GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Inwardly rectifying potassium channels (KIR): Introduction
Introduction
The family of inwardly-rectifying potassium channels, i.e., Kir channels, plays central roles in control of cellular excitability and K+ ion homeostasis. Kir channels function in many tissues, including brain, heart, kidney, endocrine and sensory. Kir channels are structurally distinct from the family of voltage-gated potassium channels; Kir channels possess only two membrane-spanning helices, and lack the four membrane helices that form the voltage sensor in voltage-gated potassium channels. As such, Kir channels have evolved distinct voltage-independent mechanisms for opening and closing, including gating by G proteins, pH and ATP. Seven structurally distinct sub-families of the Kir family have been identified in mammals. This article presents the molecular relationships and physiological roles of Kir channels and provides an introduction to their molecular, structural, physiological, and pharmacological properties.
Kir channel subunits, classification and nomenclature
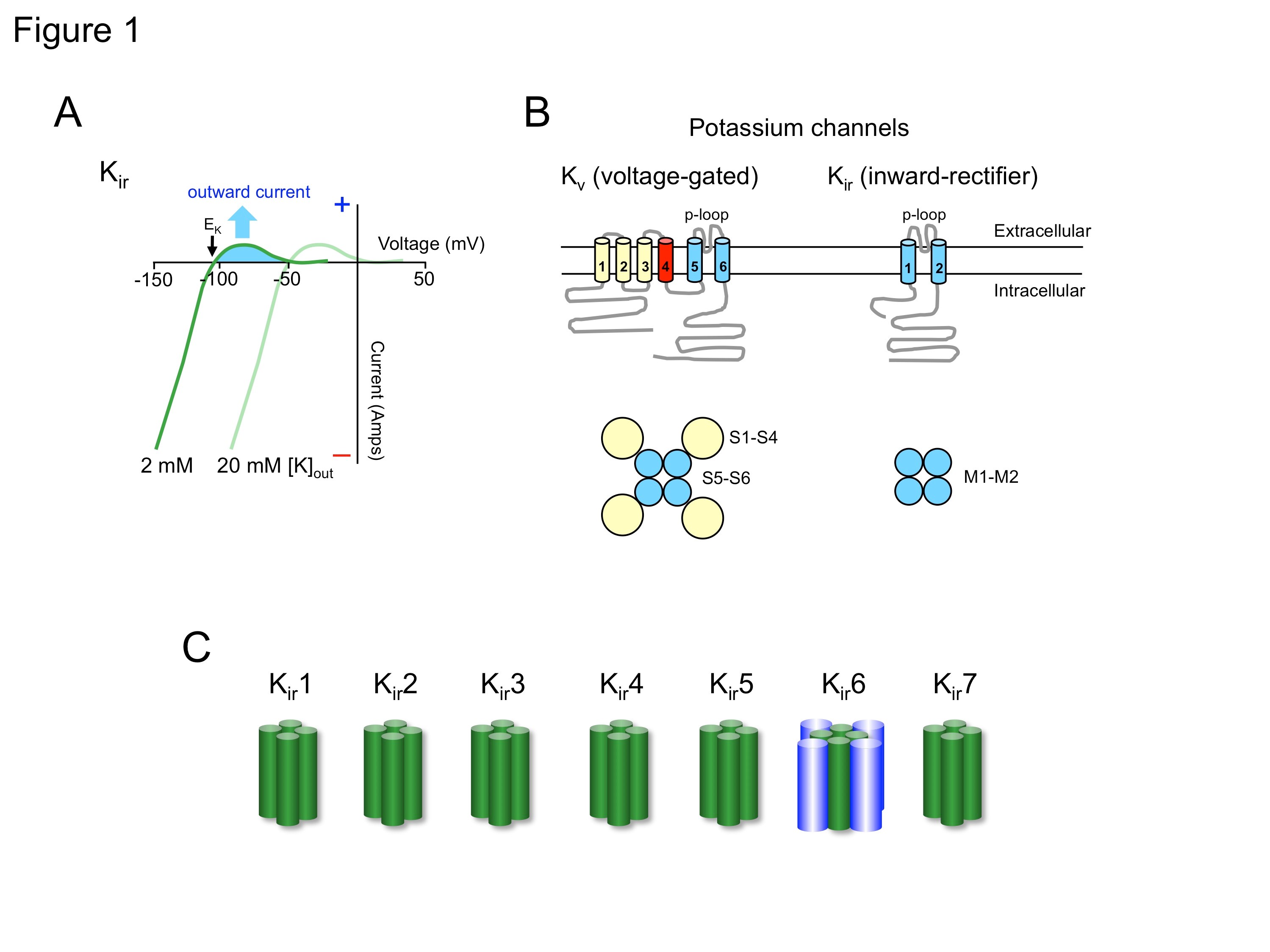
Several key studies in the 1970's led to the description of two distinguishing properties of Kir channels, (i) inward rectification and (ii) the presence of a "long" pore [21]. Kir channels derive their name, i.e., inwardly-rectifying, from the current-voltage relationship. When the current through the channel is plotted as a function of membrane potential, the inward current, i.e., negative current, is typically much larger than the positive ('outward') current (Fig. 1A). This property is referred to as inward rectification (or 'anomalous' rectification), to distinguish it from the classical 'outward' rectification expected of a passive pore in the presence of high internal and low external potassium. Increasing the concentration of extracellular potassium shifts the peak of the outward current to more depolarized potentials (Fig. 1A), such that the voltage-dependence of the Kir conductance depends on the extracellular potassium concentration [21]. Following cloning of the genes encoding Kir channel subunits [10,22,29-30], it was determined with heterologous expression systems, such as Xenopus oocytes or HEK-293 cells, that rectification is not an intrinsic property of the channel protein [33]. Rather, intracellular factors, e.g., Mg2+ and polyamines, bind to the inner ion-conducting vestibule of the channel, where they impede the outward flow of potassium ions.
