
Top ▲

GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| class A G protein-coupled receptor | ||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 7 | 372 | 1p35.3 | OPRD1 | opioid receptor delta 1 | 46,88 |
| Mouse | 7 | 372 | 4 64.78 cM | Oprd1 | opioid receptor, delta 1 | 26,44,104 |
| Rat | 7 | 372 | 5q36 | Oprd1 | opioid receptor, delta 1 | 1 |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| DOP | DOR | OP1 | Delta receptor | DOR-1 | DOPr | opioid receptor |
Database Links  |
|
| Specialist databases | |
| GPCRdb | oprd_human (Hs), oprd_mouse (Mm), oprd_rat (Rn) |
| Other databases | |
| Alphafold | P41143 (Hs), P32300 (Mm), P33533 (Rn) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL236 (Hs), CHEMBL3222 (Mm), CHEMBL269 (Rn) |
| DrugBank Target | P41143 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000116329 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000050511 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000010531 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 4985 (Hs), 18386 (Mm), 24613 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000116329 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:4985 (Hs), mmu:18386 (Mm), rno:24613 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 165195 (Hs) |
| Pharos | P41143 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_000911 (Hs), NM_013622 (Mm), NM_012617 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_000902 (Hs), NP_038650 (Mm), NP_036749 (Rn) |
| SynPHARM |
3818 (in complex with naltrindole) 3817 (in complex with naltrindole) |
| UniProtKB | P41143 (Hs), P32300 (Mm), P33533 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | OPRD1 (Hs) |
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
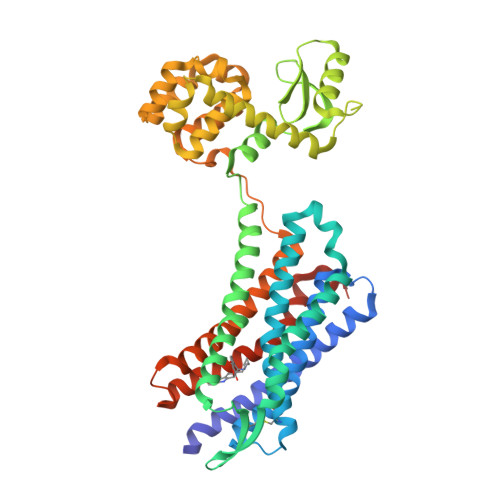
|
|
||||||||||||
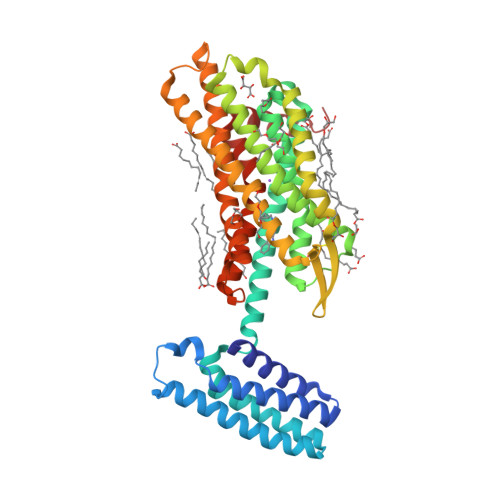
|
|
||||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| dynorphin A-(1-13) {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| dynorphin A {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| dynorphin A-(1-8) {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| dynorphin B {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| endomorphin-1 {Sp: Human} |
| β-endorphin {Sp: Human} , β-endorphin {Sp: Mouse} , β-endorphin {Sp: Rat} |
| [Leu]enkephalin {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| [Met]enkephalin {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| α-neoendorphin {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| Principal endogenous agonists (Human) |
| β-endorphin (POMC, P01189), [Leu]enkephalin (PENK, P01210), [Met]enkephalin (PENK, P01210) |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific agonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The above reported affinities are based on binding to receptors in membrane preparations with buffers optimized for agonist binding. The affinity of agonists in intact cells, or in the presence of sodium and GTP/GDP analogues is often different and multiple affinity sites have been observed [47]. Discrimination of full or partial agonism is very dependent on the level of receptor expression and on the assay used to monitor agonist effects. Many agents may behave as full agonists or potent partial agonists in cell lines expressing cloned receptors in high concentration, but in other environments they may show only weak agonist activity. The identification of agonist activity in the table is largely based on the ability to stimulate GTPγ35S binding in cell lines expressing cloned human δ receptors. Agents giving 85% or greater stimulation than that given by DPDPE have been characterized as Full Agonists [93]. Diprenorphine is a very weak partial agonist and in some assays may behave as an antagonist. Deltorphin II is endogenous in some species of amphibians. Alternative sources for binding information for the same ligands in different species can be found in the following reference [71]. Although many of the agonists are considered to be highly selective for the δ opioid receptor, data using δ and μ knockout mice show that ICV administration of opioids considered δ receptor selective, such as deltorphin and DPDPE can activate μ opioid receptors to elicit analgesia [83]. We have tagged the μ receptor as the primary drug target for hydrocodone based on this drug having the highest affinity at this receptor compared to the κ and δ receptors [68]. In [68] an affinity constant was not calculated for the δ receptor, but hydrocodone was reported to inhibit [3H]naltrindole binding by 37%. Similarly, we have tagged the μ receptor as the primary target of the drug hydromorphone [98]. