1. Bargal R, Avidan N, Ben-Asher E, Olender Z, Zeigler M, Frumkin A, Raas-Rothschild A, Glusman G, Lancet D, Bach G. (2000) Identification of the gene causing mucolipidosis type IV.
Nat Genet, 26 (1): 118-23.
[PMID:10973263]
2. Bargal R, Bach G. (1997) Mucolipidosis type IV: abnormal transport of lipids to lysosomes.
J Inherit Metab Dis, 20 (5): 625-32.
[PMID:9323557]
3. Chandra M, Zhou H, Li Q, Muallem S, Hofmann SL, Soyombo AA. (2011) A role for the Ca2+ channel TRPML1 in gastric acid secretion, based on analysis of knockout mice.
Gastroenterology, 140 (3): 857-67.
[PMID:21111738]
4. Chen CC, Keller M, Hess M, Schiffmann R, Urban N, Wolfgardt A, Schaefer M, Bracher F, Biel M, Wahl-Schott C et al.. (2014) A small molecule restores function to TRPML1 mutant isoforms responsible for mucolipidosis type IV.
Nat Commun, 5: 4681.
[PMID:25119295]
5. Chen CS, Bach G, Pagano RE. (1998) Abnormal transport along the lysosomal pathway in mucolipidosis, type IV disease.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 95 (11): 6373-8.
[PMID:9600972]
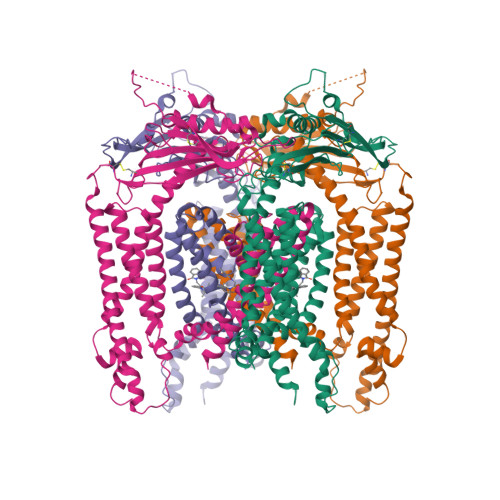
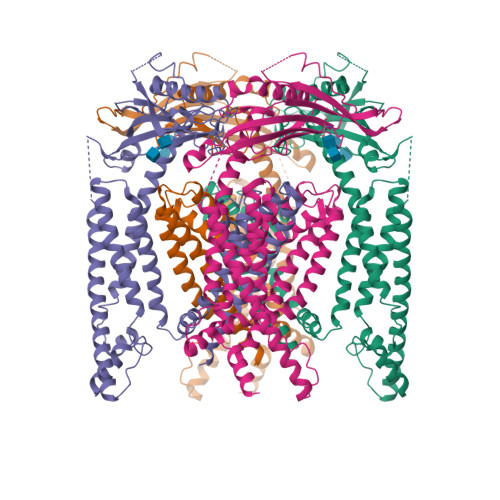
6. Chen Q, She J, Zeng W, Guo J, Xu H, Bai XC, Jiang Y. (2017) Structure of mammalian endolysosomal TRPML1 channel in nanodiscs.
Nature, 550 (7676): 415-418.
[PMID:29019981]
7. Cheng X, Shen D, Samie M, Xu H. (2010) Mucolipins: Intracellular TRPML1-3 channels.
FEBS Lett, 584 (10): 2013-21.
[PMID:20074572]
8. Colletti GA, Miedel MT, Quinn J, Andharia N, Weisz OA, Kiselyov K. (2012) Loss of lysosomal ion channel transient receptor potential channel mucolipin-1 (TRPML1) leads to cathepsin B-dependent apoptosis.
J Biol Chem, 287 (11): 8082-91.
[PMID:22262857]
9. Curcio-Morelli C, Charles FA, Micsenyi MC, Cao Y, Venugopal B, Browning MF, Dobrenis K, Cotman SL, Walkley SU, Slaugenhaupt SA. (2010) Macroautophagy is defective in mucolipin-1-deficient mouse neurons.
Neurobiol Dis, 40 (2): 370-7.
[PMID:20600908]
10. Curcio-Morelli C, Zhang P, Venugopal B, Charles FA, Browning MF, Cantiello HF, Slaugenhaupt SA. (2010) Functional multimerization of mucolipin channel proteins.
J Cell Physiol, 222 (2): 328-35.
[PMID:19885840]
11. Dong XP, Cheng X, Mills E, Delling M, Wang F, Kurz T, Xu H. (2008) The type IV mucolipidosis-associated protein TRPML1 is an endolysosomal iron release channel.
