
Top ▲

GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| class A G protein-coupled receptor | ||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 7 | 444 | 6p12.1 | HCRTR2 | hypocretin receptor 2 | 64 |
| Mouse | 7 | 460 | 9q-D | Hcrtr2 | hypocretin (orexin) receptor 2 | 14,64 |
| Rat | 7 | 460 | 8q24 | Hcrtr2 | hypocretin receptor 2 | 64 |
| Gene and Protein Information Comments | ||||||
| Splice variants of the mouse gene are reported, generating different protein isoforms. Isoform 2 lacks amino acids 444-460 of the carboxy terminal tail compared to canonical full lenghth isoform 1. | ||||||
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| hypocretin receptor 2 | orexin receptor type 2 | OX2R |
Database Links  |
|
| Specialist databases | |
| GPCRdb | ox2r_human (Hs), ox2r_mouse (Mm), ox2r_rat (Rn) |
| Other databases | |
| Alphafold | O43614 (Hs), P58308 (Mm), P58308-2 (Mm), P56719 (Rn) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL4792 (Hs), CHEMBL2434818 (Mm), CHEMBL1275216 (Rn) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000137252 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000032360 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000011251 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 3062 (Hs), 387285 (Mm), 25605 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000137252 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:3062 (Hs), mmu:387285 (Mm), rno:25605 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 602393 (Hs) |
| Pharos | O43614 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_001526 (Hs), NM_198962 (Mm), NM_013074 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_001517 (Hs), NP_945200 (Mm), NP_037206 (Rn) |
| SynPHARM | 6604 (in complex with suvorexant) |
| UniProtKB | O43614 (Hs), P58308 (Mm), P58308-2 (Mm), P56719 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | HCRTR2 (Hs) |
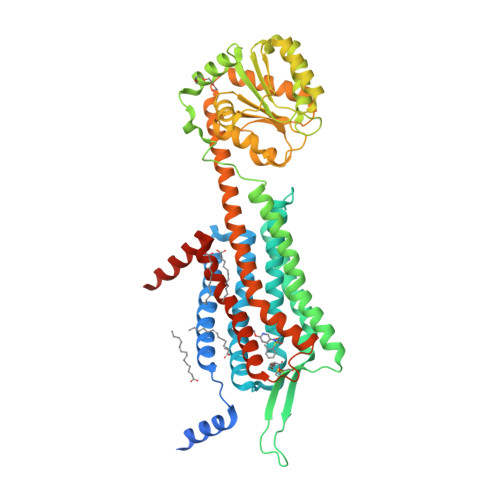
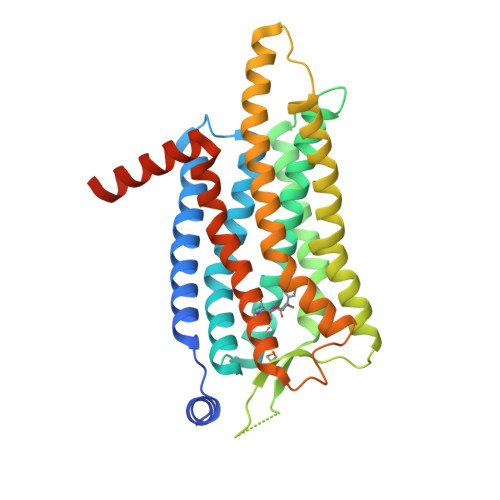
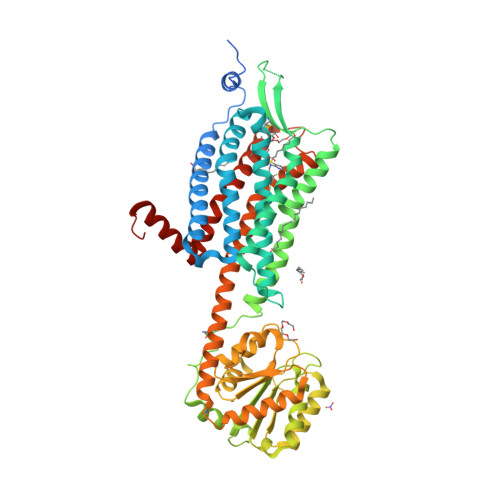
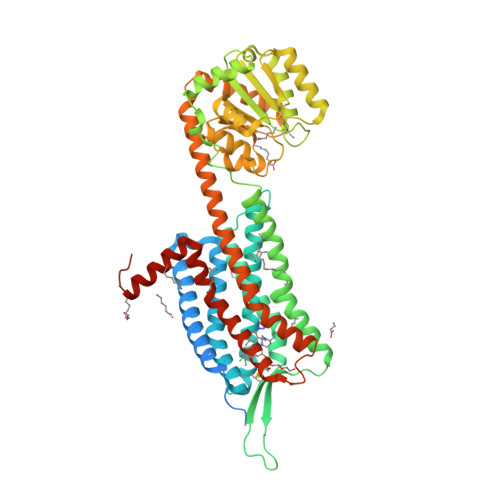
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| orexin-A {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| orexin-B {Sp: Human} , orexin-B {Sp: Mouse, Rat} |
| Potency order of endogenous ligands (Human) |
| orexin-A (HCRT, O43612) = orexin-B (HCRT, O43612) (for Ca2+ elevation, unclear/variable for other responses) |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Efficacy and potency values for agonists are highly dependent on cell type, assay conditions and the readout. Agonist activity of firazorexton (TAK-994) has been demonstrated in ERK phosphorylation, CREB phosphorylation, and tuberomamillary nucleus neuron depolarization assays, with pEC50 values of 6.8, 7.4 and 7.7 respectively [32]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific antagonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other Binding Ligands | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | Click column headers to sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Primary Transduction Mechanisms 
|
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gq/G11 family |
Adenylyl cyclase stimulation Adenylyl cyclase inhibition Phospholipase C stimulation Phospholipase A2 stimulation Phospholipase D stimulation |