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific antagonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| δ opioid receptors were one of the first G protein-coupled receptors to be shown to exhibit constitutive activity [18]. As observed with agonist binding affinities, some antagonist affinities can be modulated markedly by ions and GTP/GDP analogues [67]. The assigning of an antagonist as an inverse agonist or neutral antagonist appears to be dependent upon the state of the receptor, and following agonist treatment many neutral antagonists and weak partial agonists have been reported to become inverse agonists [56]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allosteric Modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allosteric Modulator Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Although no small molecules are considered direct allosteric regulators of δ opioid receptors, a number of proteins such as G protein-coupled receptor kinases, β-arrestins and G proteins clearly regulate receptor affinities and function. Furthermore number of proteins such as G protein-coupled receptor kinases, β-arrestins and G proteins clearly regulate receptor affinities and function. Furthermore, sodium and guanyl nucleotides can modify the functional δ opioid receptor complex and G protein interaction. Also, other G protein-coupled receptors appear to be able to form heterodimers with δ opioid receptors potentially modifying δ opioid activity [80] reviewed in [14,25]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other Binding Ligands | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | Click column headers to sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Primary Transduction Mechanisms 
|
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gi/Go family |
Adenylyl cyclase inhibition Phospholipase C stimulation Potassium channel Calcium channel Other - See Comments |
| Comments: δ receptors have been shown to modulate many kinase cascades including ERKs, Akts, JNKs, STAT3, P38 involving Src, Ras, Rac, Raf-1, Cdc42, RTKs. | |
| References: 42,48,57,86 | |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
| Tissue Distribution Comments | ||||||||
| Studies of the distribution of δ opioid receptors in humans has been limited to autoradiography and in situ hybridisation analysis [7,72]. DOP receptors in the CNS appear to have a similar distribution in rat and human [7] and mouse [34]. One notable exception is the spinal cord where DOP receptors are considerably more abundant in the dorsal horn and dorsal root ganglia than in rodent counterparts [63]. Many brain stem nuclei (such as the lateral reticular nucleus, the medial vestibular nucleus and trapezoid nucleus) express high levels of DOP mRNA yet DOP binding is undetectable [109]. For a review of δ opioid receptor expression in the rat see [59]. | ||||||||
Expression Datasets  |
|
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
| Physiological Functions Comments | ||||||||
| For reviews on the signalling and function of the δ opioid receptor see [17,48,102] | ||||||||
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression Comments | ||||||||||
| Some of the physiological effects observed with knockout mice may be mouse-strain restricted and not generalise to all backgrounds. For a review on opioid receptor knockout mice see reference [32]. |
||||||||||
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biologically Significant Variant Comments |
| δ1 and δ2 receptor subtypes have been proposed based upon in vivo pharmacology of DPDPE and deltorphin II. However, no δ opioid receptor variants have been characterised as δ1 and δ2 receptor proteins, and knockout of the δ receptor gene in mice eliminates binding of the two ligands. There is mounting evidence that hetero-oligomerisation of the δ and κ opioid receptors results in the δ1 subtype and that κ/δ hetero-oligomers are functional in the spinal cord [6,28,101,105]. δ receptors have also been proposed to interact with μ receptors (for review see [105]). The observed pharmacological cross-talk may partially arise from agonist cross-reactivity. In vivo and knockout data suggest that analgesia from ICV administration of DPDPE or deltorphan II can occur via μ opioid receptors [83]. Pharmacological diversity of δ receptors likely results from interaction with different proteins (such as the formation of heterooligomers with other GPCRs) or differential posttranslational modifications as opposed to distinct variants of the primary sequence of the receptor protein [25]. |
1. Abood ME, Noel MA, Farnsworth JS, Tao Q. (1994) Molecular cloning and expression of a delta-opioid receptor from rat brain. J Neurosci Res, 37 (6): 714-9. [PMID:7519274]
2. Akiyama K, Gee KW, Mosberg HI, Hruby VJ, Yamamura HI. (1985) Characterization of [3H][2-D-penicillamine, 5-D-penicillamine]-enkephalin binding to delta opiate receptors in the rat brain and neuroblastoma--glioma hybrid cell line (NG 108-15). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 82 (8): 2543-7. [PMID:2986120]
3. Ann DK, Hasegawa J, Ko JL, Chen ST, Lee NM, Loh HH. (1992) Specific reduction of delta-opioid receptor binding in transfected NG108-15 cells. J Biol Chem, 267 (11): 7921-6. [PMID:1313812]
4. Arora S, Keenan SM, Peng Y, Welsh W, Zhang Q. (2006) Opioid receptor subtype-selective agents. Patent number: WO2006124687 A1. Assignee: Arora S, Keenan SM, Peng Y, Welsh W, Zhang Q.. Priority date: 12/05/2005. Publication date: 23/11/2006.