The extent of inward rectification also appeared to vary in different types of cells, leading to further classification of Kir channels into two major groups, 'weak' and 'strong' inward rectifiers. The biological significance of strong inward rectification is perhaps best seen in excitable cells, such as cardiac and neuronal cells. Here, the resting membrane potential of these cells is typically slightly positive to the equilibrium potential for potassium (EK), enabling Kir channels to sustain a small amount of potassium efflux (Figure 1A). As the cell depolarizes, such as during an action potential, the property of rectification limits the contribution of Kir channels to the total potassium efflux. Thus, strongly rectifying Kir channels play an important role in controlling the resting potential and excitability, but contribute little to the action potential itself. In contrast, weak inward rectifiers will both stabilize the resting potential and shorten the action potential. A good example is the so-called KATP channel, which is gated by adenosine triphosphate (ATP). When KATP channels are activated in the heart, they can reduce the classically long action potential from a duration of hundreds of milliseconds to that of a brief spike.
Figure 1. Kir channels. A, Current-voltage relationship shows the property of inward rectification. Cells with a membrane potential that is positive to EK will conduct outward potassium current through Kir channels, which will decline substantially at more positive potentials. The apparent gating of the channel shifts with increasing extracellular K+ concentration. B, Schematic compares the membrane topology of voltage-gated K+ (Kv) channels and inwardly-rectifying K+ (Kir) channels. Both channels are tetramers and share an ion selectivity pore region (p-loop) and two transmembrane domains. Kv channels also have a voltage-sensitive domain (S4, red). C, All seven members of the Kir channels consist of a single alpha subunit that forms a tetramer. Kir6 channels uniquely require an additional subunit, the sulfonylurea receptor (SUR), to form a functional octameric channel.
A second distinguishing structural property of Kir channels is the presence of an extended pore that continues from the transmembrane regions through the cytoplasmic domain. The conductance of inward rectifiers depends on the square root of the external potassium concentration [16]. This property can be explained by the presence of a multi-ion, single-file pore [21]. Recent structural determinations of Kir channels have revealed the physical nature of the long pore (see below).
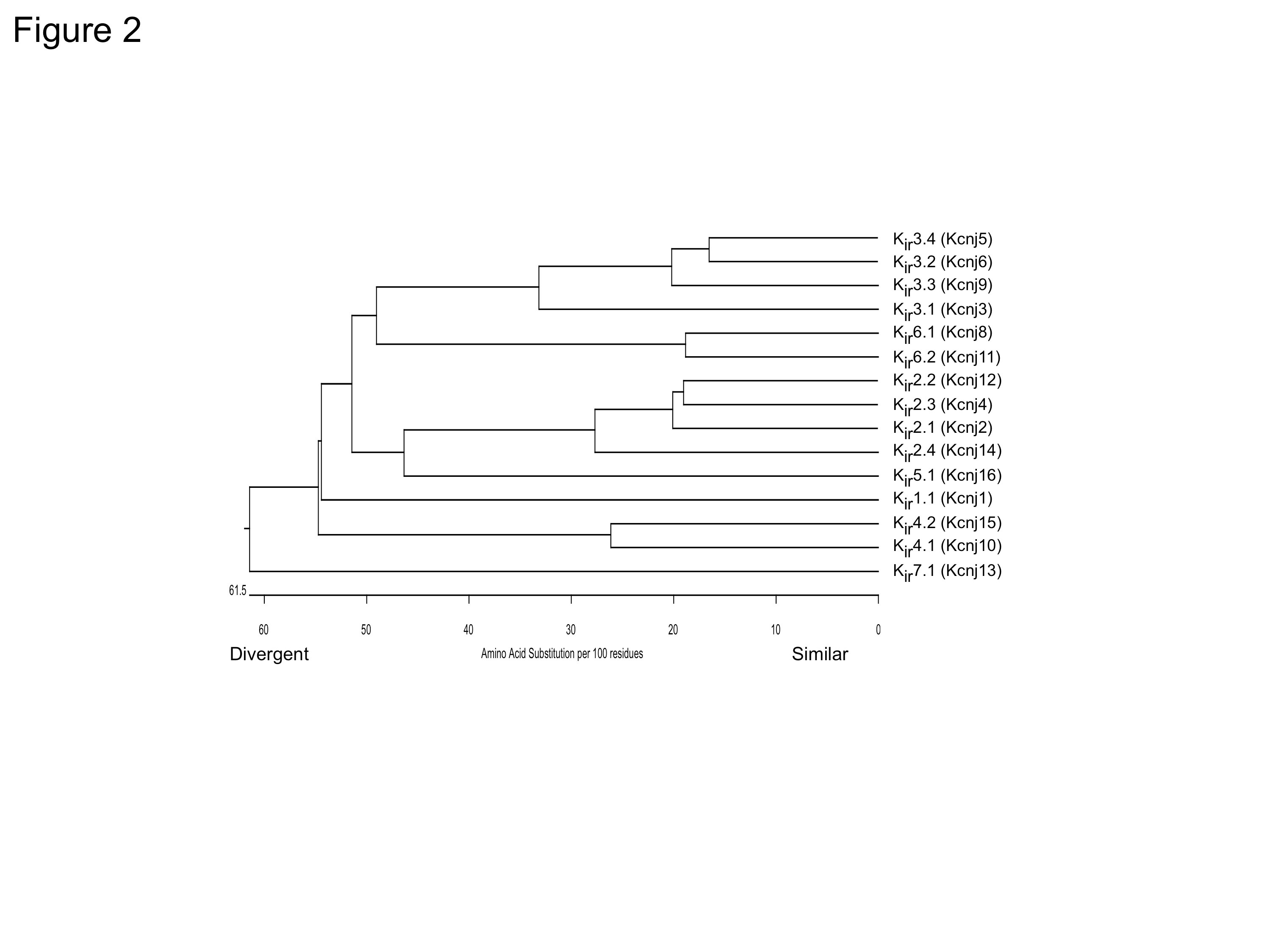
A phylogenic tree representation based on amino acid sequence alignments of the Kir genes (Fig. 2) illustrates the relationships between the seven structural Kir subfamilies. Interestingly, members of each subfamily exhibit distinct functional properties as a consequence of their structural differences. Kir1 channels, found primarily in kidney cells, are regulated by pH and protein kinases. Kir2 channels are expressed in neuronal and non-neuronal cells, and are constitutively active. Kir3 channels are activated by G proteins, alcohol and sodium ions. Strongly pH-sensitive Kir4/Kir5 channels are prominent in astrocytes. Kir6 channels coassemble with an accessory subunit, sulfonylurea receptor (SUR), to form the ATP-sensitive channels that are inhibited by ATP.
