
Top ▲

GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| class A G protein-coupled receptor | ||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 7 | 442 | 13q22.3 | EDNRB | endothelin receptor type B | 2,18,36,39,47 |
| Mouse | 7 | 442 | 14 53.05 cM | Ednrb | endothelin receptor type B | 25 |
| Rat | 7 | 442 | 15q22 | Ednrb | endothelin receptor type B | 7,48 |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| HSCR | HSCR2 | endothelin B receptor | ET-BR |
Database Links  |
|
| Specialist databases | |
| GPCRdb | ednrb_human (Hs), ednrb_mouse (Mm), ednrb_rat (Rn) |
| Other databases | |
| Alphafold | P24530 (Hs), P48302 (Mm), P21451 (Rn) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL1785 (Hs), CHEMBL1681617 (Mm), CHEMBL4631 (Rn) |
| DrugBank Target | P24530 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000136160 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000022122 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000010997 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 1910 (Hs), 13618 (Mm), 50672 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000136160 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:1910 (Hs), mmu:13618 (Mm), rno:50672 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 131244 (Hs) |
| Orphanet | ORPHA121287 (Hs) |
| Pharos | P24530 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_000115 (Hs), NM_007904 (Mm), NM_017333 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_000106 (Hs), NP_031930 (Mm), NP_059029 (Rn) |
| SynPHARM | 84537 (in complex with K-8794) |
| UniProtKB | P24530 (Hs), P48302 (Mm), P21451 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | EDNRB (Hs) |
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
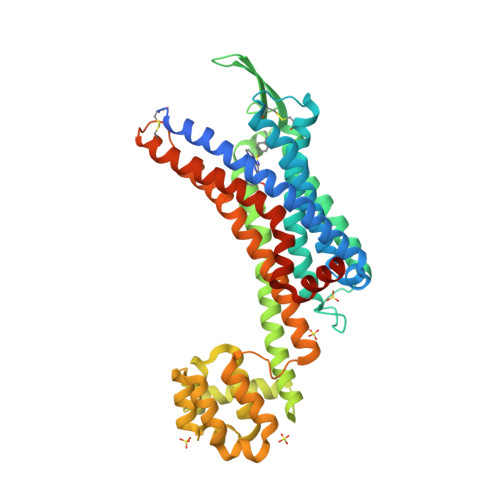
|
|
||||||||||||
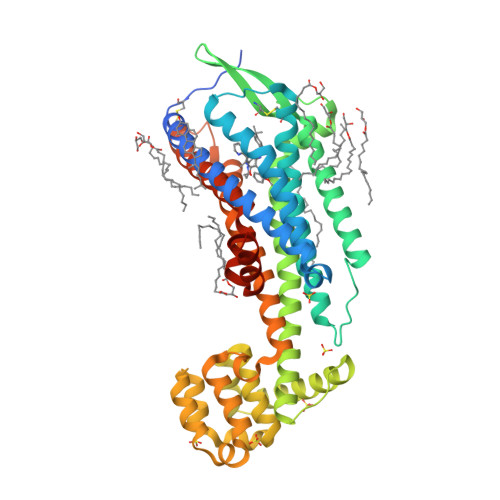
|
|
||||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| endothelin-2 {Sp: Human} |
| endothelin-1 {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| endothelin-3 {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| endothelin-2 {Sp: Mouse, Rat} |
| Potency order of endogenous ligands (Human) |
| endothelin-1 (EDN1, P05305) = endothelin-2 (EDN2, P20800), endothelin-3 (EDN3, P14138) [48] |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific agonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In mammals, the endothelin (ET) family comprises three endogenous isoforms, ET-1, ET-2 and ET-3. ET-1 is the principal isoform in the human cardiovascular system and is one of the most ubiquitous, potent and unusually long lasting constrictor of human vessels. ET-2 has been less extensively studied than other ET peptides but the peptide is present in human cardiovascular tissues and ET-2 was as potent a vasoconstrictor as ET-1 in human arteries and veins. VIC (vasoactive intestinal contractor) is the murine isoform of ET-2. Endothelial cells do not synthesise ET-3 but the mature peptide is detectable in plasma and other tissues including heart and brain. ET-3 is unique in that it is the only endogenous isoform that distinguishes between the two endothelin receptors. It has the same affinity at the ETB receptor as ET-1 but, at physiological concentrations, has little or no affinity for the ETA. The only endogenous peptides with a high degree of sequence similarity to the ETs are the sarafotoxins (S6a, S6b, S6c, S6d). This family of 21aa peptides were originally discovered in the venom of a snake, Atractaspis engadensis [11]. ETB