
Top ▲

GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Gene and Protein Information  |
|||||||
| Species | TM | P Loops | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 6 | 1 | 1214 | 19q13.33 | TRPM4 | transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 4 | 18,27-28,53 |
| Mouse | 6 | 1 | 1213 | 7 B3 | Trpm4 | transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 4 | 27 |
| Rat | 6 | 1 | 1208 | 1q22 | Trpm4 | transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 4 | 11 |
Database Links  |
|
| Alphafold | Q8TD43 (Hs), Q7TN37 (Mm), Q9ESQ5 (Rn) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL1628469 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000130529 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000038260 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000020714 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 54795 (Hs), 68667 (Mm), 171143 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000130529 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:54795 (Hs), mmu:68667 (Mm), rno:171143 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 606936 (Hs) |
| Orphanet | ORPHA209301 (Hs) |
| Pharos | Q8TD43 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_017636 (Hs), NM_175130 (Mm), NM_001136229 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_060106 (Hs), NP_780339 (Mm), NP_001129701 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | Q8TD43 (Hs), Q7TN37 (Mm), Q9ESQ5 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | TRPM4 (Hs) |
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
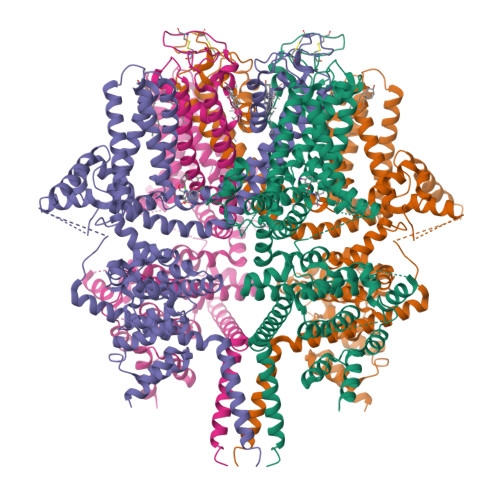
|
|
||||||||||||
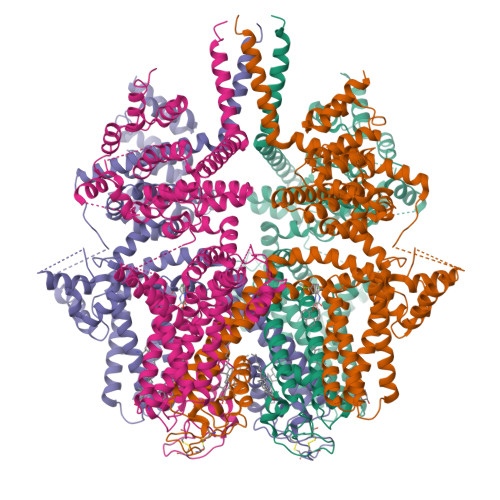
|
|
||||||||||||
Associated Proteins  |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Associated Protein Comments | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Results from Sala-Rabanal et al (2012) contradict the postulation that SUR1 modulates TRPM4, by finding no evidence of functional or structural association between TRPM4 and SUR1 [37]. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Ion Selectivity and Conductance  |
||||||
|
||||||
| Ion Selectivity and Conductance Comments | ||||||
| Ca2+ impermeable. |
Voltage Dependence  |
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Voltage Dependence Comments | ||||||||||||||||
| Range of voltage activation depends on intracellular Ca2+ concentration, PIP2, PKC phosphorylation, presence of calmodulin [25,27,30,32-33]. |
| Other channel blockers |
| Intracellular nucleotides including ATP, ADP, adenosine 5'-monophosphate and AMP-PNP with an IC50 range of 1.3-1.9 μM |
| Physical activators (Human) |
| Membrane depolarization (V½ = -20 mV to + 60 mV dependent upon conditions) in the presence of elevated [Ca2+]i, heat (Q10 = 8.5 @ +25 mV between 15 and 25°C) |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Activators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific activator tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Activator Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ca2+ affinity is regulated by PIP2, phosphorylation by PKC. Decreased Ca2+ affinity during desensitisation, strong desensitisation in inside-out patches [25,27,30,32-33]. U73122 prevents TRPM4 desensitisation and rescues activity [25]. Potentiation by BTP2 is increased at positive holding potentials [45]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gating inhibitors 