| Comments: Association with the Gq family of transducers leads to phospholipase stimulation (e.g. phospholipase families A2, C and D) and Ca2+ elevation, and with the Gi family to inhibition and with the Gs family to stimulation, respectively, of adenylyl cyclase. Ca2+/non-selective cation influx also appears to rely on Gq. However, the signal transduction has not been investigated in detail in native neurons. | |
| References: 2,18,24,26,34-38,40,58,64,71 | |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
| Tissue Distribution Comments | ||||||||
| For IHC studies, it is very important to note that selectivity issues have been raised regarding antibodies for the orexin receptors which may lead to false positive/negative results and as such, mRNA expression patterns provide important confirmatory results. | ||||||||
Expression Datasets  |
|
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression Comments | ||||||||||
| Hcrtr2 gene disruption does not appear to result in physiological problems. | ||||||||||
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Biologically Significant Variants 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
1. Akanmu MA, Honda K. (2005) Selective stimulation of orexin receptor type 2 promotes wakefulness in freely behaving rats. Brain Res, 1048 (1-2): 138-45. [PMID:15919057]
2. Ammoun S, Holmqvist T, Shariatmadari R, Oonk HB, Detheux M, Parmentier M, Akerman KE, Kukkonen JP. (2003) Distinct recognition of OX1 and OX2 receptors by orexin peptides. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 305 (2): 507-14. [PMID:12606634]
3. Asada H, Im D, Hotta Y, Yasuda S, Murata T, Suno R, Iwata S. (2022) Molecular basis for anti-insomnia drug design from structure of lemborexant-bound orexin 2 receptor. Structure, 30 (12): 1582-1589.e4. [PMID:36417909]
4. Asahi S, Egashira S, Matsuda M, Iwaasa H, Kanatani A, Ohkubo M, Ihara M, Morishima H. (2003) Development of an orexin-2 receptor selective agonist, [Ala(11), D-Leu(15)]orexin-B. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 13 (1): 111-3. [PMID:12467628]
5. Bayer L, Eggermann E, Serafin M, Saint-Mleux B, Machard D, Jones B, Mühlethaler M. (2001) Orexins (hypocretins) directly excite tuberomammillary neurons. Eur J Neurosci, 14 (9): 1571-5. [PMID:11722619]
6. Bergman JM, Roecker AJ, Mercer SP, Bednar RA, Reiss DR, Ransom RW, Meacham Harrell C, Pettibone DJ, Lemaire W, Murphy KL et al.. (2008) Proline bis-amides as potent dual orexin receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 18 (4): 1425-30. [PMID:18207395]
7. Blanco M, López M, GarcIa-Caballero T, Gallego R, Vázquez-Boquete A, Morel G, SeñarIs R, Casanueva F, Diéguez C, Beiras A. (2001) Cellular localization of orexin receptors in human pituitary. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 86 (7): 1616-9. [PMID:11443222]
8. Bonaventure P, Shelton J, Yun S, Nepomuceno D, Sutton S, Aluisio L, Fraser I, Lord B, Shoblock J, Welty N et al.. (2015) Characterization of JNJ-42847922, a Selective Orexin-2 Receptor Antagonist, as a Clinical Candidate for the Treatment of Insomnia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 354 (3): 471-82. [PMID:26177655]