receptors are initially classfied according to the the rank order of potency of ET agonists with ET-1 being equipotent to ET-3, confirmed by using selective peptide antagonists (BQ788) or non-peptide antagonists (e.g. A192621 or Ro 46-8443). |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific antagonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists are currently classified as either ETA-selective, ETB-selective or mixed antagonists that display similar affinity for both receptors. A limited number of peptide (e.g. BQ788) and non-peptide (e.g. A192621) ETB antagonists have been developed, reflecting the lack of clinical need for this type of compound. They are less potent than ETA antagonists and display lower selectivity (usually only 1-2 orders of magnitude) for the ETB receptor [11]. The approved drug, macitentan, is a dual endothelin receptor antagonist [4] with higher affinity for the ETA receptor than for the ETB receptor (IC50 0.5nM and 391nM respectively) [4]. Antagonists that block both ETA and ETB receptors (also called mixed or balanced) include peptides such as TAK044. Non-peptide compounds included bosentan (RO470203, Tracleer [8]) the first antagonist in clinical use [12] SB209670 [17], SB217242 (enrasentan, [40]) and RO610612 (tezosentan, [9]). The distinction between antagonists that are ETA selective and those that block both ETA and ETB receptors is not precise but generally the former display greater than 100-fold selectivity for the ETA subtype and the latter less than 100-fold. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Primary Transduction Mechanisms 
|
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
|
Gs family Gi/Go family Gq/G11 family |
Phospholipase C stimulation Phospholipase A2 stimulation Phospholipase D stimulation |
| Comments: Activation of ETB receptors to produce a range of biological actions in different tissues is thought to be mediated by a number of transduction systems coupled to various types of G-protein including Gq/G11, Gs, Gq/13 and Gi2. The major enzymes systems activated include phospholipase C, A2 and D. Increases of tyrosine phosphorylation of cellular proteins, stimulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and DNA synthesis are mediated by ETB receptors in certain cell types such as astrocytes [16,42,51,53]. | |
| References: 16,42,51,53 | |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
Expression Datasets  |
|
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology 
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General Comments |
| For reviews on endothelin receptors see [3,13,49]. |
1. Adner M, Cardell LO, Sjöberg T, Ottosson A, Edvinsson L. (1996) Contractile endothelin-B (ETB) receptors in human small bronchi. Eur Respir J, 9 (2): 351-5. [PMID:8777976]
2. Arai H, Nakao K, Takaya K, Hosoda K, Ogawa Y, Nakanishi S, Imura H. (1993) The human endothelin-B receptor gene. Structural organization and chromosomal assignment. J Biol Chem, 268 (5): 3463-70. [PMID:8429023]
3. Battistini B, Berthiaume N, Kelland NF, Webb DJ, Kohan DE. (2006) Profile of past and current clinical trials involving endothelin receptor antagonists: the novel "-sentan" class of drug. Exp Biol Med (Maywood), 231: 653-695. [PMID:16740981]
4. Bolli MH, Boss C, Binkert C, Buchmann S, Bur D, Hess P, Iglarz M, Meyer S, Rein J, Rey M et al.. (2012) The discovery of N-[5-(4-bromophenyl)-6-[2-[(5-bromo-2-pyrimidinyl)oxy]ethoxy]-4-pyrimidinyl]-N'-propylsulfamide (Macitentan), an orally active, potent dual endothelin receptor antagonist. J Med Chem, 55 (17): 7849-61. [PMID:22862294]