Figure 2. Phylogenetic tree for Kir channels. Amino acid sequence alignments for 15 known members of the human Kir family were created using CLUSTALV.
Structurally, all Kir channels have two membrane-spanning domains, a p-loop that forms the ion selectivity filter, and intracellular N- and C-terminal domains (Fig. 1B). Most Kir channels appear to form as alpha subunit homotetramers, or heterotetramers of related sub-family members, without need of any obligate beta subunits (Fig. 1C). Kir6 members, on the other hand, must coassemble with SUR to form an octameric channel, with four Kir6 subunits forming the pore and four SUR subunits surrounding the Kir6 subunits [48,57]. Kir channel sub-families generally associate with subunits from only the same subfamily. For example, Kir3.1 assembles with Kir3.2 but not with Kir2.1. A few exceptions to this rule have been reported, however, e.g., Kir4/Kir5 & Kir2.2/Kir4 [12,43].
In the late 1990s, a third key property for all Kir channels was discovered. The plasma membrane contains a high concentration of a particular type of phospholipid, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2). Depletion of PIP2 reduces the activity of Kir channels, indicating that PIP2 is an essential co-factor for Kir channel function [24]. Some gating modifiers, such as G proteins and ATP, appear to alter the interaction with PIP2, thereby changing the level of channel activity [5,24,49]. In addition, activation of Gq-coupled GPCRs can reduce Kir currents by temporarily depleting PIP2 [28]. Stimulation of GPCRs that couple to Gq G proteins leads to activation of phospholipase C (PLC), which generates inositol triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG) through hydrolysis of PIP2, thereby temporarily reducing the effective concentration of PIP2 within the membrane inner leaflet. All Kir channels thus far, require the membrane phospholipid, PIP2, for activity [20].
Kir interacting proteins
To date, a small handful of Kir-interacting proteins have been identified. Kir1.1 channels interact with Na+/H+ exchange regulatory factor 2 in the postsynaptic density 95/disc-large/zona occludens (PDZ) complex [56]. The Kir2 family of channels contains a class I PDZ binding motif and associates directly with synapse-associated protein 97 (SAP97) and PSD95 [25,37]. Calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase (CASK), Veli, and Mint1 have also been shown to influence Kir2 trafficking [31-32]. Kir3.2c and Kir3.3 subunits contain a class I PDZ binding motif that binds directly to the PDZ domain of sorting nexin 27 (SNX27) [4,34]. Interestingly, the PDZ binding motif of Kir3.2c/Kir3.3 does not bind to the PDZ domain of PSD95, due to specific amino acids upstream from the motif [4]. Kir4.1 in glial cells and Kir2.2 in muscle associate with the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex via α-syntrophin [8]. KATP channel complexes have been found to associate with multiple additional proteins, especially glycolytic enzymes [23], potentially through the SUR subunits.