9. Bonaventure P, Yun S, Johnson PL, Shekhar A, Fitz SD, Shireman BT, Lebold TP, Nepomuceno D, Lord B, Wennerholm M et al.. (2015) A selective orexin-1 receptor antagonist attenuates stress-induced hyperarousal without hypnotic effects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 352 (3): 590-601. [PMID:25583879]
10. Boss C, Roch-Brisbare C, Steiner MA, Treiber A, Dietrich H, Jenck F, von Raumer M, Sifferlen T, Brotschi C, Heidmann B et al.. (2014) Structure-activity relationship, biological, and pharmacological characterization of the proline sulfonamide ACT-462206: a potent, brain-penetrant dual orexin 1/orexin 2 receptor antagonist. ChemMedChem, 9 (11): 2486-96. [PMID:25147058]
11. Burdakov D, Liss B, Ashcroft FM. (2003) Orexin excites GABAergic neurons of the arcuate nucleus by activating the sodium--calcium exchanger. J Neurosci, 23 (12): 4951-7. [PMID:12832517]
12. Caillol M, Aioun J, Baly C, Persuy MA, Salesse R. (2003) Localization of orexins and their receptors in the rat olfactory system: possible modulation of olfactory perception by a neuropeptide synthetized centrally or locally. Brain Res, 960: 48-61. [PMID:12505657]
13. Callander GE, Olorunda M, Monna D, Schuepbach E, Langenegger D, Betschart C, Hintermann S, Behnke D, Cotesta S, Fendt M et al.. (2013) Kinetic properties of "dual" orexin receptor antagonists at OX1R and OX2R orexin receptors. Front Neurosci, 7: 230. [PMID:24376396]
14. Chen J, Randeva HS. (2004) Genomic organization of mouse orexin receptors: characterization of two novel tissue-specific splice variants. Mol Endocrinol, 18 (11): 2790-804. [PMID:15256537]
15. Christopher JA, Aves SJ, Brown J, Errey JC, Klair SS, Langmead CJ, Mace OJ, Mould R, Patel JC, Tehan BG. (2015) Discovery of HTL6641, a dual orexin receptor antagonist with differentiated pharmacodynamic properties. Medicinal Chemistry Communications, 6: 947-955. DOI: 10.1039/C5MD00027K
16. Cluderay JE, Harrison DC, Hervieu GJ. (2002) Protein distribution of the orexin-2 receptor in the rat central nervous system. Regul Pept, 104 (1-3): 131-44. [PMID:11830288]
17. Cox CD, Breslin MJ, Whitman DB, Schreier JD, McGaughey GB, Bogusky MJ, Roecker AJ, Mercer SP, Bednar RA, Lemaire W, Bruno JG, Reiss DR, Harrell CM, Murphy KL, Garson SL, Doran SM, Prueksaritanont T, Anderson WB, Tang C, Roller S, Cabalu TD, Cui D, Hartman GD, Young SD, Koblan KS, Winrow CJ, Renger JJ, Coleman PJ. (2010) Discovery of the dual orexin receptor antagonist [(7R)-4-(5-chloro-1,3-benzoxazol-2-yl)-7-methyl-1,4-diazepan-1-yl][5-methyl-2-(2H-1,2,3-triazol-2-yl)phenyl]methanone (MK-4305) for the treatment of insomnia. J Med Chem, 53 (14): 5320-32. [PMID:20565075]
18. Dalrymple MB, Jaeger WC, Eidne KA, Pfleger KD. (2011) Temporal profiling of orexin receptor-arrestin-ubiquitin complexes reveals differences between receptor subtypes. J Biol Chem, 286 (19): 16726-33. [PMID:21378163]
19. Eggermann E, Serafin M, Bayer L, Machard D, Saint-Mleux B, Jones BE, Mühlethaler M. (2001) Orexins/hypocretins excite basal forebrain cholinergic neurones. Neuroscience, 108 (2): 177-81. [PMID:11734353]
20. Eriksson KS, Sergeeva O, Brown RE, Haas HL. (2001) Orexin/hypocretin excites the histaminergic neurons of the tuberomammillary nucleus. J Neurosci, 21 (23): 9273-9. [PMID:11717361]
21. Fitch TE, Benvenga MJ, Jesudason CD, Zink C, Vandergriff AB, Menezes MM, Schober DA, Rorick-Kehn LM. (2014) LSN2424100: a novel, potent orexin-2 receptor antagonist with selectivity over orexin-1 receptors and activity in an animal model predictive of antidepressant-like efficacy. Front Neurosci, 8: 5. [PMID:24478625]