5. Besse D, Lombard MC, Besson JM. (1991) Autoradiographic distribution of mu, delta and kappa opioid binding sites in the superficial dorsal horn, over the rostrocaudal axis of the rat spinal cord. Brain Res, 548 (1-2): 287-91. [PMID:1651143]
6. Bhushan RG, Sharma SK, Xie Z, Daniels DJ, Portoghese PS. (2004) A bivalent ligand (KDN-21) reveals spinal delta and kappa opioid receptors are organized as heterodimers that give rise to delta(1) and kappa(2) phenotypes. Selective targeting of delta-kappa heterodimers. J Med Chem, 47: 2969-2972. [PMID:15163177]
7. Blackburn TP, Cross AJ, Hille C, Slater P. (1988) Autoradiographic localization of delta opiate receptors in rat and human brain. Neuroscience, 27 (2): 497-506. [PMID:2851117]
8. Breslin HJ, Diamond CJ, Kavash RW, Cai C, Dyatkin AB, Miskowski TA, Zhang SP, Wade PR, Hornby PJ, He W. (2012) Identification of a dual δ OR antagonist/μ OR agonist as a potential therapeutic for diarrhea-predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS-d). Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 22 (14): 4869-72. [PMID:22695132]
9. Broom DC, Guo L, Coop A, Husbands SM, Lewis JW, Woods JH, Traynor JR. (2000) BU48: a novel buprenorphine analog that exhibits delta-opioid-mediated convulsions but not delta-opioid-mediated antinociception in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 294 (3): 1195-200. [PMID:10945877]
10. Búzás B, Tóth G, Cavagnero S, Hruby VJ, Borsodi A. (1992) Synthesis and binding characteristics of the highly delta-specific new tritiated opioid peptide, [3H]deltorphin II. Life Sci, 50 (14): PL75-8. [PMID:1313131]
11. Cahill CM, Morinville A, Hoffert C, O'Donnell D, Beaudet A. (2003) Up-regulation and trafficking of delta opioid receptor in a model of chronic inflammation: implications for pain control. Pain, 101 (1-2): 199-208. [PMID:12507715]
12. Calderon SN, Rothman RB, Porreca F, Flippen-Anderson JL, McNutt RW, Xu H, Smith LE, Bilsky EJ, Davis P, Rice KC. (1994) Probes for narcotic receptor mediated phenomena. 19. Synthesis of (+)-4-[(alpha R)-alpha-((2S,5R)-4-allyl-2,5-dimethyl-1-piperazinyl)-3- methoxybenzyl]-N,N-diethylbenzamide (SNC 80): a highly selective, nonpeptide delta opioid receptor agonist. J Med Chem, 37 (14): 2125-8. [PMID:8035418]
13. Chang KJ, Rigdon GC, Howard JL, McNutt RW. (1993) A novel, potent and selective nonpeptidic delta opioid receptor agonist BW373U86. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 267 (2): 852-7. [PMID:8246159]
14. Christopoulos A, Kenakin T. (2002) G protein-coupled receptor allosterism and complexing. Pharmacol Rev, 54 (2): 323-74. [PMID:12037145]
15. Cometta-Morini C, Maguire PA, Loew GH. (1992) Molecular determinants of mu receptor recognition for the fentanyl class of compounds. Mol Pharmacol, 41 (1): 185-96. [PMID:1310142]
16. Conibear AE, Asghar J, Hill R, Henderson G, Borbely E, Tekus V, Helyes Z, Palandri J, Bailey C, Starke I et al.. (2020) A Novel G Protein-Biased Agonist at the δ Opioid Receptor with Analgesic Efficacy in Models of Chronic Pain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 372 (2): 224-236. [PMID:31594792]
17. Connor M, Christie MD. (1999) Opioid receptor signalling mechanisms. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol, 26 (7): 493-9. [PMID:10405772]
18. Costa T, Herz A. (1989) Antagonists with negative intrinsic activity at delta opioid receptors coupled to GTP-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 86 (19): 7321-5. [PMID:2552439]
19. Dekan Z, Sianati S, Yousuf A, Sutcliffe KJ, Gillis A, Mallet C, Singh P, Jin AH, Wang AM, Mohammadi SA et al.. (2019) A tetrapeptide class of biased analgesics from an Australian fungus targets the µ-opioid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 116 (44): 22353-22358. [PMID:31611414]
20. Delay-Goyet P, Seguin C, Gacel G, Roques BP. (1988) [3H][D-Ser2(O-tert-butyl),Leu5]enkephalyl-Thr6 and [D-Ser2(O-tert-butyl),Leu5]enkephalyl-Thr6(O-tert-butyl). Two new enkephalin analogs with both a good selectivity and a high affinity toward delta-opioid binding sites. J Biol Chem, 263 (9): 4124-30. [PMID:2831220]
21. Dietis N, McDonald J, Molinari S, Calo G, Guerrini R, Rowbotham DJ, Lambert DG. (2012) Pharmacological characterization of the bifunctional opioid ligand H-Dmt-Tic-Gly-NH-Bzl (UFP-505). Br J Anaesth, 108 (2): 262-70. [PMID:22194444]