Kir structures at atomic resolution
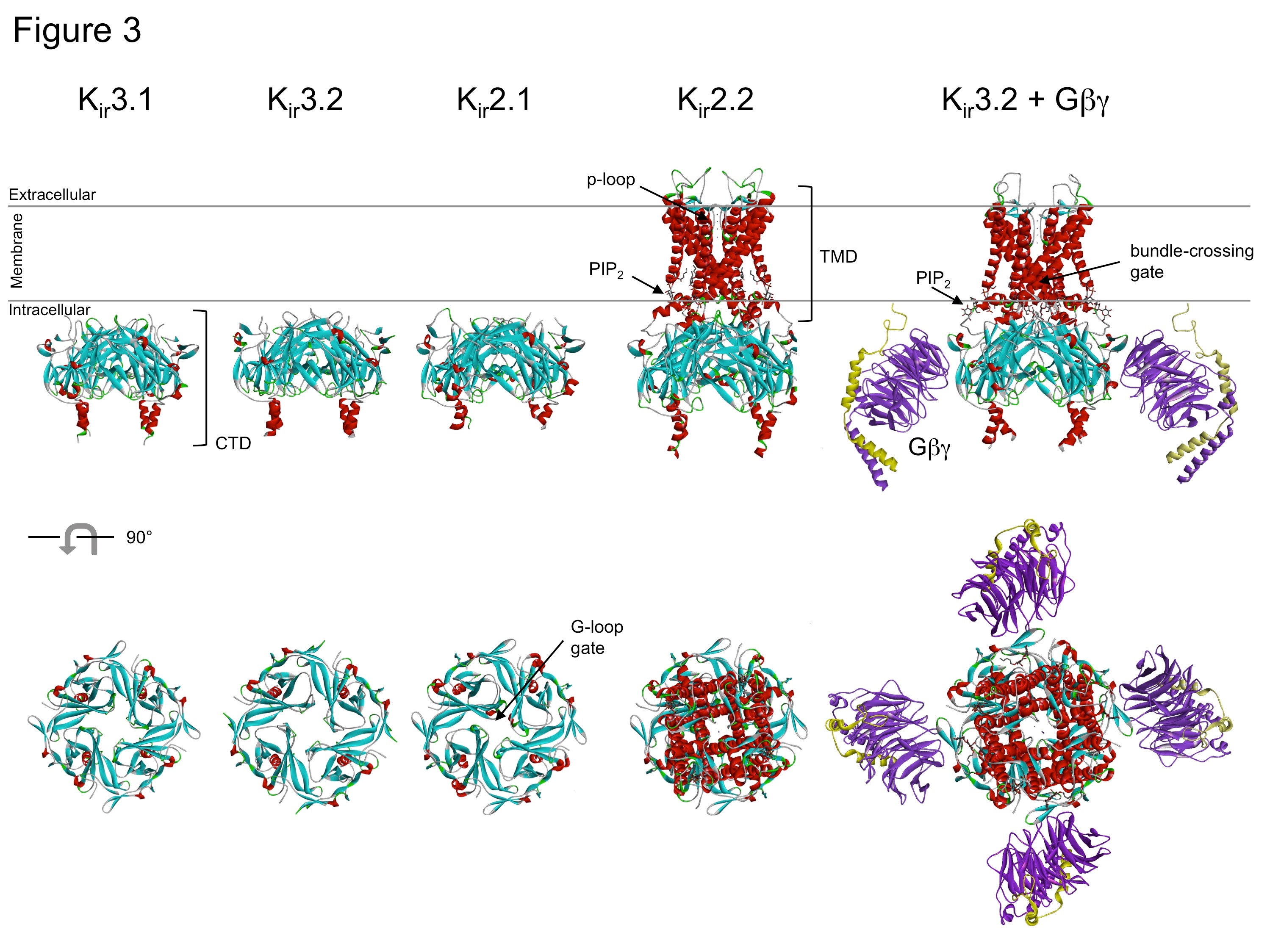
In 1998, the first atomic resolution structure of a bacterial potassium channel, Kcsa, was solved using X-ray crystallography [11]. This landmark study began a revolution of new research, moving away from mutagenesis-electrophysiology experiments, i.e., so called 'structure-function' studies, to determining the high-resolution structures of Kir channels in different states. Initially, structures were solved for the large intracellular cytoplasmic domains (CTD) of vertebrate Kir channels. To do this, the N-terminus was fused directly to the C-terminal domain, bypassing the membrane-spanning domains [26,40,42] (Fig. 3). Based on the structures of the CTDs, it was proposed that Kir channels contain two gates, a G loop gate in the CTD, and a bundle-crossing gate in the membrane-spanning domains; both of which would have to be open for the channel to conduct potassium ions [42].
