PMID:21071691]
110. Prasanna G, Fortner J, Xiang C, Zhang E, Carreiro S, Anderson S, Sartnurak S, Wu G, Gukasyan H, Niesman M et al.. (2009) Ocular pharmacokinetics and hypotensive activity of PF-04475270, an EP4 prostaglandin agonist in preclinical models. Exp Eye Res, 89 (5): 608-17. [PMID:19445930]
111. Purdy KE, Arendshorst WJ. (2000) EP(1) and EP(4) receptors mediate prostaglandin E(2) actions in the microcirculation of rat kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 279 (4): F755-64. [PMID:10997926]
112. Pöschke A, Kern N, Maruyama T, Pavenstädt H, Narumiya S, Jensen BL, Nüsing RM. (2012) The PGE(2)-EP4 receptor is necessary for stimulation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in response to low dietary salt intake in vivo. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 303 (10): F1435-42. [PMID:22993066]
113. Qian JY, Harding P, Liu Y, Shesely E, Yang XP, LaPointe MC. (2008) Reduced cardiac remodeling and function in cardiac-specific EP4 receptor knockout mice with myocardial infarction. Hypertension, 51 (2): 560-6. [PMID:18180401]
114. Rausch-Derra L, Huebner M, Wofford J, Rhodes L. (2016) A Prospective, Randomized, Masked, Placebo-Controlled Multisite Clinical Study of Grapiprant, an EP4 Prostaglandin Receptor Antagonist (PRA), in Dogs with Osteoarthritis. J Vet Intern Med, 30 (3): 756-63. [PMID:27075237]
115. Reader J, Holt D, Fulton A. (2011) Prostaglandin E2 EP receptors as therapeutic targets in breast cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 30 (3-4): 449-63. [PMID:22002714]
116. Robb CT, McSorley HJ, Lee J, Aoki T, Yu C, Crittenden S, Astier A, Felton JM, Parkinson N, Ayele A et al.. (2018) Prostaglandin E2 stimulates adaptive IL-22 production and promotes allergic contact dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 141 (1): 152-162. [PMID:28583370]
117. Rosenfield AR, Lowman RM, Taylor KJ. (1976) Urography in preoperative evaluation of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Urology, 7 (6): 652-4. [PMID:936389]
118. Rundhaug JE, Simper MS, Surh I, Fischer SM. (2011) The role of the EP receptors for prostaglandin E2 in skin and skin cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 30 (3-4): 465-80. [PMID:22012553]
119. Sakuma Y, Tanaka K, Suda M, Komatsu Y, Yasoda A, Miura M, Ozasa A, Narumiya S, Sugimoto Y, Ichikawa A et al.. (2000) Impaired bone resorption by lipopolysaccharide in vivo in mice deficient in the prostaglandin E receptor EP4 subtype. Infect Immun, 68 (12): 6819-25. [PMID:11083800]
120. Sando T, Usui T, Tanaka I, Mori K, Sasaki Y, Fukuda Y, Namba T, Sugimoto Y, Ichikawa A, Narumiya S et al.. (1994) Molecular cloning and expression of rat prostaglandin E receptor EP2 subtype. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 200 (3): 1329-33. [PMID:8185583]
121. Schlötzer-Schrehardt U, Zenkel M, Nüsing RM. (2002) Expression and localization of FP and EP prostanoid receptor subtypes in human ocular tissues. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 43 (5): 1475-87. [PMID:11980863]
122. Schneider A, Guan Y, Zhang Y, Magnuson MA, Pettepher C, Loftin CD, Langenbach R, Breyer RM, Breyer MD. (2004) Generation of a conditional allele of the mouse prostaglandin EP4 receptor. Genesis, 40 (1): 7-14. [PMID:15354288]
123. Schweda F, Klar J, Narumiya S, Nüsing RM, Kurtz A. (2004) Stimulation of renin release by prostaglandin E2 is mediated by EP2 and EP4 receptors in mouse kidneys. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 287 (3): F427-33. [PMID:15113745]
124. Segi E, Sugimoto Y, Yamasaki A, Aze Y, Oida H, Nishimura T, Murata T, Matsuoka T, Ushikubi F, Hirose M et al.. (1998) Patent ductus arteriosus and neonatal death in prostaglandin receptor EP4-deficient mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 246 (1): 7-12. [PMID:9600059]