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific gating inhibitor tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gating Inhibitor Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| We have included the TRPM4 inhibitors compound 5 and compound 6 (both from Ozhathil et al., 2018 [35]) as gating inhibitors as they are anthranilic amide derivatives of the gating inhibitor flufenamic acid. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Channel Blockers | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific channel blocker tables | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Channel Blocker Comments | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pore mutation Asp984 -> Ala results in a non-functional channel with a dominant negative phenotype; block by spermine is reduced by pore mutation Glu981 -> Ala [28]. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immunopharmacology Comments |
| TRPM4 is expressed on human T cells, mouse dendritic cells, human and mouse monocytes/macrophages, and mouse mast cells [36]. It is activated by antigen receptor-mediated Ca2+ mobilization (influx) [18]. Inhibition of TRPM4 function (genetic or pharmacological) in mouse experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) reduced clinical symptoms and slowed disease progression [3], indicating the neuroprotective potential of TRPM4 inhibitors. |
| Cell Type Associations | ||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology 
|
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology Comments | ||||||||||||
| TRPM4 has been implicated to play a role in hyper-responsiveness in immune cells, induction of pro-inflammatory conditions, allergy, defective surfactant secretion in pneumocytes, defective Bayliss effect, trigger for paroxysmal depolarisation shift, spreading depression-like hypoxic depolarisation, stroke, and cardiac conductance disturbances including cardiac hypertrophy and arrythmia; atrioventricular block or right bundle branch block [13-14,18,26,39,42-43]. | ||||||||||||
Gene Expression and Pathophysiology 
|
||||||||||||
|
| General Comments |
|
Human: long splice-variant TRPM4b (1214 AA), short splice-variant TRPM4a (1040 AA, lacks first 174 AA), shortest splice variant TRPM4c (537 AA, lacks N-terminal) [27]. Mouse: two short splice variants from brain [23]. |
1. Barbet G, Demion M, Moura IC, Serafini N, Léger T, Vrtovsnik F, Monteiro RC, Guinamard R, Kinet JP, Launay P. (2008) The calcium-activated nonselective cation channel TRPM4 is essential for the migration but not the maturation of dendritic cells. Nat Immunol, 9 (10): 1148-56. [PMID:18758465]
2. Becerra A, Echeverría C, Varela D, Sarmiento D, Armisén R, Nuñez-Villena F, Montecinos M, Simon F. (2011) Transient receptor potential melastatin 4 inhibition prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced endothelial cell death. Cardiovasc Res, 91 (4): 677-84. [PMID:21565835]
3. Bianchi B, Smith PA, Abriel H. (2018) The ion channel TRPM4 in murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and in a model of glutamate-induced neuronal degeneration. Mol Brain, 11 (1): 41. [PMID:29996905]
4. Chabardès-Garonne D, Mejéan A, Aude JC, Cheval L, Di Stefano A, Gaillard MC, Imbert-Teboul M, Wittner M, Balian C, Anthouard V et al.. (2003) A panoramic view of gene expression in the human kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 100 (23): 13710-5. [PMID:14595018]
5. Chen M, Dong Y, Simard JM. (2003) Functional coupling between sulfonylurea receptor type 1 and a nonselective cation channel in reactive astrocytes from adult rat brain. J Neurosci, 23 (24): 8568-77. [PMID:13679426]
6. Cheng H, Beck A, Launay P, Gross SA, Stokes AJ, Kinet JP, Fleig A, Penner R. (2007) TRPM4 controls insulin secretion in pancreatic beta-cells. Cell Calcium, 41 (1): 51-61. [PMID:16806463]