Subsequently full-length structures of Kir2.2 and Kir3.2 channels were solved, providing new insight to the mechanisms of PIP2-dependent gating, sodium-dependent gating, and G protein-dependent gating [18,51,54]. Most recently, a high-resolution structure of Gβγ-Kir3.2 was described [55], setting the stage for new structures of channels complexed with regulator proteins. Collectively, these structural studies demonstrated that inward rectifier K+ channels have a long cytoplasmic pore lined with negatively charged amino acids that are important for inward rectification. These studies also provided insights into the structural basis for gating by ligands such as G protein Gβγ subunits, sodium ions, ethanol, and PIP2 [3,18,26,40-42,51,54-55]. The determination of atomic resolution structures has significantly improved our understanding of Kir channel gating and function, but at the same time, raised new questions on Kir function. Thus, more atomic resolution structures of vertebrate Kir channels are anticipated in the future.
Figure 3. High resolution crystal structures of Kir channels. Kir3.1 (PDB:1N9P), Kir3.2 (PDB:2E4F), Kir2.1 (PDB:1U4F), Kir2.2 in the presence of PIP2 (PDB:3SPI) and Kir3.2 with Gβγ in the presence of PIP2 (PDB:4KFM). Highlighted regions include cytoplasmic domain (CTD), transmembrane domain (TMD), two 'gates', e.g. G-loop and bundle-crossing, PIP2 and Gβγ subunits. Modified from [18,26,40-42,51,54-55].
Kir channels in disease
Numerous studies of mice expressing Kir mutant channels have been described that elucidate the function of particular Kir channel subunits in different tissues, and multiple human diseases have now been linked to point mutations in Kir genes tissues (for review, see [1]).
Mutations in Kir1 channels underlie Bartter syndrome, antenatal, type 2 [50]. Loss of function mutations in Kir2.1 cause Andersen-Tawil syndrome (ATS), a rare multisystem disorder characterized by a long QT interval and ventricular arrhythmias, periodic paralysis and dysmorphic features [44]. In contrast, gain of function Kir2.1 mutations underlie short QT and predisposition to ventricular arrhythmias [2]. A recent genome-wide associative study (GWAS) study of alcoholics found single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in Kir3.2 (KCNJ6) [27], though it remains to be determined what impact the SNPs have on Kir3.2 function.
Kir4.1 has been associated with epilepsy in both causative and protective roles [7,13], including a role in the monogenic SESAME/EAST syndromes [45-47]. Loss of Kir4.1 expression abolishes endocochlear potential and causes deafness in Pendred syndrome [53].
Disruption of the Kir6.1 gene in mice was reported to cause phenotypes similar to those of vasospastic (Prinzmetal) angina [36], and loss of function mutations in Kir6.2 cause human hyperinsulinism [39]. Conversely, activating mutations in Kir6.2 cause permanent neonatal diabetes [14] and are linked to type 2 diabetes [15,17,52]. In humans, gain-of-function mutations in Kir6.1 have now been associated with Cantu syndrome, a complex disease mimicking effects of potassium channel opener overdose [6,9].
For additional information on different Kir channels and more comprehensive list of citations, please consider some of these more extensive reviews [19,35,38].
References
1. Abraham MR, Jahangir A, Alekseev AE, Terzic A. (1999) Channelopathies of inwardly rectifying potassium channels. FASEB J, 13 (14): 1901-10. [PMID:10544173]
2. Ambrosini E, Sicca F, Brignone MS, D'Adamo MC, Napolitano C, Servettini I, Moro F, Ruan Y, Guglielmi L, Pieroni S et al.. (2014) Genetically induced dysfunctions of Kir2.1 channels: implications for short QT3 syndrome and autism-epilepsy phenotype. Hum Mol Genet, 23 (18): 4875-86. [PMID:24794859]
3. Aryal P, Dvir H, Choe S, Slesinger PA. (2009) A discrete alcohol pocket involved in GIRK channel activation. Nat Neurosci, 12 (8): 988-95. [PMID:19561601]
4. Balana B, Maslennikov I, Kwiatkowski W, Stern KM, Bahima L, Choe S, Slesinger PA. (2011) Mechanism underlying selective regulation of G protein-gated inwardly rectifying potassium channels by the psychostimulant-sensitive sorting nexin 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 108 (14): 5831-6. [PMID:21422294]