5. Bolli MH, Marfurt J, Grisostomi C, Boss C, Binkert C, Hess P, Treiber A, Thorin E, Morrison K, Buchmann S et al.. (2004) Novel benzo[1,4]diazepin-2-one derivatives as endothelin receptor antagonists. J Med Chem, 47 (11): 2776-95. [PMID:15139756]
6. Breu V, Clozel M, Burri K, Hirth G, Neidhart W, Ramuz H. (1996) In vitro characterisation of Ro 46-8443, the first non-peptide antagonist selective for the endothelin ETB receptor. FEBS Lett, 383 (1-2): 37-41. [PMID:8612786]
7. Cai Y, Yamada T, Xin X, Agui T, Matsumoto K. (1995) Mapping of the genes for rat endothelin receptor type A (ETAR) and type B (ETBR) to chromosomes 19 and 15 respectively. Anim Genet, 26 (1): 39-41. [PMID:7702211]
8. Clozel M, Breu V, Gray GA, Kalina B, Löffler BM, Burri K, Cassal JM, Hirth G, Müller M, Neidhart W et al.. (1994) Pharmacological characterization of bosentan, a new potent orally active nonpeptide endothelin receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 270 (1): 228-35. [PMID:8035319]
9. Clozel M, Ramuz H, Clozel JP, Breu V, Hess P, Loffler BM, Coassolo P, Roux S. (1999) Pharmacology of tezosentan, new endothelin receptor antagonist designed for parenteral use. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 290: 840-846. [PMID:10411600]
10. Davenport AP. (1997) Distribution of endothelin receptors. In Endothelins in Biology and Medicine. Edited by Mille R, Pelton JT, Huggins J (CRC Press.) 45-68. [ISBN:0849369754]
11. Davenport AP. (2002) International Union of Pharmacology. XXIX. Update on endothelin receptor nomenclature. Pharmacol Rev, 54 (2): 219-26. [PMID:12037137]
12. Davenport AP, Maguire JJ. (2002) Of mice and men: advances in endothelin research and first antagonist gains FDA approval. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 23 (4): 155-7. [PMID:11931980]
13. Davenport AP, Maguire JJ. (2006) Endothelin. Handb Exp Pharmacol, (176 Pt 1): 295-329. [PMID:16999223]
14. Davenport AP, O'Reilly G, Kuc RE. (1995) Endothelin ETA and ETB mRNA and receptors expressed by smooth muscle in the human vasculature: majority of the ETA sub-type. Br J Pharmacol, 114 (6): 1110-6. [PMID:7620699]
15. Davenport AP, Russell FD. (2001) Endothelin converting enzymes and endothelin receptor localisation in human tissues. Handb Exp Pharmacol, 152: 209-237.
16. Douglas SA, Ohlstein EH. (1997) Signal transduction mechanisms mediating the vascular actions of endothelin. J Vasc Res, 34 (3): 152-64. [PMID:9226297]
17. Elliott JD, Lago MA, Cousins RD, Gao A, Leber JD, Erhard KF, Nambi P, Elshourbagy NA, Kumar C, Lee JA et al.. (1994) 1,3-Diarylindan-2-carboxylic acids, potent and selective non-peptide endothelin receptor antagonists. J Med Chem, 37 (11): 1553-7. [PMID:8201588]
18. Elshourbagy NA, Korman DR, Wu HL, Sylvester DR, Lee JA, Nuthalaganti P, Bergsma DJ, Kumar CS, Nambi P. (1993) Molecular characterization and regulation of the human endothelin receptors. J Biol Chem, 268 (6): 3873-9. [PMID:8440682]
19. Fukuroda T, Fujikawa T, Ozaki S, Ishikawa K, Yano M, Nishikibe M. (1994) Clearance of circulating endothelin-1 by ETB receptors in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 199 (3): 1461-5. [PMID:8147891]
20. Gardiner SM, Compton AM, Kemp PA, Bennett T. (1990) Regional and cardiac haemodynamic effects of NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester in conscious, Long Evans rats. Br J Pharmacol, 101 (3): 625-31. [PMID:2076481]