125. Shibata-Nozaki T, Ito H, Mitomi H, Akaogi J, Komagata T, Kanaji T, Maruyama T, Mori T, Nomoto S, Ozaki S et al.. (2011) Endogenous prostaglandin E2 inhibits aberrant overgrowth of rheumatoid synovial tissue and the development of osteoclast activity through EP4 receptor. Arthritis Rheum, 63 (9): 2595-605. [PMID:21898865]
126. Soontrapa K, Honda T, Sakata D, Yao C, Hirata T, Hori S, Matsuoka T, Kita Y, Shimizu T, Kabashima K et al.. (2011) Prostaglandin E2-prostaglandin E receptor subtype 4 (EP4) signaling mediates UV irradiation-induced systemic immunosuppression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 108 (16): 6668-73. [PMID:21460251]
127. Stillman BA, Breyer MD, Breyer RM. (1999) Importance of the extracellular domain for prostaglandin EP(2) receptor function. Mol Pharmacol, 56 (3): 545-51. [PMID:10462542]
128. Suzawa T, Miyaura C, Inada M, Maruyama T, Sugimoto Y, Ushikubi F, Ichikawa A, Narumiya S, Suda T. (2000) The role of prostaglandin E receptor subtypes (EP1, EP2, EP3, and EP4) in bone resorption: an analysis using specific agonists for the respective EPs. Endocrinology, 141 (4): 1554-9. [PMID:10746663]
129. Takayama K, García-Cardena G, Sukhova GK, Comander J, Gimbrone MA, Libby P. (2002) Prostaglandin E2 suppresses chemokine production in human macrophages through the EP4 receptor. J Biol Chem, 277 (46): 44147-54. [PMID:12215436]
130. Takeuchi K, Aihara E, Hayashi M, Sasaki Y. (2005) Role of prostaglandin E receptor subtypes in gastroduodenal HCO3- secretion. Med Chem, 1 (4): 395-403. [PMID:16789896]
131. Tang EH, Libby P, Vanhoutte PM, Xu A. (2012) Anti-inflammation therapy by activation of prostaglandin EP4 receptor in cardiovascular and other inflammatory diseases. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol, 59 (2): 116-23. [PMID:21697732]
132. Tang EH, Shimizu K, Christen T, Rocha VZ, Shvartz E, Tesmenitsky Y, Sukhova G, Shi GP, Libby P. (2011) Lack of EP4 receptors on bone marrow-derived cells enhances inflammation in atherosclerotic lesions. Cardiovasc Res, 89 (1): 234-43. [PMID:20736236]
133. Tang EH, Shvartz E, Shimizu K, Rocha VZ, Zheng C, Fukuda D, Shi GP, Sukhova G, Libby P. (2011) Deletion of EP4 on bone marrow-derived cells enhances inflammation and angiotensin II-induced abdominal aortic aneurysm formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 31 (2): 261-9. [PMID:21088251]
134. Theiler A, Konya V, Pasterk L, Maric J, Bärnthaler T, Lanz I, Platzer W, Schuligoi R, Heinemann A. (2016) The EP1/EP3 receptor agonist 17-pt-PGE2 acts as an EP4 receptor agonist on endothelial barrier function and in a model of LPS-induced pulmonary inflammation. Vascul Pharmacol, 87: 180-189. [PMID:27664754]
135. Toyoda Y, Morimoto K, Suno R, Horita S, Yamashita K, Hirata K, Sekiguchi Y, Yasuda S, Shiroishi M, Shimizu T et al.. (2019) Ligand binding to human prostaglandin E receptor EP4 at the lipid-bilayer interface. Nat Chem Biol, 15 (1): 18-26. [PMID:30510193]
136. Wang W, He J, Yang J, Zhang C, Cheng Z, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Wang P, Tang S, Wang X et al.. (2022) Scaffold Hopping Strategy to Identify Prostanoid EP4 Receptor Antagonists for Cancer Immunotherapy. J Med Chem, 65 (11): 7896-7917. [PMID:35640059]
137. Ward CL, Jamieson V, Nabata T, Sharpe J, Dozono K, Suto F, Hashimoto Y, Gussak I. (2016) First Clinical Experience with ONO-4232: A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Healthy Volunteer Study of a Novel Lusitropic Agent for Acutely Decompensated Heart Failure. Clin Ther, 38 (5): 1109-21. [PMID:27001444]
138. Whittle BJ, Silverstein AM, Mottola DM, Clapp LH. (2012) Binding and activity of the prostacyclin receptor (IP) agonists, treprostinil and iloprost, at human prostanoid receptors: treprostinil is a potent DP1 and EP2 agonist. Biochem Pharmacol, 84 (1): 68-75. [PMID:22480736]
139. Wilson RJ, Giblin GM, Roomans S, Rhodes SA, Cartwright KA, Shield VJ, Brown J, Wise A, Chowdhury J, Pritchard S et al.. (2006) GW627368X ((N-{2-[4-(4,9-diethoxy-1-oxo-1,3-dihydro-2H-benzo[f]isoindol-2-yl)phenyl]acetyl} benzene sulphonamide): a novel, potent and selective prostanoid EP4 receptor antagonist. Br J Pharmacol, 148 (3): 326-39. [PMID:16604093]