5. Baukrowitz T, Schulte U, Oliver D, Herlitze S, Krauter T, Tucker SJ, Ruppersberg JP, Fakler B. (1998) PIP2 and PIP as determinants for ATP inhibition of KATP channels. Science, 282 (5391): 1141-4. [PMID:9804555]
6. Brownstein CA, Towne MC, Luquette LJ, Harris DJ, Marinakis NS, Meinecke P, Kutsche K, Campeau PM, Yu TW, Margulies DM et al.. (2013) Mutation of KCNJ8 in a patient with Cantú syndrome with unique vascular abnormalities - support for the role of K(ATP) channels in this condition. Eur J Med Genet, 56 (12): 678-82. [PMID:24176758]
7. Buono RJ, Lohoff FW, Sander T, Sperling MR, O'Connor MJ, Dlugos DJ, Ryan SG, Golden GT, Zhao H, Scattergood TM, Berrettini WH, Ferraro TN. (2004) Association between variation in the human KCNJ10 potassium ion channel gene and seizure susceptibility. Epilepsy Res, 58 (2-3): 175-83. [PMID:15120748]
8. Connors NC, Adams ME, Froehner SC, Kofuji P. (2004) The potassium channel Kir4.1 associates with the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex via alpha-syntrophin in glia. J Biol Chem, 279 (27): 28387-92. [PMID:15102837]
9. Cooper PE, Reutter H, Woelfle J, Engels H, Grange DK, van Haaften G, van Bon BW, Hoischen A, Nichols CG. (2014) Cantú syndrome resulting from activating mutation in the KCNJ8 gene. Hum Mutat, 35 (7): 809-13. [PMID:24700710]
10. Dascal N, Lim NF, Schreibmayer W, Wang W, Davidson N, Lester HA. (1993) Expression of an atrial G-protein-activated potassium channel in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 90 (14): 6596-600. [PMID:8341673]
11. Doyle DA, Morais Cabral J, Pfuetzner RA, Kuo A, Gulbis JM, Cohen SL, Chait BT, MacKinnon R. (1998) The structure of the potassium channel: molecular basis of K+ conduction and selectivity. Science, 280 (5360): 69-77. [PMID:9525859]
12. Fakler B, Bond CT, Adelman JP, Ruppersberg JP. (1996) Heterooligomeric assembly of inward-rectifier K+ channels from subunits of different subfamilies: Kir2.1 (IRK1) and Kir4.1 (BIR10). Pflugers Arch, 433 (1-2): 77-83. [PMID:9019734]
13. Ferraro TN, Golden GT, Smith GG, Martin JF, Lohoff FW, Gieringer TA, Zamboni D, Schwebel CL, Press DM, Kratzer SO, Zhao H, Berrettini WH, Buono RJ. (2004) Fine mapping of a seizure susceptibility locus on mouse Chromosome 1: nomination of Kcnj10 as a causative gene. Mamm Genome, 15 (4): 239-51. [PMID:15112102]
14. Gloyn AL, Pearson ER, Antcliff JF, Proks P, Bruining GJ, Slingerland AS, Howard N, Srinivasan S, Silva JM, Molnes J et al.. (2004) Activating mutations in the gene encoding the ATP-sensitive potassium-channel subunit Kir6.2 and permanent neonatal diabetes. N Engl J Med, 350 (18): 1838-49. [PMID:15115830]
15. Gloyn AL, Weedon MN, Owen KR, Turner MJ, Knight BA, Hitman G, Walker M, Levy JC, Sampson M, Halford S et al.. (2003) Large-scale association studies of variants in genes encoding the pancreatic beta-cell KATP channel subunits Kir6.2 (KCNJ11) and SUR1 (ABCC8) confirm that the KCNJ11 E23K variant is associated with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes, 52 (2): 568-72. [PMID:12540637]
16. Hagiwara S, Takahashi K. (1974) The anomalous rectification and cation selectivity of the membrane of a starfish egg cell. J Membr Biol, 18 (1): 61-80. [PMID:4854650]
17. Hani EH, Boutin P, Durand E, Inoue H, Permutt MA, Velho G, Froguel P. (1998) Missense mutations in the pancreatic islet beta cell inwardly rectifying K+ channel gene (KIR6.2/BIR): a meta-analysis suggests a role in the polygenic basis of Type II diabetes mellitus in Caucasians. Diabetologia, 41 (12): 1511-5. [PMID:9867219]
18. Hansen SB, Tao X, MacKinnon R. (2011) Structural basis of PIP2 activation of the classical inward rectifier K+ channel Kir2.2. Nature, 477 (7365): 495-8. [PMID:21874019]
19. Hibino H, Inanobe A, Furutani K, Murakami S, Findlay I, Kurachi Y. (2010) Inwardly rectifying potassium channels: their structure, function, and physiological roles. Physiol Rev, 90 (1): 291-366. [PMID:20086079]
20. Hilgemann DW, Feng S, Nasuhoglu C. (2001) The complex and intriguing lives of PIP2 with ion channels and transporters. Sci STKE, 2001 (111): re19. [PMID:11734659]
