
Top ▲

GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| class B G protein-coupled receptor | ||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 7 | 463 | 6p21.2 | GLP1R | glucagon like peptide 1 receptor | 38,46 |
| Mouse | 7 | 463 | 17 15.8 cM | Glp1r | glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor | |
| Rat | 7 | 463 | 20p12 | Glp1r | glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor | 21,39 |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| GLP-1R | glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor |
Database Links  |
|
| Specialist databases | |
| GPCRdb | glp1r_human (Hs), glp1r_mouse (Mm), glp1r_rat (Rn) |
| Other databases | |
| Alphafold | P43220 (Hs), O35659 (Mm), P32301 (Rn) |
| CATH/Gene3D | 4.10.1240.10 |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL1784 (Hs), CHEMBL1075290 (Mm), CHEMBL5862 (Rn) |
| DrugBank Target | P43220 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000112164 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000024027 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000001152 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 2740 (Hs), 14652 (Mm), 25051 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000112164 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:2740 (Hs), mmu:14652 (Mm), rno:25051 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 138032 (Hs) |
| Pharos | P43220 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_002062 (Hs), NM_021332 (Mm), NM_012728 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_002053 (Hs), NP_067307 (Mm), NP_036860 (Rn) |
| SynPHARM |
84391 (in complex with Peptide 5 [PMID: 28562585]) 84392 (in complex with Peptide 5 [PMID: 28562585]) |
| UniProtKB | P43220 (Hs), O35659 (Mm), P32301 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | GLP1R (Hs) |
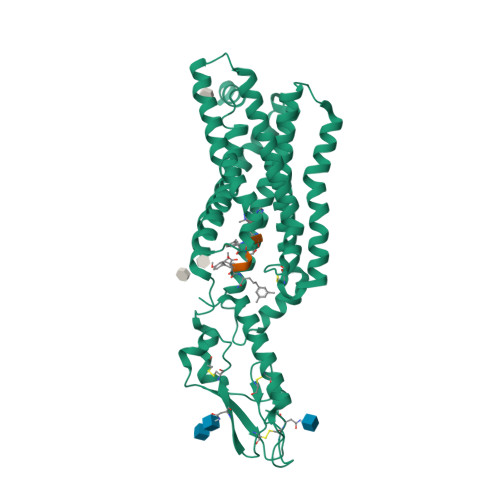
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
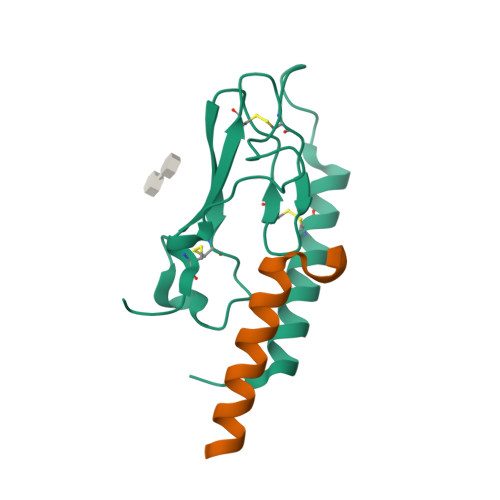
|
|
||||||||||||
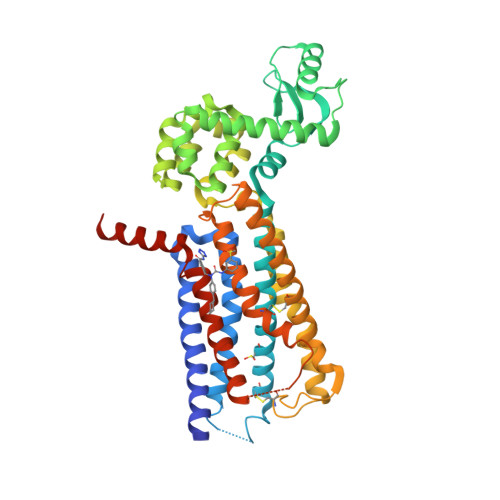
|
|
||||||||||||
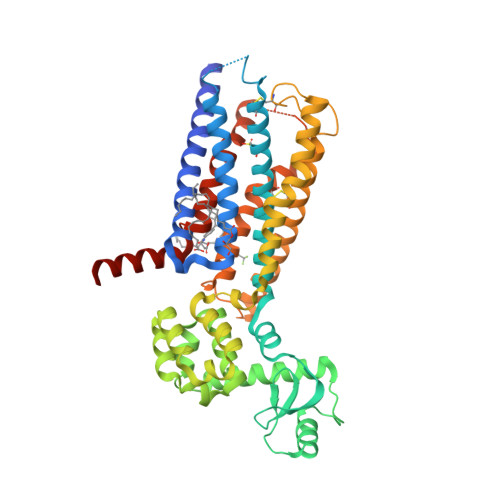
|
|
||||||||||||
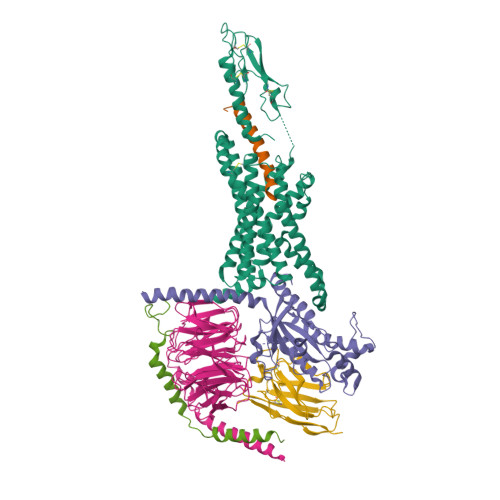
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| glucagon {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| glucagon-like peptide 1-(7-37) {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
| glucagon-like peptide 1-(7-36) amide {Sp: Human, Mouse, Rat} |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific agonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The affinities for exendin-4 and its synthetic analogue exenatide are assumed to be interchangeable. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific antagonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allosteric Modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Primary Transduction Mechanisms 
|
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gs family | Adenylyl cyclase stimulation |
| References: 36 | |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Expression Datasets  |
|
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Biologically Significant Variants 
|
||||||||||
|
| General Comments |
