
Top ▲

GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| class A G protein-coupled receptor | ||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 7 | 450 | 2q11.2 | ADRA2B | adrenoceptor alpha 2B | 42 |
| Mouse | 7 | 450 | 2 61.95 cM | Adra2b | adrenergic receptor, alpha 2b | 45 |
| Rat | 7 | 453 | 3q36 | Adra2b | adrenoceptor alpha 2B | 6 |
Database Links  |
|
| Specialist databases | |
| GPCRdb | ada2b_human (Hs), ada2b_mouse (Mm), ada2b_rat (Rn) |
| Other databases | |
| Alphafold | P18089 (Hs), P30545 (Mm), P19328 (Rn) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL1942 (Hs), CHEMBL2405 (Mm), CHEMBL266 (Rn) |
| DrugBank Target | P18089 (Hs), P18089 (Hs), P18089 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000274286 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000058620 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000013887 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 151 (Hs), 11552 (Mm), 24174 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000274286 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:151 (Hs), mmu:11552 (Mm), rno:24174 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 104260 (Hs) |
| Pharos | P18089 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_000682 (Hs), NM_009633 (Mm), NM_138505 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_000673 (Hs), NP_033763 (Mm), NP_612514 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | P18089 (Hs), P30545 (Mm), P19328 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | ADRA2B (Hs) |
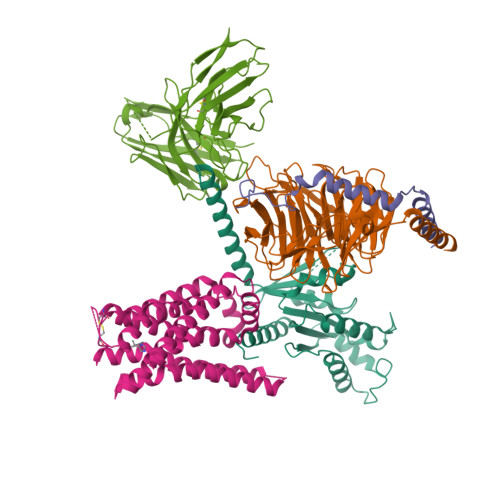
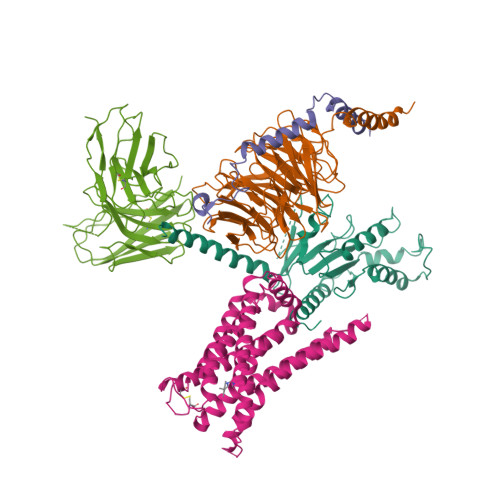
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| (-)-adrenaline |
| (-)-noradrenaline |
| Comments: Adrenaline exhibits similar potency, affinity and efficacy to noradrenaline. |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific agonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [125I]p-iodoclonidine binds to the human α2B receptor with a pKd of 8.1 [30]. Many of the compounds listed as agonists will behave as full or partial agonists depending on the system in which they are studied and tend towards full agonism in recombinant systems with high receptor expression. Rat studies suggest that tizanidine mediates its analgesic effects primarily through the α2B-adrenoceptor [19]. Guanabenz order of affinity is α2A-AR>α2B-AR>α2C-AR [1]. There are currently no selective α2B-AR agonists. Clinical uses: Clonidine is used to treat high blood pressure, guanfacine for ADHD and tizanidine to relieve muscle spasticity. Apraclonidine and brimonidine are used in eye drops to relieve glaucoma. Dexmedetomidine (stereoisomer of medetomidine) and xylazine are used for their hypnotic, anxiolytic and analgesic properties as pre-operatives prior to surgery but they may also be used to control agitation associated with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. Xylazine has recently emerged in the North American illegal drug markets as a common admixture with synthetic opioids particularly fentanyl and is associated with a marked increase in the number of fatalities associated with drug overdose. While opioid antagonists such as naloxone can rapidly reverse the effects of fentanyl, they do not counteract the sedation, bradycardia and hypotension due to xylazine. The α2-AR antagonist atipamezole is widely used to reverse the effects of xylazine in veterinary medicine but this role has yet to be established in the clinic. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific antagonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pentoxifylline has phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitory action in addition to α2B-AR antagonist activity [36]. Rauwolscine is a stereoisomer of yohimbine. AGN-209419 is an α2-AR antagonist (pKb 8.8 vs. mouse α2B-AR) [22]. The α2-AR antagonist atipamezole is widely used to reverse the effects of xylazine in veterinary medicine but this role has yet to be established in the clinic. Atipamezole and bromocriptine can exhibit partial agonist properties in some systems [32]. There are currently no selective α2B-AR antagonists. Clinical uses: α2B-AR are not specific clinical targets for antagonists. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allosteric Modulator Comments | ||