21. Hille B. (2001) Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes, 3rd Ed. In (Sinauer Associates Inc.) .
22. Ho K, Nichols CG, Lederer WJ, Lytton J, Vassilev PM, Kanazirska MV, Hebert SC. (1993) Cloning and expression of an inwardly rectifying ATP-regulated potassium channel. Nature, 362 (6415): 31-8. [PMID:7680431]
23. Hong M, Kefaloyianni E, Bao L, Malester B, Delaroche D, Neubert TA, Coetzee WA. (2011) Cardiac ATP-sensitive K+ channel associates with the glycolytic enzyme complex. FASEB J, 25 (7): 2456-67. [PMID:21482559]
24. Huang CL, Feng S, Hilgemann DW. (1998) Direct activation of inward rectifier potassium channels by PIP2 and its stabilization by Gbetagamma. Nature, 391 (6669): 803-6. [PMID:9486652]
25. Inanobe A, Fujita A, Ito M, Tomoike H, Inageda K, Kurachi Y. (2002) Inward rectifier K+ channel Kir2.3 is localized at the postsynaptic membrane of excitatory synapses. Am J Physiol, Cell Physiol, 282 (6): C1396-403. [PMID:11997254]
26. Inanobe A, Matsuura T, Nakagawa A, Kurachi Y. (2007) Structural diversity in the cytoplasmic region of G protein-gated inward rectifier K+ channels. Channels (Austin), 1 (1): 39-45. [PMID:19151589]
27. Kang SJ, Rangaswamy M, Manz N, Wang JC, Wetherill L, Hinrichs T, Almasy L, Brooks A, Chorlian DB, Dick D et al.. (2012) Family-based genome-wide association study of frontal θ oscillations identifies potassium channel gene KCNJ6. Genes Brain Behav, 11 (6): 712-9. [PMID:22554406]
28. Kobrinsky E, Mirshahi T, Zhang H, Jin T, Logothetis DE. (2000) Receptor-mediated hydrolysis of plasma membrane messenger PIP2 leads to K+-current desensitization. Nat Cell Biol, 2 (8): 507-14. [PMID:10934471]
29. Kubo Y, Baldwin TJ, Jan YN, Jan LY. (1993) Primary structure and functional expression of a mouse inward rectifier potassium channel. Nature, 362 (6416): 127-33. [PMID:7680768]
30. Kubo Y, Reuveny E, Slesinger PA, Jan YN, Jan LY. (1993) Primary structure and functional expression of a rat G-protein-coupled muscarinic potassium channel. Nature, 364 (6440): 802-6. [PMID:8355805]
31. Leonoudakis D, Conti LR, Anderson S, Radeke CM, McGuire LM, Adams ME, Froehner SC, Yates 3rd JR, Vandenberg CA. (2004) Protein trafficking and anchoring complexes revealed by proteomic analysis of inward rectifier potassium channel (Kir2.x)-associated proteins. J Biol Chem, 279 (21): 22331-46. [PMID:15024025]
32. Leonoudakis D, Conti LR, Radeke CM, McGuire LM, Vandenberg CA. (2004) A multiprotein trafficking complex composed of SAP97, CASK, Veli, and Mint1 is associated with inward rectifier Kir2 potassium channels. J Biol Chem, 279 (18): 19051-63. [PMID:14960569]
33. Lopatin AN, Makhina EN, Nichols CG. (1994) Potassium channel block by cytoplasmic polyamines as the mechanism of intrinsic rectification. Nature, 372 (6504): 366-9. [PMID:7969496]
34. Lunn ML, Nassirpour R, Arrabit C, Tan J, McLeod I, Arias CM, Sawchenko PE, Yates 3rd JR, Slesinger PA. (2007) A unique sorting nexin regulates trafficking of potassium channels via a PDZ domain interaction. Nat Neurosci, 10 (10): 1249-59. [PMID:17828261]
35. Lüscher C, Slesinger PA. (2010) Emerging roles for G protein-gated inwardly rectifying potassium (GIRK) channels in health and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci, 11 (5): 301-15. [PMID:20389305]
36. Miki T, Suzuki M, Shibasaki T, Uemura H, Sato T, Yamaguchi K, Koseki H, Iwanaga T, Nakaya H, Seino S. (2002) Mouse model of Prinzmetal angina by disruption of the inward rectifier Kir6.1. Nat Med, 8 (5): 466-72. [PMID:11984590]
37. Nehring RB, Wischmeyer E, Döring F, Veh RW, Sheng M, Karschin A. (2000) Neuronal inwardly rectifying K(+) channels differentially couple to PDZ proteins of the PSD-95/SAP90 family. J Neurosci, 20 (1): 156-62. [PMID:10627592]
38. Nichols CG, Lopatin AN. (1997) Inward rectifier potassium channels. Annu Rev Physiol, 59: 171-91. [PMID:9074760]
39. Nichols CG, Shyng SL, Nestorowicz A, Glaser B, Clement 4th JP, Gonzalez G, Aguilar-Bryan L, Permutt MA, Bryan J. (1996) Adenosine diphosphate as an intracellular regulator of insulin secretion. Science, 272 (5269): 1785-7. [PMID:8650576]