| Several GLP-1 receptor agonists have now been approved for clinical use to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus, including exenatide, liraglutide, albiglutide and lixisenatide. |
1. Baggio LL, Huang Q, Brown TJ, Drucker DJ. (2004) A recombinant human glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1-albumin protein (albugon) mimics peptidergic activation of GLP-1 receptor-dependent pathways coupled with satiety, gastrointestinal motility, and glucose homeostasis. Diabetes, 53 (9): 2492-500. [PMID:15331566]
2. Beak SA, Small CJ, Ilovaiskaia I, Hurley JD, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR, Smith DM. (1996) Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) releases thyrotropin (TSH): characterization of binding sites for GLP-1 on alpha-TSH cells. Endocrinology, 137 (10): 4130-8. [PMID:8828468]
3. Beinborn M, Worrall CI, McBride EW, Kopin AS. (2005) A human glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor polymorphism results in reduced agonist responsiveness. Regul Pept, 130 (1-2): 1-6. [PMID:15975668]
4. Bullock BP, Heller RS, Habener JF. (1996) Tissue distribution of messenger ribonucleic acid encoding the rat glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor. Endocrinology, 137 (7): 2968-78. [PMID:8770921]
5. Coskun T, Sloop KW, Loghin C, Alsina-Fernandez J, Urva S, Bokvist KB, Cui X, Briere DA, Cabrera O, Roell WC et al.. (2018) LY3298176, a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: From discovery to clinical proof of concept. Mol Metab, 18: 3-14. [PMID:30473097]
6. Coskun T, Urva S, Roell WC, Qu H, Loghin C, Moyers JS, O'Farrell LS, Briere DA, Sloop KW, Thomas MK et al.. (2022) LY3437943, a novel triple glucagon, GIP, and GLP-1 receptor agonist for glycemic control and weight loss: From discovery to clinical proof of concept. Cell Metab, 34 (9): 1234-1247.e9. [PMID:35985340]
7. Dillon JS, Tanizawa Y, Wheeler MB, Leng XH, Ligon BB, Rabin DU, Yoo-Warren H, Permutt MA, Boyd AE. (1993) Cloning and functional expression of the human glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor. Endocrinology, 133 (4): 1907-10. [PMID:8404634]
8. Dong G, Ye Q, Li W, Zhang S, Yang Z, Zhang R, Deng T, Li H, Zhang Y, Zhang X et al.. (2025) Discovery and Evaluation of DA-302168S as an Efficacious Oral Small-Molecule Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist. J Med Chem, [Epub ahead of print]. [PMID:40257122]
9. Drucker DJ, Philippe J, Mojsov S, Chick WL, Habener JF. (1987) Glucagon-like peptide I stimulates insulin gene expression and increases cyclic AMP levels in a rat islet cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 84 (10): 3434-8. [PMID:3033647]
10. During MJ, Cao L, Zuzga DS, Francis JS, Fitzsimons HL, Jiao X, Bland RJ, Klugmann M, Banks WA, Drucker DJ et al.. (2003) Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor is involved in learning and neuroprotection. Nat Med, 9 (9): 1173-9. [PMID:12925848]
11. Fan H, Gong N, Li TF, Ma AN, Wu XY, Wang MW, Wang YX. (2015) The non-peptide GLP-1 receptor agonist WB4-24 blocks inflammatory nociception by stimulating β-endorphin release from spinal microglia. Br J Pharmacol, 172 (1): 64-79. [PMID:25176008]