22. Hellmann J, Drabek M, Yin J, Gunera J, Pröll T, Kraus F, Langmead CJ, Hübner H, Weikert D, Kolb P et al.. (2020) Structure-based development of a subtype-selective orexin 1 receptor antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 117 (30): 18059-18067. [PMID:32669442]
23. Hirose M, Egashira S, Goto Y, Hashihayata T, Ohtake N, Iwaasa H, Hata M, Fukami T, Kanatani A, Yamada K. (2003) N-acyl 6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline: the first orexin-2 receptor selective non-peptidic antagonist. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 13 (24): 4497-9. [PMID:14643355]
24. Hoang QV, Bajic D, Yanagisawa M, Nakajima S, Nakajima Y. (2003) Effects of orexin (hypocretin) on GIRK channels. J Neurophysiol, 90 (2): 693-702. [PMID:12702704]
25. Holmqvist T, Akerman KE, Kukkonen JP. (2001) High specificity of human orexin receptors for orexins over neuropeptide Y and other neuropeptides. Neurosci Lett, 305 (3): 177-80. [PMID:11403934]
26. Holmqvist T, Akerman KE, Kukkonen JP. (2002) Orexin signaling in recombinant neuron-like cells. FEBS Lett, 526 (1-3): 11-4. [PMID:12208495]
27. Holmqvist T, Johansson L, Ostman M, Ammoun S, Akerman KE, Kukkonen JP. (2005) OX1 orexin receptors couple to adenylyl cyclase regulation via multiple mechanisms. J Biol Chem, 280 (8): 6570-9. [PMID:15611118]
28. Hong C, Byrne NJ, Zamlynny B, Tummala S, Xiao L, Shipman JM, Partridge AT, Minnick C, Breslin MJ, Rudd MT et al.. (2021) Structures of active-state orexin receptor 2 rationalize peptide and small-molecule agonist recognition and receptor activation. Nat Commun, 12 (1): 815. [PMID:33547286]
29. Iio K, Hashimoto K, Nagumo Y, Amezawa M, Hasegawa T, Yamamoto N, Kutsumura N, Takeuchi K, Ishikawa Y, Yamamoto H et al.. (2023) Design and Synthesis of Orexin 1 Receptor-Selective Agonists. J Med Chem, 66 (8): 5453-5464. [PMID:37043436]
30. Irukayama-Tomobe Y, Ogawa Y, Tominaga H, Ishikawa Y, Hosokawa N, Ambai S, Kawabe Y, Uchida S, Nakajima R, Saitoh T et al.. (2017) Nonpeptide orexin type-2 receptor agonist ameliorates narcolepsy-cataplexy symptoms in mouse models. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 114 (22): 5731-5736. [PMID:28507129]
31. Ishibashi M, Takano S, Yanagida H, Takatsuna M, Nakajima K, Oomura Y, Wayner MJ, Sasaki K. (2005) Effects of orexins/hypocretins on neuronal activity in the paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus in rats in vitro. Peptides, 26 (3): 471-81. [PMID:15652654]
32. Ishikawa T, Hara H, Kawano A, Tohyama K, Kajita Y, Miyanohana Y, Koike T, Kimura H. (2023) TAK-994, a Novel Orally Available Brain-Penetrant Orexin 2 Receptor-Selective Agonist, Suppresses Fragmentation of Wakefulness and Cataplexy-Like Episodes in Mouse Models of Narcolepsy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 385 (3): 193-204. [PMID:37001988]
33. Jiang T, Wang J, Yang H, Li L, Dan Z, Zhu K, Zeng Z, Su B, Chen X. (2021) Solid pharmaceutical preparation, preparation method therefor and use thereof. Patent number: WO2021208976A1. Assignee: Yangtze River Pharmaceutical Group Co Ltd, Shanghai Haiyan Pharmaceutical Technology Co Ltd. Priority date: 14/04/2021. Publication date: 21/10/2021.