Nature, 455 (7215): 992-6.
[PMID:18794901]
12. Dong XP, Shen D, Wang X, Dawson T, Li X, Zhang Q, Cheng X, Zhang Y, Weisman LS, Delling M et al.. (2010) PI(3,5)P(2) controls membrane trafficking by direct activation of mucolipin Ca(2+) release channels in the endolysosome.
Nat Commun, 1: 38.
[PMID:20802798]
13. Dong XP, Wang X, Shen D, Chen S, Liu M, Wang Y, Mills E, Cheng X, Delling M, Xu H. (2009) Activating mutations of the TRPML1 channel revealed by proline-scanning mutagenesis.
J Biol Chem, 284 (46): 32040-52.
[PMID:19638346]
14. Eichelsdoerfer JL, Evans JA, Slaugenhaupt SA, Cuajungco MP. (2010) Zinc dyshomeostasis is linked with the loss of mucolipidosis IV-associated TRPML1 ion channel.
J Biol Chem, 285 (45): 34304-8.
[PMID:20864526]
15. Falardeau JL, Kennedy JC, Acierno Jr JS, Sun M, Stahl S, Goldin E, Slaugenhaupt SA. (2002) Cloning and characterization of the mouse Mcoln1 gene reveals an alternatively spliced transcript not seen in humans.
BMC Genomics, 3: 3.
[PMID:11897010]
16. Grimm C, Cuajungco MP, van Aken AF, Schnee M, Jörs S, Kros CJ, Ricci AJ, Heller S. (2007) A helix-breaking mutation in TRPML3 leads to constitutive activity underlying deafness in the varitint-waddler mouse.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 104 (49): 19583-8.
[PMID:18048323]
17. Grimm C, Jörs S, Saldanha SA, Obukhov AG, Pan B, Oshima K, Cuajungco MP, Chase P, Hodder P, Heller S. (2010) Small molecule activators of TRPML3.
Chem Biol, 17 (2): 135-48.
[PMID:20189104]
18. LaPlante JM, Falardeau J, Sun M, Kanazirska M, Brown EM, Slaugenhaupt SA, Vassilev PM. (2002) Identification and characterization of the single channel function of human mucolipin-1 implicated in mucolipidosis type IV, a disorder affecting the lysosomal pathway.
FEBS Lett, 532 (1-2): 183-7.
[PMID:12459486]
19. LaPlante JM, Sun M, Falardeau J, Dai D, Brown EM, Slaugenhaupt SA, Vassilev PM. (2006) Lysosomal exocytosis is impaired in mucolipidosis type IV.
Mol Genet Metab, 89 (4): 339-48.
[PMID:16914343]
20. LaPlante JM, Ye CP, Quinn SJ, Goldin E, Brown EM, Slaugenhaupt SA, Vassilev PM. (2004) Functional links between mucolipin-1 and Ca2+-dependent membrane trafficking in mucolipidosis IV.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 322 (4): 1384-91.
[PMID:15336987]
21. Puertollano R, Kiselyov K. (2009) TRPMLs: in sickness and in health.
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 296 (6): F1245-54.
[PMID:19158345]
22. Rühl P, Rosato AS, Urban N, Gerndt S, Tang R, Abrahamian C, Leser C, Sheng J, Jha A, Vollmer G et al.. (2021) Estradiol analogs attenuate autophagy, cell migration and invasion by direct and selective inhibition of TRPML1, independent of estrogen receptors.
Sci Rep, 11 (1): 8313.
[PMID:33859333]
23. Samie MA, Grimm C, Evans JA, Curcio-Morelli C, Heller S, Slaugenhaupt SA, Cuajungco MP. (2009) The tissue-specific expression of TRPML2 (MCOLN-2) gene is influenced by the presence of TRPML1.
Pflugers Arch, 459 (1): 79-91.
[PMID:19763610]
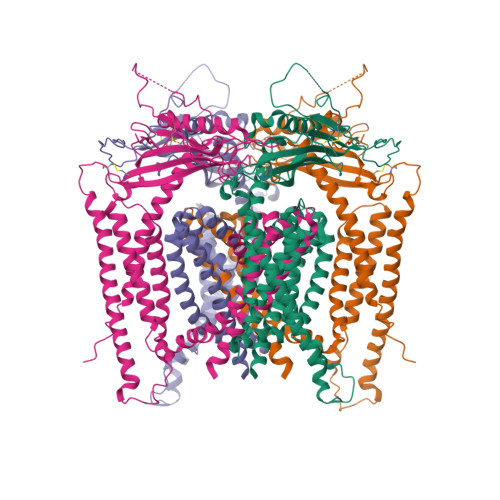
24. Schmiege P, Fine M, Blobel G, Li X. (2017) Human TRPML1 channel structures in open and closed conformations.
Nature, 550 (7676): 366-370.