12. Fehmann HC, Habener JF. (1992) Insulinotropic hormone glucagon-like peptide-I(7-37) stimulation of proinsulin gene expression and proinsulin biosynthesis in insulinoma beta TC-1 cells. Endocrinology, 130 (1): 159-66. [PMID:1309325]
13. Griffith DA, Edmonds DJ, Fortin JP, Kalgutkar AS, Kuzmiski JB, Loria PM, Saxena AR, Bagley SW, Buckeridge C, Curto JM et al.. (2022) A Small-Molecule Oral Agonist of the Human Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor. J Med Chem, 65 (12): 8208-8226. [PMID:35647711]
14. Gromada J, Rorsman P, Dissing S, Wulff BS. (1995) Stimulation of cloned human glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor expressed in HEK 293 cells induces cAMP-dependent activation of calcium-induced calcium release. FEBS Lett, 373 (2): 182-6. [PMID:7589461]
15. Gros R, You X, Baggio LL, Kabir MG, Sadi AM, Mungrue IN, Parker TG, Huang Q, Drucker DJ, Husain M. (2003) Cardiac function in mice lacking the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor. Endocrinology, 144 (6): 2242-52. [PMID:12746281]
16. Göke R, Fehmann HC, Linn T, Schmidt H, Krause M, Eng J, Göke B. (1993) Exendin-4 is a high potency agonist and truncated exendin-(9-39)-amide an antagonist at the glucagon-like peptide 1-(7-36)-amide receptor of insulin-secreting beta-cells. J Biol Chem, 268 (26): 19650-5. [PMID:8396143]
17. Jazayeri A, Rappas M, Brown AJH, Kean J, Errey JC, Robertson NJ, Fiez-Vandal C, Andrews SP, Congreve M, Bortolato A et al.. (2017) Crystal structure of the GLP-1 receptor bound to a peptide agonist. Nature, 546 (7657): 254-258. [PMID:28562585]
18. Jorgensen R, Martini L, Schwartz TW, Elling CE. (2005) Characterization of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor beta-arrestin 2 interaction: a high-affinity receptor phenotype. Mol Endocrinol, 19 (3): 812-23. [PMID:15528268]
19. Kawai T, Sun B, Yoshino H, Feng D, Suzuki Y, Fukazawa M, Nagao S, Wainscott DB, Showalter AD, Droz BA et al.. (2020) Structural basis for GLP-1 receptor activation by LY3502970, an orally active nonpeptide agonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 117 (47): 29959-29967. [PMID:33177239]
20. Knudsen LB, Nielsen PF, Huusfeldt PO, Johansen NL, Madsen K, Pedersen FZ, Thøgersen H, Wilken M, Agersø H. (2000) Potent derivatives of glucagon-like peptide-1 with pharmacokinetic properties suitable for once daily administration. J Med Chem, 43 (9): 1664-9. [PMID:10794683]
21. Lankat-Buttgereit B, Göke R, Fehmann HC, Richter G, Göke B. (1994) Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding for the GLP-1 receptor expressed in rat lung. Exp Clin Endocrinol, 102 (4): 341-7. [PMID:7813606]
22. Larsen PJ, Tang-Christensen M, Jessop DS. (1997) Central administration of glucagon-like peptide-1 activates hypothalamic neuroendocrine neurons in the rat. Endocrinology, 138 (10): 4445-55. [PMID:9322962]
23. Lau J, Bloch P, Schäffer L, Pettersson I, Spetzler J, Kofoed J, Madsen K, Knudsen LB, McGuire J, Steensgaard DB et al.. (2015) Discovery of the Once-Weekly Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Analogue Semaglutide. J Med Chem, 58 (18): 7370-80. [PMID:26308095]
