
Top ▲

GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | - | 1390 | 8q24.13 | ATAD2 | ATPase family AAA domain containing 2 | |
| Mouse | - | 1040 | 15 D1 | Atad2 | ATPase family, AAA domain containing 2 | |
| Rat | - | 1373 | 7q33 | Atad2 | ATPase family, AAA domain containing 2 | |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| ATPase family, AAA domain containing 2 | ATPase family |
Database Links  |
|
| Alphafold | Q6PL18 (Hs), Q8CDM1 (Mm) |
| BRENDA | 3.6.1.3 |
| CATH/Gene3D | 1.20.920.10 |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL2150837 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000156802 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000022360 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000025604 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 29028 (Hs), 70472 (Mm), 314993 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000156802 (Hs) |
| KEGG Enzyme | 3.6.1.3 |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:29028 (Hs), mmu:70472 (Mm), rno:314993 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 611941 (Hs) |
| Pharos | Q6PL18 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_014109 (Hs), NM_027435 (Mm), NM_001134879 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_054828 (Hs), NP_081711 (Mm), NP_001128351 (Rn) |
| SynPHARM |
82674 (in complex with compound 33 [PMID: 26230603]) 82521 (in complex with compound 60 [PMID: 26155854]) 84269 (in complex with GSK8814) 84272 (in complex with GSK8814) 84270 (in complex with GSK8814) |
| UniProtKB | Q6PL18 (Hs), Q8CDM1 (Mm) |
| Wikipedia | ATAD2 (Hs) |
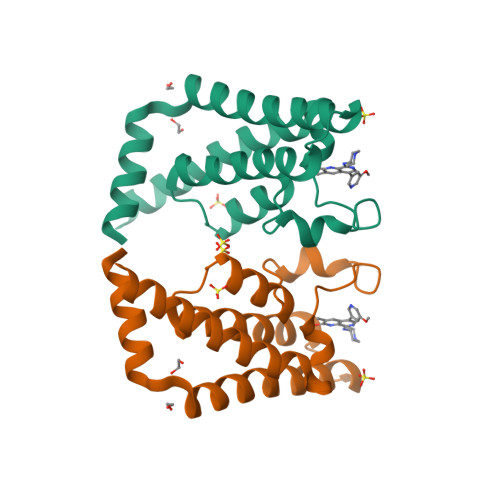
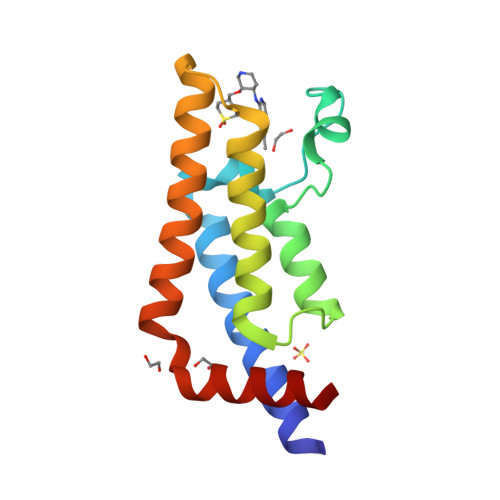
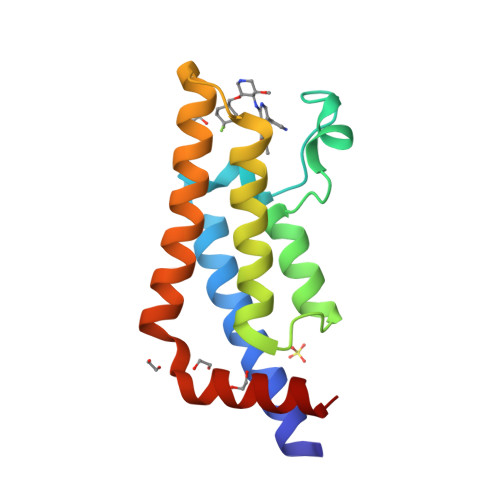
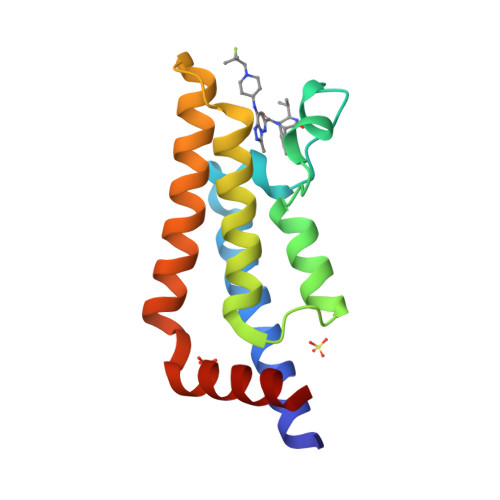
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Enzyme Reaction  |
||||
|
||||
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Inhibitors | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General Comments |
| This is a bromodomain-containing protein that is involved in chromatin modification [8]. Abnormally high levels of ATAD2 expression in a wide variety of unrelated patient cancer samples correlates with poor prognosis and disease recurrence [4,7,10]. Design of selective ATAD2 inhibitors as novel anti-cancer agents is being pursued [1,9]. |
1. Bamborough P, Chung CW, Demont EH, Bridges AM, Craggs PD, Dixon DP, Francis P, Furze RC, Grandi P, Jones EJ et al.. (2019) A Qualified Success: Discovery of a New Series of ATAD2 Bromodomain Inhibitors with a Novel Binding Mode Using High-Throughput Screening and Hit Qualification. J Med Chem, 62 (16): 7506-7525. [PMID:31398032]