140. Wilson RJ, Giles H. (2005) Piglet saphenous vein contains multiple relaxatory prostanoid receptors: evidence for EP4, EP2, DP and IP receptor subtypes. Br J Pharmacol, 144 (3): 405-15. [PMID:15655509]
141. Wilson RJ, Rhodes SA, Wood RL, Shield VJ, Noel LS, Gray DW, Giles H. (2004) Functional pharmacology of human prostanoid EP2 and EP4 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol, 501 (1-3): 49-58. [PMID:15464062]
142. Wise H. (1998) Activation of the prostaglandin EP4-receptor subtype is highly coupled to inhibition of N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-stimulated rat neutrophil aggregation. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids, 58 (1): 77-84. [PMID:9482170]
143. Xu HM, Wei W, Jia XY, Chang Y, Zhang L. (2007) Effects and mechanisms of total glucosides of paeony on adjuvant arthritis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol, 109 (3): 442-8. [PMID:17000070]
144. Yao C, Hirata T, Soontrapa K, Ma X, Takemori H, Narumiya S. (2013) Prostaglandin E₂ promotes Th1 differentiation via synergistic amplification of IL-12 signalling by cAMP and PI3-kinase. Nat Commun, 4: 1685. [PMID:23575689]
145. Yao C, Narumiya S. (2019) Prostaglandin-cytokine crosstalk in chronic inflammation. Br J Pharmacol, 176 (3): 337-354. [PMID:30381825]
146. Yao C, Sakata D, Esaki Y, Li Y, Matsuoka T, Kuroiwa K, Sugimoto Y, Narumiya S. (2009) Prostaglandin E2-EP4 signaling promotes immune inflammation through Th1 cell differentiation and Th17 cell expansion. Nat Med, 15 (6): 633-40. [PMID:19465928]
147. Yokoyama U, Ishiwata R, Jin MH, Kato Y, Suzuki O, Jin H, Ichikawa Y, Kumagaya S, Katayama Y, Fujita T et al.. (2012) Inhibition of EP4 signaling attenuates aortic aneurysm formation. PLoS ONE, 7 (5): e36724. [PMID:22570740]
148. Yokoyama U, Iwatsubo K, Umemura M, Fujita T, Ishikawa Y. (2013) The prostanoid EP4 receptor and its signaling pathway. Pharmacol Rev, 65 (3): 1010-52. [PMID:23776144]
149. Yokoyama U, Minamisawa S, Quan H, Ghatak S, Akaike T, Segi-Nishida E, Iwasaki S, Iwamoto M, Misra S, Tamura K et al.. (2006) Chronic activation of the prostaglandin receptor EP4 promotes hyaluronan-mediated neointimal formation in the ductus arteriosus. J Clin Invest, 116 (11): 3026-34. [PMID:17080198]
150. Yoshida K, Oida H, Kobayashi T, Maruyama T, Tanaka M, Katayama T, Yamaguchi K, Segi E, Tsuboyama T, Matsushita M et al.. (2002) Stimulation of bone formation and prevention of bone loss by prostaglandin E EP4 receptor activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 99 (7): 4580-5. [PMID:11917107]
151. Yoshida Y, Matsumura H, Nakajima T, Mandai M, Urakami T, Kuroda K, Yoneda H. (2000) Prostaglandin E (EP) receptor subtypes and sleep: promotion by EP4 and inhibition by EP1/EP2. Neuroreport, 11 (10): 2127-31. [PMID:10923657]
152. Young RN, Billot X, Han Y, Slipetz DA, Chauret N, Belley M, Metters K, Mathieu MC, Greig GM, Denis D, Girard M. (2004) Discovery and Synthesis of a Potent, Selective and Orally Bioavailable EP4 Receptor Agonist. Heterocycles, 64 (1): 437-446.
153. Zhan P, Alander C, Kaneko H, Pilbeam CC, Guan Y, Zhang Y, Breyer MD, Raisz LG. (2005) Effect of deletion of the prostaglandin EP4 receptor on stimulation of calcium release from cultured mouse calvariae: impaired responsiveness in heterozygotes. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat, 78 (1-4): 19-26. [PMID:16303601]
154. Zhang J, Rivest S. (1999) Distribution, regulation and colocalization of the genes encoding the EP2- and EP4-PGE2 receptors in the rat brain and neuronal responses to systemic inflammation. Eur J Neurosci, 11 (8): 2651-68. [PMID:10457163]
155. Zheng Y, Ritzenthaler JD, Sun X, Roman J, Han S. (2009) Prostaglandin E2 stimulates human lung carcinoma cell growth through induction of integrin-linked kinase: the involvement of EP4 and Sp1. Cancer Res, 69 (3): 896-904. [PMID:19176380]