40. Nishida M, MacKinnon R. (2002) Structural basis of inward rectification: cytoplasmic pore of the G protein-gated inward rectifier GIRK1 at 1.8 A resolution. Cell, 111 (7): 957-65. [PMID:12507423]
41. Pegan S, Arrabit C, Slesinger PA, Choe S. (2006) Andersen's syndrome mutation effects on the structure and assembly of the cytoplasmic domains of Kir2.1. Biochemistry, 45 (28): 8599-606. [PMID:16834334]
42. Pegan S, Arrabit C, Zhou W, Kwiatkowski W, Collins A, Slesinger PA, Choe S. (2005) Cytoplasmic domain structures of Kir2.1 and Kir3.1 show sites for modulating gating and rectification. Nat Neurosci, 8 (3): 279-87. [PMID:15723059]
43. Pessia M, Tucker SJ, Lee K, Bond CT, Adelman JP. (1996) Subunit positional effects revealed by novel heteromeric inwardly rectifying K+ channels. EMBO J, 15 (12): 2980-7. [PMID:8670799]
44. Plaster NM, Tawil R, Tristani-Firouzi M, Canún S, Bendahhou S, Tsunoda A, Donaldson MR, Iannaccone ST, Brunt E, Barohn R et al.. (2001) Mutations in Kir2.1 cause the developmental and episodic electrical phenotypes of Andersen's syndrome. Cell, 105 (4): 511-9. [PMID:11371347]
45. Reichold M, Zdebik AA, Lieberer E, Rapedius M, Schmidt K, Bandulik S, Sterner C, Tegtmeier I, Penton D, Baukrowitz T et al.. (2010) KCNJ10 gene mutations causing EAST syndrome (epilepsy, ataxia, sensorineural deafness, and tubulopathy) disrupt channel function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 107 (32): 14490-5. [PMID:20651251]
46. Sala-Rabanal M, Kucheryavykh LY, Skatchkov SN, Eaton MJ, Nichols CG. (2010) Molecular mechanisms of EAST/SeSAME syndrome mutations in Kir4.1 (KCNJ10). J Biol Chem, 285 (46): 36040-8. [PMID:20807765]
47. Scholl UI, Choi M, Liu T, Ramaekers VT, Häusler MG, Grimmer J, Tobe SW, Farhi A, Nelson-Williams C, Lifton RP. (2009) Seizures, sensorineural deafness, ataxia, mental retardation, and electrolyte imbalance (SeSAME syndrome) caused by mutations in KCNJ10. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 106 (14): 5842-7. [PMID:19289823]
48. Shyng S, Nichols CG. (1997) Octameric stoichiometry of the KATP channel complex. J Gen Physiol, 110 (6): 655-64. [PMID:9382894]
49. Shyng SL, Nichols CG. (1998) Membrane phospholipid control of nucleotide sensitivity of KATP channels. Science, 282 (5391): 1138-41. [PMID:9804554]
50. Simon DB, Karet FE, Rodriguez-Soriano J, Hamdan JH, DiPietro A, Trachtman H, Sanjad SA, Lifton RP. (1996) Genetic heterogeneity of Bartter's syndrome revealed by mutations in the K+ channel, ROMK. Nat Genet, 14 (2): 152-6. [PMID:8841184]
51. Tao X, Avalos JL, Chen J, MacKinnon R. (2009) Crystal structure of the eukaryotic strong inward-rectifier K+ channel Kir2.2 at 3.1 A resolution. Science, 326 (5960): 1668-74. [PMID:20019282]
52. Villareal DT, Koster JC, Robertson H, Akrouh A, Miyake K, Bell GI, Patterson BW, Nichols CG, Polonsky KS. (2009) Kir6.2 variant E23K increases ATP-sensitive K+ channel activity and is associated with impaired insulin release and enhanced insulin sensitivity in adults with normal glucose tolerance. Diabetes, 58 (8): 1869-78. [PMID:19491206]
53. Wangemann P, Itza EM, Albrecht B, Wu T, Jabba SV, Maganti RJ, Lee JH, Everett LA, Wall SM, Royaux IE et al.. (2004) Loss of KCNJ10 protein expression abolishes endocochlear potential and causes deafness in Pendred syndrome mouse model. BMC Med, 2: 30. [PMID:15320950]
54. Whorton MR, MacKinnon R. (2011) Crystal structure of the mammalian GIRK2 K+ channel and gating regulation by G proteins, PIP2, and sodium. Cell, 147 (1): 199-208. [PMID:21962516]
55. Whorton MR, MacKinnon R. (2013) X-ray structure of the mammalian GIRK2-βγ G-protein complex. Nature, 498 (7453): 190-7. [PMID:23739333]
56. Yoo D, Flagg TP, Olsen O, Raghuram V, Foskett JK, Welling PA. (2004) Assembly and trafficking of a multiprotein ROMK (Kir 1.1) channel complex by PDZ interactions. J Biol Chem, 279 (8): 6863-73. [PMID:14604981]
57. Zerangue N, Schwappach B, Jan YN, Jan LY. (1999) A new ER trafficking signal regulates the subunit stoichiometry of plasma membrane K(ATP) channels. Neuron, 22 (3): 537-48. [PMID:10197533]