7. Earley S, Waldron BJ, Brayden JE. (2004) Critical role for transient receptor potential channel TRPM4 in myogenic constriction of cerebral arteries. Circ Res, 95 (9): 922-9. [PMID:15472118]
8. Ekundayo B, Arullampalam P, Gerber CE, Hämmerli AF, Guichard S, Boukenna M, Ross-Kaschitza D, Lochner M, Rougier JS, Stahlberg H et al.. (2025) Identification of a binding site for small molecule inhibitors targeting human TRPM4. Nature Communications,. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-56131-2
9. Fonfria E, Murdock PR, Cusdin FS, Benham CD, Kelsell RE, McNulty S. (2006) Tissue distribution profiles of the human TRPM cation channel family. J Recept Signal Transduct Res, 26 (3): 159-78. [PMID:16777713]
10. Garcia ZI, Bruhl A, Gonzales AL, Earley S. (2011) Basal protein kinase Cδ activity is required for membrane localization and activity of TRPM4 channels in cerebral artery smooth muscle cells. Channels (Austin), 5 (3): 210-4. [PMID:21406958]
11. Gibbs RA, Weinstock GM, Metzker ML, Muzny DM, Sodergren EJ, Scherer S, Scott G, Steffen D, Worley KC, Burch PE et al.. (2004) Genome sequence of the Brown Norway rat yields insights into mammalian evolution. Nature, 428 (6982): 493-521. [PMID:15057822]
12. Grand T, Demion M, Norez C, Mettey Y, Launay P, Becq F, Bois P, Guinamard R. (2008) 9-phenanthrol inhibits human TRPM4 but not TRPM5 cationic channels. Br J Pharmacol, 153 (8): 1697-705. [PMID:18297105]
13. Guinamard R, Chatelier A, Demion M, Potreau D, Patri S, Rahmati M, Bois P. (2004) Functional characterization of a Ca(2+)-activated non-selective cation channel in human atrial cardiomyocytes. J Physiol (Lond.), 558 (Pt 1): 75-83. [PMID:15121803]
14. Guinamard R, Chatelier A, Lenfant J, Bois P. (2004) Activation of the Ca(2+)-activated nonselective cation channel by diacylglycerol analogues in rat cardiomyocytes. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 15 (3): 342-8. [PMID:15030426]
15. Hofmann T, Chubanov V, Gudermann T, Montell C. (2003) TRPM5 is a voltage-modulated and Ca(2+)-activated monovalent selective cation channel. Curr Biol, 13 (13): 1153-8. [PMID:12842017]
16. Iwata Y, Katanosaka Y, Arai Y, Komamura K, Miyatake K, Shigekawa M. (2003) A novel mechanism of myocyte degeneration involving the Ca2+-permeable growth factor-regulated channel. J Cell Biol, 161 (5): 957-67. [PMID:12796481]
17. Jang Y, Lee Y, Kim SM, Yang YD, Jung J, Oh U. (2012) Quantitative analysis of TRP channel genes in mouse organs. Arch Pharm Res, 35 (10): 1823-30. [PMID:23139135]
18. Launay P, Cheng H, Srivatsan S, Penner R, Fleig A, Kinet JP. (2004) TRPM4 regulates calcium oscillations after T cell activation. Science, 306 (5700): 1374-7. [PMID:15550671]
19. Launay P, Fleig A, Perraud AL, Scharenberg AM, Penner R, Kinet JP. (2002) TRPM4 is a Ca2+-activated nonselective cation channel mediating cell membrane depolarization. Cell, 109 (3): 397-407. [PMID:12015988]
20. Liu H, Chatel S, Simard C, Syam N, Salle L, Probst V, Morel J, Millat G, Lopez M, Abriel H et al.. (2013) Molecular genetics and functional anomalies in a series of 248 Brugada cases with 11 mutations in the TRPM4 channel. PLoS ONE, 8 (1): e54131. [PMID:23382873]
21. Marigo V, Courville K, Hsu WH, Feng JM, Cheng H. (2009) TRPM4 impacts on Ca2+ signals during agonist-induced insulin secretion in pancreatic beta-cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 299 (2): 194-203. [PMID:19063936]
22. Mathar I, Vennekens R, Meissner M, Kees F, Van der Mieren G, Camacho Londoño JE, Uhl S, Voets T, Hummel B, van den Bergh A et al.. (2010) Increased catecholamine secretion contributes to hypertension in TRPM4-deficient mice. J Clin Invest, 120 (9): 3267-79. [PMID:20679729]