21. Gellai M, De Wolf R, Fletcher T, Nambi P. (1997) Contribution of endogenous endothelin-1 to the maintenance of vascular tone: role of nitric oxide. Pharmacology, 55 (6): 299-308. [PMID:9413859]
22. Griswold DE, Douglas SA, Martin LD, Davis TG, Davis L, Ao Z, Luttmann MA, Pullen M, Nambi P, Hay DW et al.. (1999) Endothelin B receptor modulates inflammatory pain and cutaneous inflammation. Mol Pharmacol, 56 (4): 807-12. [PMID:10496965]
23. Harland SP, Kuc RE, Pickard JD, Davenport AP. (1995) Characterization of endothelin receptors in human brain cortex, gliomas, and meningiomas. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol, 26 Suppl 3: S408-11. [PMID:8587429]
24. Hoshino T, Yamauchi R, Kikkawa K, Yabana H, Murata S. (1998) Pharmacological profile of T-0201, a highly potent and orally active endothelin receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 286 (2): 643-9. [PMID:9694915]
25. Hosoda K, Hammer RE, Richardson JA, Baynash AG, Cheung JC, Giaid A, Yanagisawa M. (1994) Targeted and natural (piebald-lethal) mutations of endothelin-B receptor gene produce megacolon associated with spotted coat color in mice. Cell, 79 (7): 1267-76. [PMID:8001159]
26. Iglarz M, Binkert C, Morrison K, Fischli W, Gatfield J, Treiber A, Weller T, Bolli MH, Boss C, Buchmann S et al.. (2008) Pharmacology of macitentan, an orally active tissue-targeting dual endothelin receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 327 (3): 736-45. [PMID:18780830]
27. Karet FE, Kuc RE, Davenport AP. (1993) Novel ligands BQ123 and BQ3020 characterize endothelin receptor subtypes ETA and ETB in human kidney. Kidney Int, 44 (1): 36-42. [PMID:8355464]
28. Kilpatrick SJ, Roberts JM, Lykins DL, Taylor RN. (1993) Characterization and ontogeny of endothelin receptors in human placenta. Am J Physiol, 264 (3 Pt 1): E367-72. [PMID:8460684]
29. Kondo S, Morita T, Tashima Y. (1994) Endothelin receptor density in human hypertrophic and non-hypertrophic prostate tissue. Tohoku J Exp Med, 172 (4): 381-4. [PMID:7524189]
30. Kuc RE, Karet FE, Davenport AP. (1995) Characterization of peptide and nonpeptide antagonists in human kidney. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol, 26 Suppl 3: S373-5. [PMID:8587419]
31. Liu G, Henry Jr KJ, Szczepankiewicz BG, Winn M, Kozmina NS, Boyd SA, Wasicak J, von Geldern TW, Wu-Wong JR, Chiou WJ et al.. (1998) Pyrrolidine-3-carboxylic acids as endothelin antagonists. 3. Discovery of a potent, 2-nonaryl, highly selective ETA antagonist (A-216546). J Med Chem, 41 (17): 3261-75. [PMID:9703472]
32. Mizuguchi T, Nishiyama M, Moroi K, Tanaka H, Saito T, Masuda Y, Masaki T, de Wit D, Yanagisawa M, Kimura S. (1997) Analysis of two pharmacologically predicted endothelin B receptor subtypes by using the endothelin B receptor gene knockout mouse. Br J Pharmacol, 120 (8): 1427-30. [PMID:9113361]
33. Molenaar P, Kuc RE, Davenport AP. (1992) Characterization of two new ETB selective radioligands, [125I]-BQ3020 and [125I]-[Ala1,3,11,15]ET-1 in human heart. Br J Pharmacol, 107 (3): 637-9. [PMID:1472961]
34. Murugesan N, Gu Z, Stein PD, Spergel S, Mathur A, Leith L, Liu EC, Zhang R, Bird E, Waldron T et al.. (2000) Biphenylsulfonamide endothelin receptor antagonists. 2. Discovery of 4'-oxazolyl biphenylsulfonamides as a new class of potent, highly selective ET(A) antagonists. J Med Chem, 43 (16): 3111-7. [PMID:10956219]
35. Nagase T, Aoki T, Oka T, Fukuchi Y, Ouchi Y. (1997) ET-1-induced bronchoconstriction is mediated via ETB receptor in mice. J Appl Physiol, 83 (1): 46-51. [PMID:9216943]