[PMID:29019983]
25. Shen D, Wang X, Li X, Zhang X, Yao Z, Dibble S, Dong XP, Yu T, Lieberman AP, Showalter HD et al.. (2012) Lipid storage disorders block lysosomal trafficking by inhibiting a TRP channel and lysosomal calcium release.
Nat Commun, 3: 731.
[PMID:22415822]
26. Slaugenhaupt SA. (2002) The molecular basis of mucolipidosis type IV.
Curr Mol Med, 2 (5): 445-50.
[PMID:12125810]
27. Spix B, Butz ES, Chen CC, Rosato AS, Tang R, Jeridi A, Kudrina V, Plesch E, Wartenberg P, Arlt E et al.. (2022) Lung emphysema and impaired macrophage elastase clearance in mucolipin 3 deficient mice.
Nat Commun, 13 (1): 318.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-27860-x
[PMID:35031603]
28. Sun M, Goldin E, Stahl S, Falardeau JL, Kennedy JC, Acierno JS, Bove C, Kaneski CR, Nagle J, Bromley MC, Colman M, Schiffmann R, Slaugenhaupt SA. (2000) Mucolipidosis type IV is caused by mutations in a gene encoding a novel transient receptor potential channel.
Hum Mol Genet, 9 (17): 2471-8.
[PMID:11030752]
29. Venugopal B, Mesires NT, Kennedy JC, Curcio-Morelli C, Laplante JM, Dice JF, Slaugenhaupt SA. (2009) Chaperone-mediated autophagy is defective in mucolipidosis type IV.
J Cell Physiol, 219 (2): 344-53.
[PMID:19117012]
30. Vergarajauregui S, Connelly PS, Daniels MP, Puertollano R. (2008) Autophagic dysfunction in mucolipidosis type IV patients.
Hum Mol Genet, 17 (17): 2723-37.
[PMID:18550655]
31. Vergarajauregui S, Martina JA, Puertollano R. (2009) Identification of the penta-EF-hand protein ALG-2 as a Ca2+-dependent interactor of mucolipin-1.
J Biol Chem, 284 (52): 36357-66.
[PMID:19864416]
32. Vergarajauregui S, Martina JA, Puertollano R. (2011) LAPTMs regulate lysosomal function and interact with mucolipin 1: new clues for understanding mucolipidosis type IV.
J Cell Sci, 124 (Pt 3): 459-68.
[PMID:21224396]
33. Wang X, Zhang X, Dong XP, Samie M, Li X, Cheng X, Goschka A, Shen D, Zhou Y, Harlow J et al.. (2012) TPC proteins are phosphoinositide- activated sodium-selective ion channels in endosomes and lysosomes.
Cell, 151 (2): 372-83.
[PMID:23063126]
34. Xu H, Delling M, Li L, Dong X, Clapham DE. (2007) Activating mutation in a mucolipin transient receptor potential channel leads to melanocyte loss in varitint-waddler mice.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 104 (46): 18321-6.
[PMID:17989217]
35. Yamaguchi S, Jha A, Li Q, Soyombo AA, Dickinson GD, Churamani D, Brailoiu E, Patel S, Muallem S. (2011) Transient receptor potential mucolipin 1 (TRPML1) and two-pore channels are functionally independent organellar ion channels.
J Biol Chem, 286 (26): 22934-42.
[PMID:21540176]
36. Yu L, Zhang X, Yang Y, Li D, Tang K, Zhao Z, He W, Wang C, Sahoo N, Converso-Baran K et al.. (2020) Small-molecule activation of lysosomal TRP channels ameliorates Duchenne muscular dystrophy in mouse models.
Sci Adv, 6 (6): eaaz2736.
[PMID:32128386]
37. Zeevi DA, Lev S, Frumkin A, Minke B, Bach G. (2010) Heteromultimeric TRPML channel assemblies play a crucial role in the regulation of cell viability models and starvation-induced autophagy.
J Cell Sci, 123 (Pt 18): 3112-24.
[PMID:20736310]
38. Zhang X, Li X, Xu H. (2012) Phosphoinositide isoforms determine compartment-specific ion channel activity.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 109 (28): 11384-9.
[PMID:22733759]