23. Murakami M, Xu F, Miyoshi I, Sato E, Ono K, Iijima T. (2003) Identification and characterization of the murine TRPM4 channel. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 307 (3): 522-8. [PMID:12893253]
24. Nelson PL, Zolochevska O, Figueiredo ML, Soliman A, Hsu WH, Feng JM, Zhang H, Cheng H. (2011) Regulation of Ca(2+)-entry in pancreatic α-cell line by transient receptor potential melastatin 4 plays a vital role in glucagon release. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 335 (2): 126-34. [PMID:21238535]
25. Nilius B, Mahieu F, Prenen J, Janssens A, Owsianik G, Vennekens R, Voets T. (2006) The Ca2+-activated cation channel TRPM4 is regulated by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphate. EMBO J, 25 (3): 467-78. [PMID:16424899]
26. Nilius B, Owsianik G, Voets T, Peters JA. (2007) Transient receptor potential cation channels in disease. Physiol Rev, 87 (1): 165-217. [PMID:17237345]
27. Nilius B, Prenen J, Droogmans G, Voets T, Vennekens R, Freichel M, Wissenbach U, Flockerzi V. (2003) Voltage dependence of the Ca2+-activated cation channel TRPM4. J Biol Chem, 278 (33): 30813-20. [PMID:12799367]
28. Nilius B, Prenen J, Janssens A, Owsianik G, Wang C, Zhu MX, Voets T. (2005) The selectivity filter of the cation channel TRPM4. J Biol Chem, 280 (24): 22899-906. [PMID:15845551]
29. Nilius B, Prenen J, Janssens A, Voets T, Droogmans G. (2004) Decavanadate modulates gating of TRPM4 cation channels. J Physiol (Lond.), 560 (Pt 3): 753-65. [PMID:15331675]
30. Nilius B, Prenen J, Tang J, Wang C, Owsianik G, Janssens A, Voets T, Zhu MX. (2005) Regulation of the Ca2+ sensitivity of the nonselective cation channel TRPM4. J Biol Chem, 280 (8): 6423-33. [PMID:15590641]
31. Nilius B, Prenen J, Voets T, Droogmans G. (2004) Intracellular nucleotides and polyamines inhibit the Ca2+-activated cation channel TRPM4b. Pflugers Arch, 448 (1): 70-5. [PMID:14758478]
32. Nilius B, Talavera K, Owsianik G, Prenen J, Droogmans G, Voets T. (2005) Gating of TRP channels: a voltage connection?. J Physiol (Lond.), 567 (Pt 1): 35-44. [PMID:15878939]
33. Nilius B, Vennekens R. (2006) From cardiac cation channels to the molecular dissection of the transient receptor potential channel TRPM4. Pflugers Arch, 453 (3): 313-21. [PMID:16680483]
34. Nina DUllrich. (2005) PhD Thesis. In TRPM4 and TRPM5: Functional characterisation and comparison of two novel Ca2+-activated cation channels of the TRPM subfamily. (Faculteit Geneeskunde, Dept. Moleculaire Celbiologie, KU Leuven) .
35. Ozhathil LC, Delalande C, Bianchi B, Nemeth G, Kappel S, Thomet U, Ross-Kaschitza D, Simonin C, Rubin M, Gertsch J et al.. (2018) Identification of potent and selective small molecule inhibitors of the cation channel TRPM4. Br J Pharmacol, 175 (12): 2504-2519. [PMID:29579323]
36. Parenti A, De Logu F, Geppetti P, Benemei S. (2016) What is the evidence for the role of TRP channels in inflammatory and immune cells?. Br J Pharmacol, 173 (6): 953-69. [PMID:26603538]
37. Sala-Rabanal M, Wang S, Nichols CG. (2012) On potential interactions between non-selective cation channel TRPM4 and sulfonylurea receptor SUR1. J Biol Chem, 287 (12): 8746-56. [PMID:22291026]
38. Schattling B, Steinbach K, Thies E, Kruse M, Menigoz A, Ufer F, Flockerzi V, Brück W, Pongs O, Vennekens R et al.. (2012) TRPM4 cation channel mediates axonal and neuronal degeneration in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis. Nat Med, 18 (12): 1805-11. [PMID:23160238]
39. Schiller Y. (2004) Activation of a calcium-activated cation current during epileptiform discharges and its possible role in sustaining seizure-like events in neocortical slices. J Neurophysiol, 92 (2): 862-72. [PMID:15277598]