| 5-(N-ethyl-N-isopropyl)-amiloride and chlorobenzyldimethylbenzamil are non-selective, negative allosteric regulators at the α2B receptor [43]. However, no binding affinity data is available for these ligands at this receptor. |
Primary Transduction Mechanisms 
|
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gi/Go family |
Potassium channel Calcium channel Other - See Comments |
|
Comments:
ERK1/2 phosphorylation Inhibition of voltage dependent Ca2+ channels Augmentation of inwardly rectifying K+ channels |
|
| References: 5,20,32,34 | |
Secondary Transduction Mechanisms  |
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gs family | |
| Comments: The physiological significance of this mechanism is unknown. Although this seems to be a contradiction of the primary transduction mechanism, some α2-AR agonists activate adenylyl cyclase at concentrations higher than those that inhibit adenylyl cyclase - hence biphasic responses can be observed. | |
| References: 11,32,34 | |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Expression Datasets  |
|
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Biologically Significant Variants 
|
||||||||
|
1. Auerbach SS, DrugMatrix® and ToxFX® Coordinator National Toxicology Program. National Toxicology Program: Dept of Health and Human Services. Accessed on 02/05/2014. Modified on 02/05/2014. DrugMatrix, https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/drugmatrix/index.html
2. Basarrate S, Monzel AS, Smith JLM, Marsland AL, Trumpff C, Picard M. (2024) Glucocorticoid and Adrenergic Receptor Distribution Across Human Organs and Tissues: A Map for Stress Transduction. Psychosom Med, 86 (2): 89-98. [PMID:38193786]
3. Blaxall HS, Hass NA, Bylund DB. (1994) Expression of alpha 2-adrenergic receptor genes in rat tissues. Receptor, 4 (3): 191-9. [PMID:7812219]
4. Bylund DB, Blaxall HS, Iversen LJ, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ, Lomasney JW. (1992) Pharmacological characteristics of alpha 2-adrenergic receptors: comparison of pharmacologically defined subtypes with subtypes identified by molecular cloning. Mol Pharmacol, 42: 1-5. [PMID:1353247]
5. Bylund DB, Ray-Prenger C. (1989) Alpha-2A and alpha-2B adrenergic receptor subtypes: attenuation of cyclic AMP production in cell lines containing only one receptor subtype. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 251 (2): 640-4. [PMID:2553931]
6. Chen WM, Chang AC, Shie BJ, Chang YH, Chang NC. (1992) Molecular cloning and characterization of a mouse alpha 2C2 adrenoceptor subtype gene. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1171 (2): 219-23. [PMID:1336396]
7. Chu KL, Xu J, Frost J, Li L, Gomez E, Dart MJ, Jarvis MF, Meyer MD, McGaraughty S. (2015) A selective α2 B adrenoceptor agonist (A-1262543) and duloxetine modulate nociceptive neurones in the medial prefrontal cortex, but not in the spinal cord of neuropathic rats. Eur J Pain, 19 (5): 649-60. [PMID:25154730]
8. Deupree JD, Hinton KA, Cerutis DR, Bylund DB. (1996) Buffers differentially alter the binding of [3H]rauwolscine and [3H]RX821002 to the alpha-2 adrenergic receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 278 (3): 1215-27. [PMID:8819505]
9. Devedjian JC, Esclapez F, Denis-Pouxviel C, Paris H. (1994) Further characterization of human alpha 2-adrenoceptor subtypes: [3H]RX821002 binding and definition of additional selective drugs. Eur J Pharmacol, 252 (1): 43-9. [PMID:7908642]
10. Diamanti E, Del Bello F, Carbonara G, Carrieri A, Fracchiolla G, Giannella M, Mammoli V, Piergentili A, Pohjanoksa K, Quaglia W et al.. (2012) Might the observed α(2A)-adrenoreceptor agonism or antagonism of allyphenyline analogues be ascribed to different molecular conformations?. Bioorg Med Chem, 20 (6): 2082-90. [PMID:22341244]
11. Eason MG, Kurose H, Holt BD, Raymond JR, Liggett SB. (1992) Simultaneous coupling of alpha 2-adrenergic receptors to two G-proteins with opposing effects. Subtype-selective coupling of alpha 2C10, alpha 2C4, and alpha 2C2 adrenergic receptors to Gi and Gs. J Biol Chem, 267 (22): 15795-801. [PMID:1322406]