2. Bamborough P, Chung CW, Demont EH, Furze RC, Bannister AJ, Che KH, Diallo H, Douault C, Grandi P, Kouzarides T et al.. (2016) A Chemical Probe for the ATAD2 Bromodomain. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 55 (38): 11382-6. [PMID:27530368]
3. Bamborough P, Chung CW, Furze RC, Grandi P, Michon AM, Sheppard RJ, Barnett H, Diallo H, Dixon DP, Douault C et al.. (2015) Structure-Based Optimization of Naphthyridones into Potent ATAD2 Bromodomain Inhibitors. J Med Chem, 58 (15): 6151-78. [PMID:26230603]
4. Caron C, Lestrat C, Marsal S, Escoffier E, Curtet S, Virolle V, Barbry P, Debernardi A, Brambilla C, Brambilla E et al.. (2010) Functional characterization of ATAD2 as a new cancer/testis factor and a predictor of poor prognosis in breast and lung cancers. Oncogene, 29 (37): 5171-81. [PMID:20581866]
5. Demont EH, Chung CW, Furze RC, Grandi P, Michon AM, Wellaway C, Barrett N, Bridges AM, Craggs PD, Diallo H et al.. (2015) Fragment-Based Discovery of Low-Micromolar ATAD2 Bromodomain Inhibitors. J Med Chem, 58 (14): 5649-73. [PMID:26155854]
6. Fernández-Montalván AE, Berger M, Kuropka B, Koo SJ, Badock V, Weiske J, Puetter V, Holton SJ, Stöckigt D, Ter Laak A et al.. (2017) Isoform-Selective ATAD2 Chemical Probe with Novel Chemical Structure and Unusual Mode of Action. ACS Chem Biol, 12 (11): 2730-2736. [PMID:29043777]
7. Kalashnikova EV, Revenko AS, Gemo AT, Andrews NP, Tepper CG, Zou JX, Cardiff RD, Borowsky AD, Chen HW. (2010) ANCCA/ATAD2 overexpression identifies breast cancer patients with poor prognosis, acting to drive proliferation and survival of triple-negative cells through control of B-Myb and EZH2. Cancer Res, 70 (22): 9402-12. [PMID:20864510]
8. Morozumi Y, Boussouar F, Tan M, Chaikuad A, Jamshidikia M, Colak G, He H, Nie L, Petosa C, de Dieuleveult M et al.. (2016) Atad2 is a generalist facilitator of chromatin dynamics in embryonic stem cells. J Mol Cell Biol, 8 (4): 349-62. [PMID:26459632]
9. Winter-Holt JJ, Bardelle C, Chiarparin E, Dale IL, Davey PRJ, Davies NL, Denz C, Fillery SM, Guérot CM, Han F et al.. (2022) Discovery of a Potent and Selective ATAD2 Bromodomain Inhibitor with Antiproliferative Activity in Breast Cancer Models. J Med Chem, 65 (4): 3306-3331. [PMID:35133824]
10. Zou JX, Revenko AS, Li LB, Gemo AT, Chen HW. (2007) ANCCA, an estrogen-regulated AAA+ ATPase coactivator for ERalpha, is required for coregulator occupancy and chromatin modification. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 104 (46): 18067-72. [PMID:17998543]
3.6.1.3 ATPases: ATPase family AAA domain containing 2. Last modified on 25/06/2025. Accessed on 20/12/2025. IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY, https://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=2719.