34. Karteris E, Randeva HS, Grammatopoulos DK, Jaffe RB, Hillhouse EW. (2001) Expression and coupling characteristics of the CRH and orexin type 2 receptors in human fetal adrenals. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 86 (9): 4512-9. [PMID:11549701]
35. Kukkonen JP. (2016) G-protein-dependency of orexin/hypocretin receptor signalling in recombinant Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 476 (4): 379-85. [PMID:27237973]
36. Kukkonen JP. (2016) OX2 orexin/hypocretin receptor signal transduction in recombinant Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cell Signal, 28 (2): 51-60. [PMID:26582739]
37. Kukkonen JP. (2017) Orexin/Hypocretin Signaling. Curr Top Behav Neurosci, 33: 17-50. [PMID:27909990]
38. Kukkonen JP, Leonard CS. (2014) Orexin/hypocretin receptor signalling cascades. Br J Pharmacol, 171 (2): 314-31. [PMID:23902572]
39. Langmead CJ, Jerman JC, Brough SJ, Scott C, Porter RA, Herdon HJ. (2004) Characterisation of the binding of [3H]-SB-674042, a novel nonpeptide antagonist, to the human orexin-1 receptor. Br J Pharmacol, 141 (2): 340-6. [PMID:14691055]
40. Leonard CS, Kukkonen JP. (2014) Orexin/hypocretin receptor signalling: a functional perspective. Br J Pharmacol, 171 (2): 294-313. [PMID:23848055]
41. López M, Señarís R, Gallego R, García-Caballero T, Lago F, Seoane L, Casanueva F, Diéguez C. (1999) Orexin receptors are expressed in the adrenal medulla of the rat. Endocrinology, 140 (12): 5991-4. [PMID:10579367]
42. Malherbe P, Borroni E, Gobbi L, Knust H, Nettekoven M, Pinard E, Roche O, Rogers-Evans M, Wettstein JG, Moreau JL. (2009) Biochemical and behavioural characterization of EMPA, a novel high-affinity, selective antagonist for the OX(2) receptor. Br J Pharmacol, 156 (8): 1326-41. [PMID:19751316]
43. Malherbe P, Borroni E, Pinard E, Wettstein JG, Knoflach F. (2009) Biochemical and electrophysiological characterization of almorexant, a dual orexin 1 receptor (OX1)/orexin 2 receptor (OX2) antagonist: comparison with selective OX1 and OX2 antagonists. Mol Pharmacol, 76 (3): 618-31. [PMID:19542319]
44. Malherbe P, Roche O, Marcuz A, Kratzeisen C, Wettstein JG, Bissantz C. (2010) Mapping the binding pocket of dual antagonist almorexant to human orexin 1 and orexin 2 receptors: comparison with the selective OX1 antagonist SB-674042 and the selective OX2 antagonist N-ethyl-2-[(6-methoxy-pyridin-3-yl)-(toluene-2-sulfonyl)-amino]-N-pyridin-3-ylmethyl-acetamide (EMPA). Mol Pharmacol, 78 (1): 81-93. [PMID:20404073]
45. McAtee LC, Sutton SW, Rudolph DA, Li X, Aluisio LE, Phuong VK, Dvorak CA, Lovenberg TW, Carruthers NI, Jones TK. (2004) Novel substituted 4-phenyl-[1,3]dioxanes: potent and selective orexin receptor 2 (OX(2)R) antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 14 (16): 4225-9. [PMID:15261275]
46. Mikkelsen JD, Hauser F, deLecea L, Sutcliffe JG, Kilduff TS, Calgari C, Pévet P, Simonneaux V. (2001) Hypocretin (orexin) in the rat pineal gland: a central transmitter with effects on noradrenaline-induced release of melatonin. Eur J Neurosci, 14 (3): 419-25. [PMID:11553292]
47. Mitsukawa K, Kimura H. (2022) Orexin 2 receptor (OX2R) protein distribution measured by autoradiography using radiolabeled OX2R-selective antagonist EMPA in rodent brain and peripheral tissues. Sci Rep, 12 (1): 8473. [PMID:35589803]