12. Eason MG, Liggett SB. (1993) Human alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtype distribution: widespread and subtype-selective expression of alpha 2C10, alpha 2C4, and alpha 2C2 mRNA in multiple tissues. Mol Pharmacol, 44 (1): 70-5. [PMID:7688069]
13. Handy DE, Flordellis CS, Bogdanova NN, Bresnahan MR, Gavras H. (1993) Diverse tissue expression of rat alpha 2-adrenergic receptor genes. Hypertension, 21 (6 Pt 1): 861-5. [PMID:7684725]
14. Jasper JR, Lesnick JD, Chang LK, Yamanishi SS, Chang TK, Hsu SA, Daunt DA, Bonhaus DW, Eglen RM. (1998) Ligand efficacy and potency at recombinant alpha2 adrenergic receptors: agonist-mediated [35S]GTPgammaS binding. Biochem Pharmacol, 55 (7): 1035-43. [PMID:9605427]
15. Kable JW, Murrin LC, Bylund DB. (2000) In vivo gene modification elucidates subtype-specific functions of alpha(2)-adrenergic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 293 (1): 1-7. [PMID:10734146]
16. Kanagy NL. (2005) Alpha(2)-adrenergic receptor signalling in hypertension. Clin Sci (Lond), 109 (5): 431-7. [PMID:16232127]
17. Kennis LE, Bischoff FP, Mertens CJ, Love CJ, Van den Keybus FA, Pieters S, Braeken M, Megens AA, Leysen JE. (2000) New 2-substituted 1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzofuro[3,2-c]pyridine having highly active and potent central alpha 2-antagonistic activity as potential antidepressants. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 10 (1): 71-4. [PMID:10636247]
18. Knaus AE, Muthig V, Schickinger S, Moura E, Beetz N, Gilsbach R, Hein L. (2007) Alpha2-adrenoceptor subtypes--unexpected functions for receptors and ligands derived from gene-targeted mouse models. Neurochem Int, 51 (5): 277-81. [PMID:17664025]
19. Leiphart JW, Dills CV, Levy RM. (2004) Alpha2-adrenergic receptor subtype specificity of intrathecally administered tizanidine used for analgesia for neuropathic pain. J Neurosurg, 101 (4): 641-7. [PMID:15481719]
20. Limbird LE. (1988) Receptors linked to inhibition of adenylate cyclase: additional signaling mechanisms. FASEB J, 2 (11): 2686-95. [PMID:2840317]
21. Link RE, Desai K, Hein L, Stevens ME, Chruscinski A, Bernstein D, Barsh GS, Kobilka BK. (1996) Cardiovascular regulation in mice lacking alpha2-adrenergic receptor subtypes b and c. Science, 273 (5276): 803-5. [PMID:8670422]
22. Luhrs L, Manlapaz C, Kedzie K, Rao S, Cabrera-Ghayouri S, Donello J, Gil D. (2016) Function of brain α2B-adrenergic receptor characterized with subtype-selective α2B antagonist and KO mice. Neuroscience, 339: 608-621. [PMID:27751959]
23. MacDonald E, Kobilka BK, Scheinin M. (1997) Gene targeting--homing in on alpha 2-adrenoceptor-subtype function. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 18 (6): 211-9. [PMID:9227000]
24. Makaritsis KP, Handy DE, Johns C, Kobilka B, Gavras I, Gavras H. (1999) Role of the alpha2B-adrenergic receptor in the development of salt-induced hypertension. Hypertension, 33 (1): 14-7. [PMID:9931075]
25. Michel AD, Loury DN, Whiting RL. (1990) Assessment of imiloxan as a selective alpha 2B-adrenoceptor antagonist. Br J Pharmacol, 99 (3): 560-4. [PMID:1970500]
26. Millan MJ, Maiofiss L, Cussac D, Audinot V, Boutin JA, Newman-Tancredi A. (2002) Differential actions of antiparkinson agents at multiple classes of monoaminergic receptor. I. A multivariate analysis of the binding profiles of 14 drugs at 21 native and cloned human receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 303 (2): 791-804. [PMID:12388666]
27. Nicholas AP, Pieribone V, Hökfelt T. (1993) Distributions of mRNAs for alpha-2 adrenergic receptor subtypes in rat brain: an in situ hybridization study. J Comp Neurol, 328 (4): 575-94. [PMID:8381444]
28. Peltonen JM, Pihlavisto M, Scheinin M. (1998) Subtype-specific stimulation of [35S]GTPgammaS binding by recombinant alpha2-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol, 355 (2-3): 275-9. [PMID:9760042]
29. Pihlavisto M, Sjöholm B, Scheinin M, Wurster S. (1998) Modulation of agonist binding to recombinant human alpha2-adrenoceptors by sodium ions. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1448 (1): 135-46. [PMID:9824686]