24. Li B, Xi X, Roane DS, Ryan DH, Martin RJ. (2003) Distribution of glucokinase, glucose transporter GLUT2, sulfonylurea receptor-1, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor and neuropeptide Y messenger RNAs in rat brain by quantitative real time RT-PCR. Brain Res Mol Brain Res, 113 (1-2): 139-42. [PMID:12750016]
25. MacLusky NJ, Cook S, Scrocchi L, Shin J, Kim J, Vaccarino F, Asa SL, Drucker DJ. (2000) Neuroendocrine function and response to stress in mice with complete disruption of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor signaling. Endocrinology, 141 (2): 752-62. [PMID:10650957]
26. Mezo AR, Chen Y, Valenzuela FA, Qu H. (2018) Glucagon and GLP-1 co-agonist compounds. Patent number: US9938335B2. Assignee: Eli Lilly and Co. Priority date: 16/06/2016. Publication date: 10/04/2018.
27. Miao L, Lou J, Xu S, Zhang J, Zhong Y, Wang G, Li Y, Lei S, Shao S, Wang J et al.. (2025) Discovery of New Difluorocyclobutyl Derivatives as Effective Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists with Reduced hERG Inhibitory Activities. J Med Chem, [Epub ahead of print]. [PMID:40167442]
28. Miranda LP, Winters KA, Gegg CV, Patel A, Aral J, Long J, Zhang J, Diamond S, Guido M, Stanislaus S et al.. (2008) Design and synthesis of conformationally constrained glucagon-like peptide-1 derivatives with increased plasma stability and prolonged in vivo activity. J Med Chem, 51 (9): 2758-65. [PMID:18412318]
29. Montrose-Rafizadeh C, Yang H, Rodgers BD, Beday A, Pritchette LA, Eng J. (1997) High potency antagonists of the pancreatic glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor. J Biol Chem, 272 (34): 21201-6. [PMID:9261127]
30. Nolte WM, Fortin JP, Stevens BD, Aspnes GE, Griffith DA, Hoth LR, Ruggeri RB, Mathiowetz AM, Limberakis C, Hepworth D et al.. (2014) A potentiator of orthosteric ligand activity at GLP-1R acts via covalent modification. Nat Chem Biol, 10 (8): 629-31. [PMID:24997604]
31. Nyström T, Gonon AT, Sjöholm A, Pernow J. (2005) Glucagon-like peptide-1 relaxes rat conduit arteries via an endothelium-independent mechanism. Regul Pept, 125 (1-3): 173-7. [PMID:15582729]
32. Raufman JP, Singh L, Eng J. (1991) Exendin-3, a novel peptide from Heloderma horridum venom, interacts with vasoactive intestinal peptide receptors and a newly described receptor on dispersed acini from guinea pig pancreas. Description of exendin-3(9-39) amide, a specific exendin receptor antagonist. J Biol Chem, 266 (5): 2897-902. [PMID:1704369]
33. Runge S, Thøgersen H, Madsen K, Lau J, Rudolph R. (2008) Crystal structure of the ligand-bound glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor extracellular domain. J Biol Chem, 283 (17): 11340-7. [PMID:18287102]
34. Sebokova E, Christ AD, Wang H, Sewing S, Dong JZ, Taylor J, Cawthorne MA, Culler MD. (2010) Taspoglutide, an analog of human glucagon-like Peptide-1 with enhanced stability and in vivo potency. Endocrinology, 151 (6): 2474-82. [PMID:20382695]
35. Shughrue PJ, Lane MV, Merchenthaler I. (1996) Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP1-R) mRNA in the rat hypothalamus. Endocrinology, 137 (11): 5159-62. [PMID:8895391]