22. Dietis N, Niwa H, Tose R, McDonald J, Ruggieri V, Filaferro M, Vitale G, Micheli L, Ghelardini C, Salvadori S et al.. (2018) In vitro and in vivo characterization of the bifunctional μ and δ opioid receptor ligand UFP-505. Br J Pharmacol, 175 (14): 2881-2896. [PMID:29524334]
23. Erbs E, Faget L, Scherrer G, Matifas A, Filliol D, Vonesch JL, Koch M, Kessler P, Hentsch D, Birling MC et al.. (2015) A mu-delta opioid receptor brain atlas reveals neuronal co-occurrence in subcortical networks. Brain Struct Funct, 220 (2): 677-702. [PMID:24623156]
24. Erspamer V, Melchiorri P, Falconieri-Erspamer G, Negri L, Corsi R, Severini C, Barra D, Simmaco M, Kreil G. (1989) Deltorphins: a family of naturally occurring peptides with high affinity and selectivity for delta opioid binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 86 (13): 5188-92. [PMID:2544892]
25. Evans CJ. (2004) Secrets of the opium poppy revealed. Neuropharmacology, 47 Suppl 1: 293-9. [PMID:15464145]
26. Evans CJ, Keith Jr DE, Morrison H, Magendzo K, Edwards RH. (1992) Cloning of a delta opioid receptor by functional expression. Science, 258 (5090): 1952-5. [PMID:1335167]
27. Fenalti G, Giguere PM, Katritch V, Huang XP, Thompson AA, Cherezov V, Roth BL, Stevens RC. (2014) Molecular control of δ-opioid receptor signalling. Nature, 506 (7487): 191-6. [PMID:24413399]
28. Filliol D, Ghozland S, Chluba J, Martin M, Matthes HW, Simonin F, Befort K, Gavériaux-Ruff C, Dierich A, LeMeur M et al.. (2000) Mice deficient for delta- and mu-opioid receptors exhibit opposing alterations of emotional responses. Nat Genet, 25 (2): 195-200. [PMID:10835636]
29. Fraser GL, Gaudreau GA, Clarke PB, Ménard DP, Perkins MN. (2000) Antihyperalgesic effects of delta opioid agonists in a rat model of chronic inflammation. Br J Pharmacol, 129 (8): 1668-72. [PMID:10780972]
30. Fujii H, Kawai K, Kawamura K, Mizusuna A, Onoda Y, Murachi M, Tanaka T, Endoh T, Nagase H. (2001) Synthesis of optically active TAN-67, a highly selective delta opioid receptor agonist, and investigation of its pharmacological properties. Drug Des Discov, 17 (4): 325-30. [PMID:11765135]
31. Gavériaux C, Peluso J, Simonin F, Laforet J, Kieffer B. (1995) Identification of kappa- and delta-opioid receptor transcripts in immune cells. FEBS Lett, 369 (2-3): 272-6. [PMID:7649271]
32. Gavériaux-Ruff C, Kieffer BL. (2002) Opioid receptor genes inactivated in mice: the highlights. Neuropeptides, 36 (2-3): 62-71. [PMID:12359497]
33. Gong J, Strong JA, Zhang S, Yue X, DeHaven RN, Daubert JD, Cassel JA, Yu G, Mansson E, Yu L. (1998) Endomorphins fully activate a cloned human mu opioid receptor. FEBS Lett, 439 (1-2): 152-6. [PMID:9849897]
34. Goody RJ, Oakley SM, Filliol D, Kieffer BL, Kitchen I. (2002) Quantitative autoradiographic mapping of opioid receptors in the brain of delta-opioid receptor gene knockout mice. Brain Res, 945 (1): 9-19. [PMID:12113946]
35. Granier S, Manglik A, Kruse AC, Kobilka TS, Thian FS, Weis WI, Kobilka BK. (2012) Structure of the δ-opioid receptor bound to naltrindole. Nature, 485 (7398): 400-4. [PMID:22596164]
36. Guan JS, Xu ZZ, Gao H, He SQ, Ma GQ, Sun T, Wang LH, Zhang ZN, Lena I, Kitchen I et al.. (2005) Interaction with vesicle luminal protachykinin regulates surface expression of delta-opioid receptors and opioid analgesia. Cell, 122 (4): 619-31. [PMID:16122428]
37. Guerrero M, Urbano M, Kim EK, Gamo AM, Riley S, Abgaryan L, Leaf N, Van Orden LJ, Brown SJ, Xie JY et al.. (2019) Design and Synthesis of a Novel and Selective Kappa Opioid Receptor (KOR) Antagonist (BTRX-335140). J Med Chem, 62 (4): 1761-1780. [PMID:30707578]
38. Hiller JM, Fan LQ, Simon EJ. (1996) Autoradiographic comparison of [3H]DPDPE and [3H]DSLET binding: evidence for distinct delta 1 and delta 2 opioid receptor populations in rat brain. Brain Res, 719 (1-2): 85-95. [PMID:8782867]
39. Hughes J, Kosterlitz HW, Leslie FM. (1975) Effect of morphine on adrenergic transmission in the mouse vas deferens. Assessment of agonist and antogonist potencies of narcotic analgesics. Br J Pharmacol, 53 (3): 371-81. [PMID:236796]
40. Inagaki M, Kume M, Tamura Y, Hara S, Goto Y, Haga N, Hasegawa T, Nakamura T, Koike K, Oonishi S et al.. (2019) Discovery of naldemedine: A potent and orally available opioid receptor antagonist for treatment of opioid-induced adverse effects. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 29 (1): 73-77. [PMID:30446313]