30. Piletz JE, Zhu H, Chikkala DN. (1996) Comparison of ligand binding affinities at human I1-imidazoline binding sites and the high affinity state of alpha-2 adrenoceptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 279 (2): 694-702. [PMID:8930173]
31. Proudman RGW, Akinaga J, Baker JG. (2022) The affinity and selectivity of α-adrenoceptor antagonists, antidepressants and antipsychotics for the human α2A, α2B, and α2C-adrenoceptors and comparison with human α1 and β-adrenoceptors. Pharmacol Res Perspect, 10 (2): e00936. [PMID:35224877]
32. Proudman RGW, Akinaga J, Baker JG. (2022) The signaling and selectivity of α-adrenoceptor agonists for the human α2A, α2B and α2C-adrenoceptors and comparison with human α1 and β-adrenoceptors. Pharmacol Res Perspect, 10 (5): e01003. [PMID:36101495]
33. Scheinin M, Lomasney JW, Hayden-Hixson DM, Schambra UB, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ, Fremeau Jr RT. (1994) Distribution of alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtype gene expression in rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res, 21 (1-2): 133-49. [PMID:8164514]
34. Scheinin M, Pihlavisto M. (2000) Molecular pharmacology of alpha2-adrenoceptor agonists. Best Practice & Research Clinical Anaesthesiology, 14 (2): 247-260. DOI: 10.1053/bean.2000.00
35. Schotte A, Janssen PF, Gommeren W, Luyten WH, Van Gompel P, Lesage AS, De Loore K, Leysen JE. (1996) Risperidone compared with new and reference antipsychotic drugs: in vitro and in vivo receptor binding. Psychopharmacology (Berl.), 124 (1-2): 57-73. [PMID:8935801]
36. Semmler J, Gebert U, Eisenhut T, Moeller J, Schönharting MM, Alléra A, Endres S. (1993) Xanthine derivatives: comparison between suppression of tumour necrosis factor-alpha production and inhibition of cAMP phosphodiesterase activity. Immunology, 78 (4): 520-5. [PMID:8388363]
37. Shimokawa T, Nakagawa T, Hayashi K, Yamagata M, Yoneda K. (2022) Subcellular distribution of α2-adrenoceptor subtypes in the rodent kidney. Cell Tissue Res, 387 (2): 303-314. [PMID:34837110]
38. Snapir A, Heinonen P, Tuomainen TP, Alhopuro P, Karvonen MK, Lakka TA, Nyyssönen K, Salonen R, Kauhanen J, Valkonen VP et al.. (2001) An insertion/deletion polymorphism in the alpha2B-adrenergic receptor gene is a novel genetic risk factor for acute coronary events. J Am Coll Cardiol, 37 (6): 1516-22. [PMID:11345359]
39. Snapir A, Mikkelsson J, Perola M, Penttilä A, Scheinin M, Karhunen PJ. (2003) Variation in the alpha2B-adrenoceptor gene as a risk factor for prehospital fatal myocardial infarction and sudden cardiac death. J Am Coll Cardiol, 41 (2): 190-4. [PMID:12535806]
40. Uhlén S, Porter AC, Neubig RR. (1994) The novel alpha-2 adrenergic radioligand [3H]-MK912 is alpha-2C selective among human alpha-2A, alpha-2B and alpha-2C adrenoceptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 271 (3): 1558-65. [PMID:7996470]
41. Weinshank RL, Adham N, Macchi M, Olsen MA, Branchek TA, Hartig PR. (1991) Molecular cloning and characterization of a high affinity dopamine receptor (D1 beta) and its pseudogene. J Biol Chem, 266 (33): 22427-35. [PMID:1834671]
42. Weinshank RL, Zgombick JM, Macchi M, Adham N, Lichtblau H, Branchek TA, Hartig PR. (1990) Cloning, expression, and pharmacological characterization of a human alpha 2B-adrenergic receptor. Mol Pharmacol, 38 (5): 681-8. [PMID:2172775]
43. Wilson AL, Seibert K, Brandon S, Cragoe Jr EJ, Limbird LE. (1991) Monovalent cation and amiloride analog modulation of adrenergic ligand binding to the unglycosylated alpha 2B-adrenergic receptor subtype. Mol Pharmacol, 39 (4): 481-6. [PMID:1850091]
44. Yuan D, Liu Z, Kaindl J, Maeda S, Zhao J, Sun X, Xu J, Gmeiner P, Wang HW, Kobilka BK. (2020) Activation of the α2B adrenoceptor by the sedative sympatholytic dexmedetomidine. Nat Chem Biol, 16 (5): 507-512. [PMID:32152538]
45. Zeng DW, Harrison JK, D'Angelo DD, Barber CM, Tucker AL, Lu ZH, Lynch KR. (1990) Molecular characterization of a rat alpha 2B-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 87 (8): 3102-6. [PMID:2158103]