48. Mitsukawa K, Terada M, Yamada R, Monjo T, Hiyoshi T, Nakakariya M, Kajita Y, Ando T, Koike T, Kimura H. (2024) TAK-861, a potent, orally available orexin receptor 2-selective agonist, produces wakefulness in monkeys and improves narcolepsy-like phenotypes in mouse models. Sci Rep, 14 (1): 20838. [PMID:39242684]
49. Mould R, Brown J, Marshall FH, Langmead CJ. (2014) Binding kinetics differentiates functional antagonism of orexin-2 receptor ligands. Br J Pharmacol, 171 (2): 351-63. [PMID:23692283]
50. Nagahara T, Saitoh T, Kutsumura N, Irukayama-Tomobe Y, Ogawa Y, Kuroda D, Gouda H, Kumagai H, Fujii H, Yanagisawa M et al.. (2015) Design and Synthesis of Non-Peptide, Selective Orexin Receptor 2 Agonists. J Med Chem, 58 (20): 7931-7. [PMID:26267383]
51. Nowak KW, Strowski MZ, Switonska MM, Kaczmarek P, Singh V, Fabis M, Mackowiak P, Nowak M, Malendowicz LK. (2005) Evidence that orexins A and B stimulate insulin secretion from rat pancreatic islets via both receptor subtypes. Int J Mol Med, 15 (6): 969-72. [PMID:15870901]
52. Okumura T, Takeuchi S, Motomura W, Yamada H, Egashira Si S, Asahi S, Kanatani A, Ihara M, Kohgo Y. (2001) Requirement of intact disulfide bonds in orexin-A-induced stimulation of gastric acid secretion that is mediated by OX1 receptor activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 280 (4): 976-81. [PMID:11162621]
53. Pennington LD, Choi Y, Huynh H, Aquila BM, Mugge I, Hu Y, Woods JR, Valiulin RA, Raymer BK, Bentzien JM et al.. (2021) Substituted macrocyclic compounds and related methods of treatment. Patent number: WO2021108628A1. Assignee: Alkermes, Inc.. Priority date: 25/11/2020. Publication date: 03/06/2021.
54. Porter RA, Chan WN, Coulton S, Johns A, Hadley MS, Widdowson K, Jerman JC, Brough SJ, Coldwell M, Smart D et al.. (2001) 1,3-Biarylureas as selective non-peptide antagonists of the orexin-1 receptor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 11 (14): 1907-10. [PMID:11459658]
55. Putula J, Pihlajamaa T, Kukkonen JP. (2014) Calcium affects OX1 orexin (hypocretin) receptor responses by modifying both orexin binding and the signal transduction machinery. Br J Pharmacol, 171 (24): 5816-28. [PMID:25132134]
56. Putula J, Turunen PM, Jäntti MH, Ekholm ME, Kukkonen JP. (2011) Agonist ligand discrimination by the two orexin receptors depends on the expression system. Neurosci Lett, 494 (1): 57-60. [PMID:21362456]
57. Rainero I, Gallone S, Valfrè W, Ferrero M, Angilella G, Rivoiro C, Rubino E, De Martino P, Savi L, Ferrone M et al.. (2004) A polymorphism of the hypocretin receptor 2 gene is associated with cluster headache. Neurology, 63 (7): 1286-8. [PMID:15477554]
58. Randeva HS, Karteris E, Grammatopoulos D, Hillhouse EW. (2001) Expression of orexin-A and functional orexin type 2 receptors in the human adult adrenals: implications for adrenal function and energy homeostasis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 86 (10): 4808-13. [PMID:11600545]
