
Top ▲

GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Target not currently curated in GtoImmuPdb
Target id: 2152
Nomenclature: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase catalytic subunit type 3
Abbreviated Name: VPS34
Family: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase family, Phosphatidylinositol kinases
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | - | 887 | 18q12.3 | PIK3C3 | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase catalytic subunit type 3 | |
| Mouse | - | 887 | 18 B1 | Pik3c3 | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase catalytic subunit type 3 | |
| Rat | - | 887 | 18p12 | Pik3c3 | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, catalytic subunit type 3 | |
Database Links  |
|
| Alphafold | Q8NEB9 (Hs), Q6PF93 (Mm), O88763 (Rn) |
| BRENDA | 2.7.1.137 |
| CATH/Gene3D | 1.10.1070.11, 2.60.40.150 |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL1075165 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000078142 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000033628 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000017840 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 5289 (Hs), 225326 (Mm), 65052 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000078142 (Hs) |
| KEGG Enzyme | 2.7.1.137 |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:5289 (Hs), mmu:225326 (Mm), rno:65052 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 602609 (Hs) |
| Pharos | Q8NEB9 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_002647 (Hs), NM_181414 (Mm), NM_022958 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_002638 (Hs), NP_852079 (Mm), NP_075247 (Rn) |
| SynPHARM | 83984 (in complex with PIK-III) |
| UniProtKB | Q8NEB9 (Hs), Q6PF93 (Mm), O88763 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | PIK3C3 (Hs) |
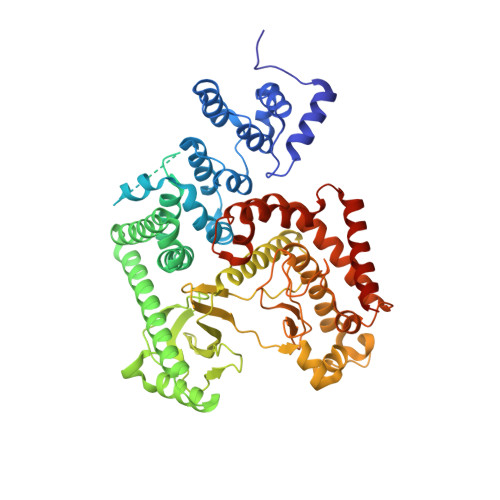
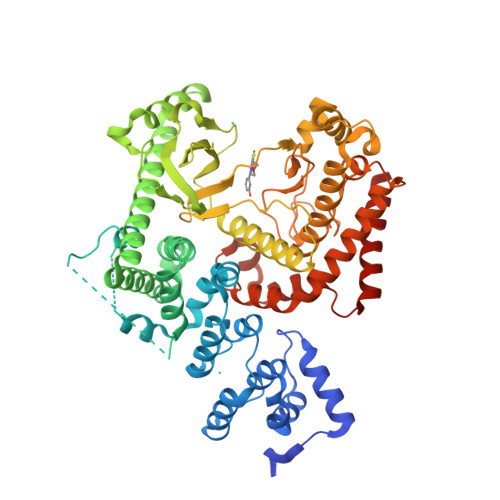
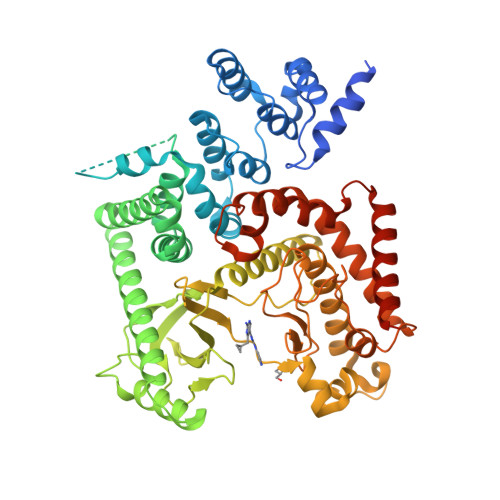
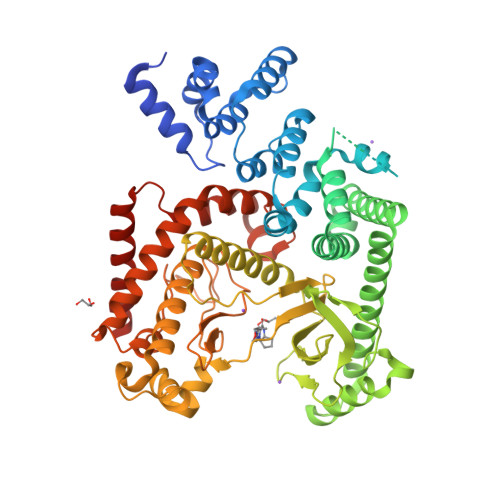
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||

|
|
||||||||||||
Enzyme Reaction  |
||||
|
||||
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Inhibitors | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General Comments |
| VPS34 is the only Class III PI 3-kinase (a lipid kinase) that has been identified. Human VPS34 is ubiquitously expressed and is the enzymatic component of a multiprotein complex. VPS34 substrate specificity is limited to phosphatidylinositol. Mammalian VPS34 plays roles in autophagy, endosomal trafficking, other aspects of membrane biology, and nutrient sensing [1]. VPS34 activity is required for some viruses to replicate in human host cells: e.g. SARS-CoV-2 [13] and hepatitis C virus [11], likely because viruses rely heavily on host cell lipids for replication. Pharmacological inhibition of VPS34 has been shown to reduce SARS-CoV-2 replication in vitro (IC50 ~600 nM) [13]. |
1. Backer JM. (2008) The regulation and function of Class III PI3Ks: novel roles for Vps34. Biochem J, 410 (1): 1-17. [PMID:18215151]
2. Borsari C, Rageot D, Dall'Asen A, Bohnacker T, Melone A, Sele AM, Jackson E, Langlois JB, Beaufils F, Hebeisen P et al.. (2019) A Conformational Restriction Strategy for the Identification of a Highly Selective Pyrimido-pyrrolo-oxazine mTOR Inhibitor. J Med Chem, 62 (18): 8609-8630. [PMID:31465220]