36. Skoglund G, Hussain MA, Holz GG. (2000) Glucagon-like peptide 1 stimulates insulin gene promoter activity by protein kinase A-independent activation of the rat insulin I gene cAMP response element. Diabetes, 49: 1156-1164. [PMID:10909973]
37. Song G, Yang D, Wang Y, de Graaf C, Zhou Q, Jiang S, Liu K, Cai X, Dai A, Lin G et al.. (2017) Human GLP-1 receptor transmembrane domain structure in complex with allosteric modulators. Nature, 546 (7657): 312-315. [PMID:28514449]
38. Stoffel M, Espinosa 3rd R, Le Beau MM, Bell GI. (1993) Human glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor gene. Localization to chromosome band 6p21 by fluorescence in situ hybridization and linkage of a highly polymorphic simple tandem repeat DNA polymorphism to other markers on chromosome 6. Diabetes, 42 (8): 1215-8. [PMID:8392011]
39. Thorens B. (1992) Expression cloning of the pancreatic beta cell receptor for the gluco-incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 89 (18): 8641-5. [PMID:1326760]
40. Tibaduiza EC, Chen C, Beinborn M. (2001) A small molecule ligand of the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor targets its amino-terminal hormone binding domain. J Biol Chem, 276 (41): 37787-93. [PMID:11498540]
41. Tseng CC, Zhang XY, Wolfe MM. (1999) Effect of GIP and GLP-1 antagonists on insulin release in the rat. Am J Physiol, 276 (6): E1049-54. [PMID:10362617]
42. Uttenthal LO, Blázquez E. (1990) Characterization of high-affinity receptors for truncated glucagon-like peptide-1 in rat gastric glands. FEBS Lett, 262 (1): 139-41. [PMID:2156728]
43. Véniant MM, Lu SC, Atangan L, Komorowski R, Stanislaus S, Cheng Y, Wu B, Falsey JR, Hager T, Thomas VA et al.. (2024) A GIPR antagonist conjugated to GLP-1 analogues promotes weight loss with improved metabolic parameters in preclinical and phase 1 settings. Nat Metab, 6 (2): 290-303. [PMID:38316982]
44. Wei Y, Mojsov S. (1995) Tissue-specific expression of the human receptor for glucagon-like peptide-I: brain, heart and pancreatic forms have the same deduced amino acid sequences. FEBS Lett, 358 (3): 219-24. [PMID:7843404]
45. Werner U, Haschke G, Herling AW, Kramer W. (2010) Pharmacological profile of lixisenatide: A new GLP-1 receptor agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Regul Pept, 164 (2-3): 58-64. [PMID:20570597]
46. Wheeler MB, Lu M, Dillon JS, Leng XH, Chen C, Boyd 3rd AE. (1993) Functional expression of the rat glucagon-like peptide-I receptor, evidence for coupling to both adenylyl cyclase and phospholipase-C. Endocrinology, 133 (1): 57-62. [PMID:8391428]
47. Willard FS, Wainscott DB, Showalter AD, Stutsman C, Ma W, Cardona GR, Zink RW, Corkins CM, Chen Q, Yumibe N et al.. (2021) Discovery of an Orally Efficacious Positive Allosteric Modulator of the Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor. J Med Chem, 64 (6): 3439-3448. [PMID:33721487]
48. Zimmermann T, Thomas L, Baader-Pagler T, Haebel P, Simon E, Reindl W, Bajrami B, Rist W, Uphues I, Drucker DJ et al.. (2022) BI 456906: Discovery and preclinical pharmacology of a novel GCGR/GLP-1R dual agonist with robust anti-obesity efficacy. Mol Metab, 66: 101633. [PMID:36356832]