41. Jongkamonwiwat N, Phansuwan-Pujito P, Sarapoke P, Chetsawang B, Casalotti SO, Forge A, Dodson H, Govitrapong P. (2003) The presence of opioid receptors in rat inner ear. Hear Res, 181 (1-2): 85-93. [PMID:12855366]
42. Kam AY, Chan AS, Wong YH. (2003) Rac and Cdc42-dependent regulation of c-Jun N-terminal kinases by the delta-opioid receptor. J Neurochem, 84 (3): 503-13. [PMID:12558970]
43. Khroyan TV, Polgar WE, Cami-Kobeci G, Husbands SM, Zaveri NT, Toll L. (2011) The first universal opioid ligand, (2S)-2-[(5R,6R,7R,14S)-N-cyclopropylmethyl-4,5-epoxy-6,14-ethano-3-hydroxy-6-methoxymorphinan-7-yl]-3,3-dimethylpentan-2-ol (BU08028): characterization of the in vitro profile and in vivo behavioral effects in mouse models of acute pain and cocaine-induced reward. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 336 (3): 952-61. [PMID:21177476]
44. Kieffer BL, Befort K, Gaveriaux-Ruff C, Hirth CG. (1992) Delta-opioid receptor: isolation of a cDNA by expression cloning and pharmacological characerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 89: 12048-12052. [PMID:1334555]
45. Kitchen I, Slowe SJ, Matthes HW, Kieffer B. (1997) Quantitative autoradiographic mapping of mu-, delta- and kappa-opioid receptors in knockout mice lacking the mu-opioid receptor gene. Brain Res, 778 (1): 73-88. [PMID:9462879]
46. Knapp RJ, Malatynska E, Fang L, Li X, Babin E, Nguyen M, Santoro G, Varga EV, Hruby VJ, Roeske WR et al.. (1994) Identification of a human delta opioid receptor: cloning and expression. Life Sci, 54 (25): PL463-9. [PMID:8201839]
47. Law PY, Hom DS, Loh HH. (1985) Multiple affinity states of opiate receptor in neuroblastoma x glioma NG108-15 hybrid cells. Opiate agonist association rate is a function of receptor occupancy. J Biol Chem, 260 (6): 3561-9. [PMID:2982865]
48. Law PY, Wong YH, Loh HH. (2000) Molecular mechanisms and regulation of opioid receptor signaling. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol, 40: 389-430. [PMID:10836142]
49. Le Bourdonnec B, Barker WM, Belanger S, Wiant DD, Conway-James NC, Cassel JA, O'Neill TJ, Little PJ, DeHaven RN, DeHaven-Hudkins DL et al.. (2008) Novel trans-3,4-dimethyl-4-(3-hydroxyphenyl)piperidines as mu opioid receptor antagonists with improved opioid receptor selectivity profiles. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 18 (6): 2006-12. [PMID:18313920]
50. Le Bourdonnec B, Windh RT, Ajello CW, Leister LK, Gu M, Chu GH, Tuthill PA, Barker WM, Koblish M, Wiant DD et al.. (2008) Potent, orally bioavailable delta opioid receptor agonists for the treatment of pain: discovery of N,N-diethyl-4-(5-hydroxyspiro[chromene-2,4'-piperidine]-4-yl)benzamide (ADL5859). J Med Chem, 51 (19): 5893-6. [PMID:18788723]
51. Le Bourdonnec B, Windh RT, Leister LK, Zhou QJ, Ajello CW, Gu M, Chu GH, Tuthill PA, Barker WM, Koblish M et al.. (2009) Spirocyclic delta opioid receptor agonists for the treatment of pain: discovery of N,N-diethyl-3-hydroxy-4-(spiro[chromene-2,4'-piperidine]-4-yl) benzamide (ADL5747). J Med Chem, 52 (18): 5685-702. [PMID:19694468]
52. Le Merrer J, Plaza-Zabala A, Del Boca C, Matifas A, Maldonado R, Kieffer BL. (2011) Deletion of the δ opioid receptor gene impairs place conditioning but preserves morphine reinforcement. Biol Psychiatry, 69 (7): 700-3. [PMID:21168121]
53. Le Merrer J, Rezai X, Scherrer G, Becker JA, Kieffer BL. (2013) Impaired hippocampus-dependent and facilitated striatum-dependent behaviors in mice lacking the δ opioid receptor. Neuropsychopharmacology, 38 (6): 1050-9. [PMID:23303070]
54. Lei W, Vekariya RH, Ananthan S, Streicher JM. (2020) A Novel Mu-Delta Opioid Agonist Demonstrates Enhanced Efficacy With Reduced Tolerance and Dependence in Mouse Neuropathic Pain Models. J Pain, 21 (1-2): 146-160. [PMID:31201990]
55. Linz K, Christoph T, Tzschentke TM, Koch T, Schiene K, Gautrois M, Schröder W, Kögel BY, Beier H, Englberger W et al.. (2014) Cebranopadol: a novel potent analgesic nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide and opioid receptor agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 349 (3): 535-48. [PMID:24713140]
56. Liu JG, Prather PL. (2002) Chronic agonist treatment converts antagonists into inverse agonists at delta-opioid receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 302 (3): 1070-9. [PMID:12183665]
57. Lo RK, Wong YH. (2004) Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation by the delta-opioid receptor via Galpha14 involves multiple intermediates. Mol Pharmacol, 65 (6): 1427-39. [PMID:15155836]