36. Nakamuta M, Takayanagi R, Sakai Y, Sakamoto S, Hagiwara H, Mizuno T, Saito Y, Hirose S, Yamamoto M, Nawata H. (1991) Cloning and sequence analysis of a cDNA encoding human non-selective type of endothelin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 177: 34-39. [PMID:1710450]
37. Nambi P, Pullen M, Spielman W. (1994) Species differences in the binding characteristics of [125I]IRL-1620, a potent agonist specific for endothelin-B receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 268 (1): 202-7. [PMID:8301559]
38. O'Donnell SR, Kay CS. (1995) Effects of endothelin receptor selective antagonists, BQ-123 and BQ-788, on IRL 1620 and endothelin-1 responses of airway and vascular preparations from rats. Pulm Pharmacol, 8 (1): 11-9. [PMID:8535094]
39. Ogawa Y, Nakao K, Arai H, Nakagawa O, Hosoda K, Suga S, Nakanishi S, Imura H. (1991) Molecular cloning of a non-isopeptide-selective human endothelin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 178 (1): 248-55. [PMID:1648908]
40. Ohlstein EH, Nambi P, Lago A, Hay DW, Beck G, Fong KL, Eddy EP, Smith P, Ellens H, Elliott JD. (1996) Nonpeptide endothelin receptor antagonists. VI: Pharmacological characterization of SB 217242, a potent and highly bioavailable endothelin receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 276 (2): 609-15. [PMID:8632328]
41. Peter MG, Davenport AP. (1995) Selectivity of [125I]-PD151242 for human, rat and porcine endothelin ETA receptors in the heart. Br J Pharmacol, 114 (2): 297-302. [PMID:7881728]
42. Pollock DM, Highsmith RF. (1998) Endothelin receptors and signalling mechanisms. In . (Springer) 1-224. [ISBN:3540559701]
43. Puffenberger EG, Hosoda K, Washington SS, Nakao K, deWit D, Yanagisawa M, Chakravart A. (1994) A missense mutation of the endothelin-B receptor gene in multigenic Hirschsprung's disease. Cell, 79 (7): 1257-66. [PMID:8001158]
44. Ranjan AK, Gulati A. (2022) Sovateltide Mediated Endothelin B Receptors Agonism and Curbing Neurological Disorders. Int J Mol Sci, 23 (6). [PMID:35328566]
45. Reynolds EE, Hwang O, Flynn MA, Welch KM, Cody WL, Steinbaugh B, He JX, Chung FZ, Doherty AM. (1995) Pharmacological differences between rat and human endothelin B receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 209 (2): 506-12. [PMID:7733918]
46. Russell FD, Davenport AP. (1996) Characterization of the binding of endothelin ETB selective ligands in human and rat heart. Br J Pharmacol, 119 (4): 631-6. [PMID:8904635]
47. Sakamoto A, Yanagisawa M, Sakurai T, Takuwa Y, Yanagisawa H, Masaki T. (1991) Cloning and functional expression of human cDNA for the ETB endothelin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 178 (2): 656-63. [PMID:1713452]
48. Sakurai T, Yanagisawa M, Takuwa Y, Miyazaki H, Kimura S, Goto K, Masaki T. (1990) Cloning of a cDNA encoding a non-isopeptide-selective subtype of the endothelin receptor. Nature, 348 (6303): 732-5. [PMID:2175397]
49. Schneider MP, Boesen EI, Pollock DM. (2007) Contrasting actions of endothelin ET(A) and ET(B) receptors in cardiovascular disease. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol, 47: 731-59. [PMID:17002597]
50. Shihoya W, Nishizawa T, Yamashita K, Inoue A, Hirata K, Kadji FMN, Okuta A, Tani K, Aoki J, Fujiyoshi Y et al.. (2017) X-ray structures of endothelin ETB receptor bound to clinical antagonist bosentan and its analog. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 24 (9): 758-764. [PMID:28805809]