59. Rappas M, Ali AAE, Bennett KA, Brown JD, Bucknell SJ, Congreve M, Cooke RM, Cseke G, de Graaf C, Doré AS et al.. (2020) Comparison of Orexin 1 and Orexin 2 Ligand Binding Modes Using X-ray Crystallography and Computational Analysis. J Med Chem, 63 (4): 1528-1543. [PMID:31860301]
60. Rinne MK, Leino TO, Turku A, Turunen PM, Steynen Y, Xhaard H, Wallén EAA, Kukkonen JP. (2018) Pharmacological characterization of the orexin/hypocretin receptor agonist Nag 26. Eur J Pharmacol, 837: 137-144. [PMID:30194937]
61. Roch C, Bergamini G, Steiner MA, Clozel M. (2021) Nonclinical pharmacology of daridorexant: a new dual orexin receptor antagonist for the treatment of insomnia. Psychopharmacology (Berl), 238 (10): 2693-2708. [PMID:34415378]
62. Roecker AJ, Mercer SP, Schreier JD, Cox CD, Fraley ME, Steen JT, Lemaire W, Bruno JG, Harrell CM, Garson SL et al.. (2014) Discovery of 5''-chloro-N-[(5,6-dimethoxypyridin-2-yl)methyl]-2,2':5',3''-terpyridine-3'-carboxamide (MK-1064): a selective orexin 2 receptor antagonist (2-SORA) for the treatment of insomnia. ChemMedChem, 9 (2): 311-22. [PMID:24376006]
63. Roecker AJ, Reger TS, Mattern MC, Mercer SP, Bergman JM, Schreier JD, Cube RV, Cox CD, Li D, Lemaire W et al.. (2014) Discovery of MK-3697: a selective orexin 2 receptor antagonist (2-SORA) for the treatment of insomnia. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 24 (20): 4884-90. [PMID:25248679]
64. Sakurai T, Amemiya A, Ishii M, Matsuzaki I, Chemelli RM, Tanaka H, Williams SC, Richardson JA, Kozlowski GP, Wilson S et al.. (1998) Orexins and orexin receptors: a family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell, 92 (4): 573-85. [PMID:9491897]
65. Schneeberger M, Brice NL, Pellegrino K, Parolari L, Shaked JT, Page KJ, Marchildon F, Barrows DW, Carroll TS, Topilko T et al.. (2022) Pharmacological targeting of glutamatergic neurons within the brainstem for weight reduction. Nat Metab, 4 (11): 1495-1513. [PMID:36411386]
66. Shoblock JR, Welty N, Aluisio L, Fraser I, Motley ST, Morton K, Palmer J, Bonaventure P, Carruthers NI, Lovenberg TW et al.. (2011) Selective blockade of the orexin-2 receptor attenuates ethanol self-administration, place preference, and reinstatement. Psychopharmacology (Berl.), 215 (1): 191-203. [PMID:21181123]
67. Smart D, Jerman JC, Brough SJ, Rushton SL, Murdock PR, Jewitt F, Elshourbagy NA, Ellis CE, Middlemiss DN, Brown F. (1999) Characterization of recombinant human orexin receptor pharmacology in a Chinese hamster ovary cell-line using FLIPR. Br J Pharmacol, 128 (1): 1-3. [PMID:10498827]
68. Steiner MA, Gatfield J, Brisbare-Roch C, Dietrich H, Treiber A, Jenck F, Boss C. (2013) Discovery and characterization of ACT-335827, an orally available, brain penetrant orexin receptor type 1 selective antagonist. ChemMedChem, 8 (6): 898-903. [PMID:23589487]
69. Suno R, Kimura KT, Nakane T, Yamashita K, Wang J, Fujiwara T, Yamanaka Y, Im D, Horita S, Tsujimoto H et al.. (2018) Crystal Structures of Human Orexin 2 Receptor Bound to the Subtype-Selective Antagonist EMPA. Structure, 26 (1): 7-19.e5. [PMID:29225076]
70. Sunter D, Morgan I, Edwards CM, Dakin CL, Murphy KG, Gardiner J, Taheri S, Rayes E, Bloom SR. (2001) Orexins: effects on behavior and localisation of orexin receptor 2 messenger ribonucleic acid in the rat brainstem. Brain Res, 907 (1-2): 27-34. [PMID:11430882]