58. Lupica CR. (1995) Delta and mu enkephalins inhibit spontaneous GABA-mediated IPSCs via a cyclic AMP-independent mechanism in the rat hippocampus. J Neurosci, 15 (1 Pt 2): 737-49. [PMID:7823176]
59. Mansour A, Fox CA, Akil H, Watson SJ. (1995) Opioid-receptor mRNA expression in the rat CNS: anatomical and functional implications. Trends Neurosci, 18: 22-29. [PMID:7535487]
60. Mansour A, Thompson RC, Akil H, Watson SJ. (1993) Delta opioid receptor mRNA distribution in the brain: comparison to delta receptor binding and proenkephalin mRNA. J Chem Neuroanat, 6: 351-362. [PMID:8142072]
61. Marie N, Landemore G, Debout C, Jauzac P, Allouche S. (2003) Pharmacological characterization of AR-M1000390 at human delta opioid receptors. Life Sci, 73 (13): 1691-704. [PMID:12875901]
62. Martin M, Matifas A, Maldonado R, Kieffer BL. (2003) Acute antinociceptive responses in single and combinatorial opioid receptor knockout mice: distinct mu, delta and kappa tones. Eur J Neurosci, 17 (4): 701-8. [PMID:12603260]
63. Mennicken F, Zhang J, Hoffert C, Ahmad S, Beaudet A, O'Donnell D. (2003) Phylogenetic changes in the expression of delta opioid receptors in spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia. J Comp Neurol, 465 (3): 349-60. [PMID:12966560]
64. Miyazaki T, Choi IY, Rubas W, Anand NK, Ali C, Evans J, Gursahani H, Hennessy M, Kim G, McWeeney D et al.. (2017) NKTR-181: A Novel Mu-Opioid Analgesic with Inherently Low Abuse Potential. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 363 (1): 104-113. [PMID:28778859]
65. Mosberg HI, Hurst R, Hruby VJ, Gee K, Yamamura HI, Galligan JJ, Burks TF. (1983) Bis-penicillamine enkephalins possess highly improved specificity toward delta opioid receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 80 (19): 5871-4. [PMID:6310598]
66. MRC. AZD7268 δ‐Opioid receptor agonist. Accessed on 28/10/2014. Modified on 28/10/2014. MRC/AstraZeneca: Mechanisms of Disease Call, http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20120104105854/http://www.mrc.ac.uk/consumption/groups/public/documents/content/mrc008373.pdf
67. Neilan CL, Akil H, Woods JH, Traynor JR. (1999) Constitutive activity of the delta-opioid receptor expressed in C6 glioma cells: identification of non-peptide delta-inverse agonists. Br J Pharmacol, 128 (3): 556-62. [PMID:10516632]
68. Neumeyer JL, Zhang B, Zhang T, Sromek AW, Knapp BI, Cohen DJ, Bidlack JM. (2012) Synthesis, binding affinity, and functional in vitro activity of 3-benzylaminomorphinan and 3-benzylaminomorphine ligands at opioid receptors. J Med Chem, 55 (8): 3878-90. [PMID:22439881]
69. Pan YZ, Li DP, Chen SR, Pan HL. (2002) Activation of delta-opioid receptors excites spinally projecting locus coeruleus neurons through inhibition of GABAergic inputs. J Neurophysiol, 88 (5): 2675-83. [PMID:12424303]
70. Patkar KA, Yan X, Murray TF, Aldrich JV. (2005) [Nalpha-benzylTyr1,cyclo(D-Asp5,Dap8)]- dynorphin A-(1-11)NH2 cyclized in the "address" domain is a novel kappa-opioid receptor antagonist. J Med Chem, 48 (14): 4500-3. [PMID:15999987]
71. Payza K. (2003) Binding and activity of opioid ligands at the cloned human delta, mu and kappa receptors. In The Delta Receptor. Edited by Chang KJ (CRC Press) 261-275. [ISBN:0824740319]
72. Peckys D, Landwehrmeyer GB. (1999) Expression of mu, kappa, and delta opioid receptor messenger RNA in the human CNS: a 33P in situ hybridization study. Neuroscience, 88 (4): 1093-135. [PMID:10336124]
73. Pol O, Palacio JR, Puig MM. (2003) The expression of delta- and kappa-opioid receptor is enhanced during intestinal inflammation in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 306 (2): 455-62. [PMID:12724348]
74. Poole DP, Pelayo JC, Scherrer G, Evans CJ, Kieffer BL, Bunnett NW. (2011) Localization and regulation of fluorescently labeled delta opioid receptor, expressed in enteric neurons of mice. Gastroenterology, 141 (3): 982-991.e1-8. [PMID:21699782]
75. Portoghese PS, Sultana M, Takemori AE. (1988) Naltrindole, a highly selective and potent non-peptide delta opioid receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol, 146 (1): 185-6. [PMID:2832195]
76. Poulain R, Horvath D, Bonnet B, Eckhoff C, Chapelain B, Bodinier MC, Déprez B. (2001) From hit to lead. Combining two complementary methods for focused library design. Application to mu opiate ligands. J Med Chem, 44 (21): 3378-90. [PMID:11585443]