3. Certal V, Carry JC, Halley F, Virone-Oddos A, Thompson F, Filoche-Rommé B, El-Ahmad Y, Karlsson A, Charrier V, Delorme C et al.. (2014) Discovery and optimization of pyrimidone indoline amide PI3Kβ inhibitors for the treatment of phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN)-deficient cancers. J Med Chem, 57 (3): 903-20. [PMID:24387221]
4. D'Angelo ND, Kim TS, Andrews K, Booker SK, Caenepeel S, Chen K, D'Amico D, Freeman D, Jiang J, Liu L et al.. (2011) Discovery and optimization of a series of benzothiazole phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) dual inhibitors. J Med Chem, 54 (6): 1789-811. [PMID:21332118]
5. Dowdle WE, Nyfeler B, Nagel J, Elling RA, Liu S, Triantafellow E, Menon S, Wang Z, Honda A, Pardee G et al.. (2014) Selective VPS34 inhibitor blocks autophagy and uncovers a role for NCOA4 in ferritin degradation and iron homeostasis in vivo. Nat Cell Biol, 16 (11): 1069-79. [PMID:25327288]
6. Henley ZA, Amour A, Barton N, Bantscheff M, Bergamini G, Bertrand SM, Convery M, Down K, Dümpelfeld B, Edwards CD et al.. (2020) Optimization of Orally Bioavailable PI3Kδ Inhibitors and Identification of Vps34 as a Key Selectivity Target. J Med Chem, 63 (2): 638-655. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01585 [PMID:31855425]
7. Hu DX, Patel S, Chen H, Wang S, Staben ST, Dimitrova YN, Wallweber HA, Lee JY, Chan GKY, Sneeringer CJ et al.. (2022) Structure-Based Design of Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable VPS34 Kinase Inhibitors. J Med Chem, 65 (17): 11500-11512. [PMID:34779204]
8. Liu Q, Wang J, Kang SA, Thoreen CC, Hur W, Ahmed T, Sabatini DM, Gray NS. (2011) Discovery of 9-(6-aminopyridin-3-yl)-1-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)benzo[h][1,6]naphthyridin-2(1H)-one (Torin2) as a potent, selective, and orally available mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor for treatment of cancer. J Med Chem, 54 (5): 1473-80. [PMID:21322566]
9. Rageot D, Bohnacker T, Melone A, Langlois JB, Borsari C, Hillmann P, Sele AM, Beaufils F, Zvelebil M, Hebeisen P et al.. (2018) Discovery and Preclinical Characterization of 5-[4,6-Bis({3-oxa-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-8-yl})-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl]-4-(difluoromethyl)pyridin-2-amine (PQR620), a Highly Potent and Selective mTORC1/2 Inhibitor for Cancer and Neurological Disorders. J Med Chem, 61 (22): 10084-10105. [PMID:30359003]
10. Ronan B, Flamand O, Vescovi L, Dureuil C, Durand L, Fassy F, Bachelot MF, Lamberton A, Mathieu M, Bertrand T et al.. (2014) A highly potent and selective Vps34 inhibitor alters vesicle trafficking and autophagy. Nat Chem Biol, 10 (12): 1013-9. [PMID:25326666]
11. Su WC, Chao TC, Huang YL, Weng SC, Jeng KS, Lai MM. (2011) Rab5 and class III phosphoinositide 3-kinase Vps34 are involved in hepatitis C virus NS4B-induced autophagy. J Virol, 85 (20): 10561-71. [PMID:21835792]
12. Taracido IC, Harrington EM, Honda A, Keaney E. (2014) Bi-heteroaryl compounds as Vps34 inhibitors. Patent number: US8685993. Assignee: Novartis Ag. Priority date: 21/12/2010. Publication date: 01/04/2014.
13. Williams CG, Jureka AS, Silvas JA, Nicolini AM, Chvatal SA, Carlson-Stevermer J, Oki J, Holden K, Basler CF. (2021) Inhibitors of VPS34 and fatty-acid metabolism suppress SARS-CoV-2 replication. Cell Rep, 36 (5): 109479. [PMID:34320401]