71. Tang J, Chen J, Ramanjaneya M, Punn A, Conner AC, Randeva HS. (2008) The signalling profile of recombinant human orexin-2 receptor. Cell Signal, 20 (9): 1651-61. [PMID:18599270]
72. Tran DT, Bonaventure P, Hack M, Mirzadegan T, Dvorak C, Letavic M, Carruthers N, Lovenberg T, Sutton SW. (2011) Chimeric, mutant orexin receptors show key interactions between orexin receptors, peptides and antagonists. Eur J Pharmacol, 667 (1-3): 120-8. [PMID:21679703]
73. Treiber A, de Kanter R, Roch C, Gatfield J, Boss C, von Raumer M, Schindelholz B, Muehlan C, van Gerven J, Jenck F. (2017) The Use of Physiology-Based Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Modeling in the Discovery of the Dual Orexin Receptor Antagonist ACT-541468. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 362 (3): 489-503. [PMID:28663311]
74. Trivedi P, Yu H, MacNeil DJ, Van der Ploeg LH, Guan XM. (1998) Distribution of orexin receptor mRNA in the rat brain. FEBS Lett, 438: 71-75. [PMID:9821961]
75. Voisin T, Firar AE, Avondo V, Laburthe M. (2006) Orexin-induced apoptosis: the key role of the seven-transmembrane domain orexin type 2 receptor. Endocrinology, 147 (10): 4977-84. [PMID:16857748]
76. Willie JT, Chemelli RM, Sinton CM, Tokita S, Williams SC, Kisanuki YY, Marcus JN, Lee C, Elmquist JK, Kohlmeier KA et al.. (2003) Distinct narcolepsy syndromes in Orexin receptor-2 and Orexin null mice: molecular genetic dissection of Non-REM and REM sleep regulatory processes. Neuron, 38 (5): 715-30. [PMID:12797957]
77. Winrow CJ, Gotter AL, Cox CD, Tannenbaum PL, Garson SL, Doran SM, Breslin MJ, Schreier JD, Fox SV, Harrell CM et al.. (2012) Pharmacological characterization of MK-6096 - A dual orexin receptor antagonist for insomnia. Neuropharmacology, 62 (2): 978-87. [PMID:22019562]
78. Wu M, Zhang Z, Leranth C, Xu C, van den Pol AN, Alreja M. (2002) Hypocretin increases impulse flow in the septohippocampal GABAergic pathway: implications for arousal via a mechanism of hippocampal disinhibition. J Neurosci, 22 (17): 7754-65. [PMID:12196599]
79. Yin J, Mobarec JC, Kolb P, Rosenbaum DM. (2015) Crystal structure of the human OX2 orexin receptor bound to the insomnia drug suvorexant. Nature, 519 (7542): 247-50. [PMID:25533960]
80. Yoshida Y, Naoe Y, Terauchi T, Ozaki F, Doko T, Takemura A, Tanaka T, Sorimachi K, Beuckmann CT, Suzuki M et al.. (2015) Discovery of (1R,2S)-2-{[(2,4-Dimethylpyrimidin-5-yl)oxy]methyl}-2-(3-fluorophenyl)-N-(5-fluoropyridin-2-yl)cyclopropanecarboxamide (E2006): A Potent and Efficacious Oral Orexin Receptor Antagonist. J Med Chem, 58 (11): 4648-64. [PMID:25953512]
81. Yukitake H, Fujimoto T, Ishikawa T, Suzuki A, Shimizu Y, Rikimaru K, Ito M, Suzuki M, Kimura H. (2019) TAK-925, an orexin 2 receptor-selective agonist, shows robust wake-promoting effects in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav, 187: 172794. [PMID:31654653]
82. Zhu Y, Miwa Y, Yamanaka A, Yada T, Shibahara M, Abe Y, Sakurai T, Goto K. (2003) Orexin receptor type-1 couples exclusively to pertussis toxin-insensitive G-proteins, while orexin receptor type-2 couples to both pertussis toxin-sensitive and -insensitive G-proteins. J Pharmacol Sci, 92: 259-266. [PMID:12890892]