51. Simonson MS. (2001) Cell signalling by endothelin peptides. Handb Exp Pharmacol, 152: 115-140.
52. Strachan FE, Spratt JC, Wilkinson IB, Johnston NR, Gray GA, Webb DJ. (1999) Systemic blockade of the endothelin-B receptor increases peripheral vascular resistance in healthy men. Hypertension, 33 (1 Pt 2): 581-5. [PMID:9931169]
53. Takigawa M, Sakurai T, Kasuya Y, Abe Y, Masaki T, Goto K. (1995) Molecular identification of guanine-nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins which couple to endothelin receptors. Eur J Biochem, 228 (1): 102-8. [PMID:7882989]
54. Tanaka H, Moroi K, Iwai J, Takahashi H, Ohnuma N, Hori S, Takimoto M, Nishiyama M, Masaki T, Yanagisawa M et al.. (1998) Novel mutations of the endothelin B receptor gene in patients with Hirschsprung's disease and their characterization. J Biol Chem, 273 (18): 11378-83. [PMID:9556633]
55. Tanaka T, Tsukuda E, Nozawa M, Nonaka H, Ohno T, Kase H, Yamada K, Matsuda Y. (1994) RES-701-1, a novel, potent, endothelin type B receptor-selective antagonist of microbial origin. Mol Pharmacol, 45 (4): 724-30. [PMID:8183252]
56. Uhlig S, von Bethmann AN, Featherstone RL, Wendel A. (1995) Pharmacologic characterization of endothelin receptor responses in the isolated perfused rat lung. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 152 (5 Pt 1): 1449-60. [PMID:7582276]
57. von Geldern TW, Tasker AS, Sorensen BK, Winn M, Szczepankiewicz BG, Dixon DB, Chiou WJ, Wang L, Wessale JL, Adler A et al.. (1999) Pyrrolidine-3-carboxylic acids as endothelin antagonists. 4. Side chain conformational restriction leads to ET(B) selectivity. J Med Chem, 42 (18): 3668-78. [PMID:10479298]
58. Watakabe T, Urade Y, Takai M, Umemura I, Okada T. (1992) A reversible radioligand specific for the ETB receptor: [125I]Tyr13-Suc-[Glu9,Ala11,15]-endothelin-1(8- 21), [125I]IRL 1620. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 185 (3): 867-73. [PMID:1320877]
59. Watanabe T, Awane Y, Ikeda S, Fujiwara S, Kubo K, Kikuchi T, Kusumoto K, Wakimasu M, Fujino M. (1995) Pharmacology of a non-selective ETA and ETB receptor antagonist, TAK-044 and the inhibition of myocardial infarct size in rats. Br J Pharmacol, 114 (5): 949-54. [PMID:7780649]
60. Williams Jr DL, Jones KL, Pettibone DJ, Lis EV, Clineschmidt BV. (1991) Sarafotoxin S6c: an agonist which distinguishes between endothelin receptor subtypes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 175 (2): 556-61. [PMID:1850245]
61. Winn M, von Geldern TW, Opgenorth TJ, Jae HS, Tasker AS, Boyd SA, Kester JA, Mantei RA, Bal R, Sorensen BK et al.. (1996) 2,4-Diarylpyrrolidine-3-carboxylic acids--potent ETA selective endothelin receptor antagonists. 1. Discovery of A-127722. J Med Chem, 39 (5): 1039-48. [PMID:8676339]
62. Yamaji T, Fukuhara T, Kinoshita M. (1993) Increased capillary permeability to albumin in diabetic rat myocardium. Circ Res, 72 (5): 947-57. [PMID:8477528]