77. Prchalová E, Hin N, Thomas AG, Veeravalli V, Ng J, Alt J, Rais R, Rojas C, Li Z, Hihara H et al.. (2019) Discovery of Benzamidine- and 1-Aminoisoquinoline-Based Human MAS-Related G-Protein-Coupled Receptor X1 (MRGPRX1) Agonists. J Med Chem, 62 (18): 8631-8641. [PMID:31498617]
78. Quock RM, Hosohata Y, Knapp RJ, Burkey TH, Hosohata K, Zhang X, Rice KC, Nagase H, Hruby VJ, Porreca F et al.. (1997) Relative efficacies of delta-opioid receptor agonists at the cloned human delta-opioid receptor. Eur J Pharmacol, 326 (1): 101-4. [PMID:9178661]
79. Raynor K, Kong H, Chen Y, Yasuda K, Yu L, Bell GI, Reisine T. (1994) Pharmacological characterization of the cloned kappa-, delta-, and mu-opioid receptors. Mol Pharmacol, 45 (2): 330-4. [PMID:8114680]
80. Rios CD, Jordan BA, Gomes I, Devi LA. (2001) G-protein-coupled receptor dimerization: modulation of receptor function. Pharmacol Ther, 92 (2-3): 71-87. [PMID:11916530]
81. Rorick-Kehn LM, Witkin JM, Statnick MA, Eberle EL, McKinzie JH, Kahl SD, Forster BM, Wong CJ, Li X, Crile RS et al.. (2014) LY2456302 is a novel, potent, orally-bioavailable small molecule kappa-selective antagonist with activity in animal models predictive of efficacy in mood and addictive disorders. Neuropharmacology, 77: 131-44. [PMID:24071566]
82. Salemi S, Aeschlimann A, Reisch N, Jüngel A, Gay RE, Heppner FL, Michel BA, Gay S, Sprott H. (2005) Detection of kappa and delta opioid receptors in skin--outside the nervous system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 338 (2): 1012-7. [PMID:16263089]
83. Scherrer G, Befort K, Contet C, Becker J, Matifas A, Kieffer BL. (2004) The delta agonists DPDPE and deltorphin II recruit predominantly mu receptors to produce thermal analgesia: a parallel study of mu, delta and combinatorial opioid receptor knockout mice. Eur J Neurosci, 19 (8): 2239-48. [PMID:15090050]
84. Scherrer G, Tryoen-Tóth P, Filliol D, Matifas A, Laustriat D, Cao YQ, Basbaum AI, Dierich A, Vonesh JL, Gavériaux-Ruff C et al.. (2006) Knockin mice expressing fluorescent delta-opioid receptors uncover G protein-coupled receptor dynamics in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 103 (25): 9691-6. [PMID:16766653]
85. Schiller PW, Weltrowska G, Nguyen TM, Wilkes BC, Chung NN, Lemieux C. (1993) TIPP[psi]: a highly potent and stable pseudopeptide delta opioid receptor antagonist with extraordinary delta selectivity. J Med Chem, 36 (21): 3182-7. [PMID:8230106]
86. Schulz R, Eisinger DA, Wehmeyer A. (2004) Opioid control of MAP kinase cascade. Eur J Pharmacol, 500 (1-3): 487-97. [PMID:15464054]
87. Sharma SK, Klee WA, Nirenberg M. (1977) Opiate-dependent modulation of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 74 (8): 3365-9. [PMID:269396]
88. Simonin F, Befort K, Gavériaux-Ruff C, Matthes H, Nappey V, Lannes B, Micheletti G, Kieffer B. (1994) The human delta-opioid receptor: genomic organization, cDNA cloning, functional expression, and distribution in human brain. Mol Pharmacol, 46 (6): 1015-21. [PMID:7808419]
89. Smith CF, Waldron C, Brook NA. (1988) Opioid receptors in the mouse ileum. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther, 291: 122-31. [PMID:2835021]
90. Sofuoglu M, Portoghese PS, Takemori AE. (1991) Differential antagonism of delta opioid agonists by naltrindole and its benzofuran analog (NTB) in mice: evidence for delta opioid receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 257 (2): 676-80. [PMID:1851833]
91. Stefano GB, Melchiorri P, Negri L, Hughes TK, Scharrer B. (1992) [D-Ala2]deltorphin I binding and pharmacological evidence for a special subtype of delta opioid receptor on human and invertebrate immune cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 89 (19): 9316-20. [PMID:1329092]
92. Szekeres PG, Traynor JR. (1997) Delta opioid modulation of the binding of guanosine-5'-O-(3-[35S]thio)triphosphate to NG108-15 cell membranes: characterization of agonist and inverse agonist effects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 283 (3): 1276-84. [PMID:9400003]
93. Toll L, Berzetei-Gurske IP, Polgar WE, Brandt SR, Adapa ID, Rodriguez L, Schwartz RW, Haggart D, O'Brien A, White A et al.. (1998) Standard binding and functional assays related to medications development division testing for potential cocaine and opiate narcotic treatment medications. NIDA Res Monogr, 178: 440-66. [PMID:9686407]
94. Varga BR, Bernhard SM, El Daibani A, Zaidi SA, Lam JH, Aguilar J, Appourchaux K, Nazarova AL, Kouvelis A, Shinouchi R et al.. (2025) Structure-guided design of partial agonists at an opioid receptor. Nat Commun, 16 (1): 2518. [PMID:40082451]
95. Varty GB, Lu SX, Morgan CA, Cohen-Williams ME, Hodgson RA, Smith-Torhan A, Zhang H, Fawzi AB, Graziano MP, Ho GD et al.. (2008) The anxiolytic-like effects of the novel, orally active nociceptin opioid receptor agonist 8-[bis(2-methylphenyl)methyl]-3-phenyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-ol (SCH 221510). J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 326 (2): 672-82. [PMID:18492950]
96. Vergura R, Balboni G, Spagnolo B, Gavioli E, Lambert DG, McDonald J, Trapella C, Lazarus LH, Regoli D, Guerrini R et al.. (2008) Anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like activities of H-Dmt-Tic-NH-CH(CH2-COOH)-Bid (UFP-512), a novel selective delta opioid receptor agonist. Peptides, 29 (1): 93-103. [PMID:18069089]
97. Vu LY, Luo D, Johnson K, Denehy ED, Songrady JC, Martin J, Trivedi R, Alsum AR, Shaykin JD, Chaudhary CL et al.. (2024) Searching for Synthetic Opioid Rescue Agents: Identification of a Potent Opioid Agonist with Reduced Respiratory Depression. J Med Chem, 67 (11): 9173-9193. [PMID:38810170]
98. Wentland MP, Lou R, Lu Q, Bu Y, Denhardt C, Jin J, Ganorkar R, VanAlstine MA, Guo C, Cohen DJ et al.. (2009) Syntheses of novel high affinity ligands for opioid receptors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 19 (8): 2289-94. [PMID:19282177]
99. Wentland MP, Lou R, Lu Q, Bu Y, VanAlstine MA, Cohen DJ, Bidlack JM. (2009) Syntheses and opioid receptor binding properties of carboxamido-substituted opioids. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 19 (1): 203-8. [PMID:19027293]
100. Wentland MP, Lu Q, Lou R, Bu Y, Knapp BI, Bidlack JM. (2005) Synthesis and opioid receptor binding properties of a highly potent 4-hydroxy analogue of naltrexone. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 15 (8): 2107-10. [PMID:15808478]
101. Xie Z, Bhushan RG, Daniels DJ, Portoghese PS. (2005) Interaction of bivalent ligand KDN21 with heterodimeric delta-kappa opioid receptors in human embryonic kidney 293 cells. Mol Pharmacol, 68: 1079-1086. [PMID:16006595]
102. Yaksh TL, Noueihed R. (1985) The physiology and pharmacology of spinal opiates. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol, 25: 433-62. [PMID:2988422]
103. Yamamura MS, Horvath R, Toth G, Otvos F, Malatynska E, Knapp RJ, Porreca F, Hruby VJ, Yamamura HI. (1992) Characterization of [3H]naltrindole binding to delta opioid receptors in rat brain. Life Sci, 50 (16): PL119-24. [PMID:1313133]
104. Yasuda K, Raynor K, Kong H, Breder CD, Takeda J, Reisine T, Bell GI. (1993) Cloning and functional comparison of kappa and delta opioid receptors from mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 90 (14): 6736-40. [PMID:8393575]
105. Zaki PA, Bilsky EJ, Vanderah TW, Lai J, Evans CJ, Porreca F. (1996) Opioid receptor types and subtypes: the delta receptor as a model. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol, 36: 379-401. [PMID:8725395]
106. Zaveri N. (2003) Peptide and nonpeptide ligands for the nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor ORL1: research tools and potential therapeutic agents. Life Sci, 73: 663-678. [PMID:12801588]
107. Zheng Y, Obeng S, Wang H, Jali AM, Peddibhotla B, Williams DA, Zou C, Stevens DL, Dewey WL, Akbarali HI et al.. (2019) Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of the Third Generation 17-Cyclopropylmethyl-3,14β-dihydroxy-4,5α-epoxy-6β-[(4'-pyridyl)carboxamido]morphinan (NAP) Derivatives as μ/κ Opioid Receptor Dual Selective Ligands. J Med Chem, 62 (2): 561-574. [PMID:30608693]
108. Zhu Y, Hsu MS, Pintar JE. (1998) Developmental expression of the mu, kappa, and delta opioid receptor mRNAs in mouse. J Neurosci, 18 (7): 2538-49. [PMID:9502813]
109. Zhu Y, King MA, Schuller AG, Nitsche JF, Reidl M, Elde RP, Unterwald E, Pasternak GW, Pintar JE. (1999) Retention of supraspinal delta-like analgesia and loss of morphine tolerance in delta opioid receptor knockout mice. Neuron, 24: 243-252. [PMID:10677041]
110. Zhu Y, Pintar JE. (1998) Expression of opioid receptors and ligands in pregnant mouse uterus and placenta. Biol Reprod, 59 (4): 925-32. [PMID:9746745]