40. Serafini N, Dahdah A, Barbet G, Demion M, Attout T, Gautier G, Arcos-Fajardo M, Souchet H, Jouvin MH, Vrtovsnik F et al.. (2012) The TRPM4 channel controls monocyte and macrophage, but not neutrophil, function for survival in sepsis. J Immunol, 189 (7): 3689-99. [PMID:22933633]
41. Shimizu T, Owsianik G, Freichel M, Flockerzi V, Nilius B, Vennekens R. (2009) TRPM4 regulates migration of mast cells in mice. Cell Calcium, 45 (3): 226-32. [PMID:19046767]
42. Simard JM, Chen M, Tarasov KV, Bhatta S, Ivanova S, Melnitchenko L, Tsymbalyuk N, West GA, Gerzanich V. (2006) Newly expressed SUR1-regulated NC(Ca-ATP) channel mediates cerebral edema after ischemic stroke. Nat Med, 12 (4): 433-40. [PMID:16550187]
43. Stallmeyer B, Zumhagen S, Denjoy I, Duthoit G, Hébert JL, Ferrer X, Maugenre S, Schmitz W, Kirchhefer U, Schulze-Bahr E et al.. (2012) Mutational spectrum in the Ca(2+)--activated cation channel gene TRPM4 in patients with cardiac conductance disturbances. Hum Mutat, 33 (1): 109-17. [PMID:21887725]
44. Stokłosa P, Borgström A, Hauert B, Baur R, Peinelt C. (2021) Investigation of Novel Small Molecular TRPM4 Inhibitors in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers (Basel), 13 (21). [PMID:34771564]
45. Takezawa R, Cheng H, Beck A, Ishikawa J, Launay P, Kubota H, Kinet JP, Fleig A, Yamada T, Penner R. (2006) A pyrazole derivative potently inhibits lymphocyte Ca2+ influx and cytokine production by facilitating transient receptor potential melastatin 4 channel activity. Mol Pharmacol, 69 (4): 1413-20. [PMID:16407466]
46. Teruyama R, Sakuraba M, Kurotaki H, Armstrong WE. (2011) Transient receptor potential channel m4 and m5 in magnocellular cells in rat supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei. J Neuroendocrinol, 23 (12): 1204-13. [PMID:21848647]
47. Ullrich ND, Voets T, Prenen J, Vennekens R, Talavera K, Droogmans G, Nilius B. (2005) Comparison of functional properties of the Ca2+-activated cation channels TRPM4 and TRPM5 from mice. Cell Calcium, 37 (3): 267-78. [PMID:15670874]
48. Vaeth M, Feske S. (2018) Ion channelopathies of the immune system. Curr Opin Immunol, 52: 39-50. [PMID:29635109]
49. Vandewiele F, Pironet A, Jacobs G, Kecskés M, Wegener J, Kerselaers S, Hendrikx L, Verelst J, Philippaert K, Oosterlinck W et al.. (2022) TRPM4 inhibition by meclofenamate suppresses Ca2+-dependent triggered arrhythmias. Eur Heart J, 43 (40): 4195-4207. [PMID:35822895]
50. Vennekens R, Olausson J, Meissner M, Bloch W, Mathar I, Philipp SE, Schmitz F, Weissgerber P, Nilius B, Flockerzi V et al.. (2007) Increased IgE-dependent mast cell activation and anaphylactic responses in mice lacking the calcium-activated nonselective cation channel TRPM4. Nat Immunol, 8 (3): 312-20. [PMID:17293867]
51. Weber KS, Hildner K, Murphy KM, Allen PM. (2010) Trpm4 differentially regulates Th1 and Th2 function by altering calcium signaling and NFAT localization. J Immunol, 185 (5): 2836-46. [PMID:20656926]
52. Woo SK, Kwon MS, Ivanov A, Gerzanich V, Simard JM. (2013) The sulfonylurea receptor 1 (Sur1)-transient receptor potential melastatin 4 (Trpm4) channel. J Biol Chem, 288 (5): 3655-67. [PMID:23255597]
53. Xu XZ, Moebius F, Gill DL, Montell C. (2001) Regulation of melastatin, a TRP-related protein, through interaction with a cytoplasmic isoform. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 98 (19): 10692-7. [PMID:11535825]
54. Yu W, Hill WG, Apodaca G, Zeidel ML. (2011) Expression and distribution of transient receptor potential (TRP) channels in bladder epithelium. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 300 (1): F49-59. [PMID:20943764]
55. Zhang Z, Okawa H, Wang Y, Liman ER. (2005) Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate rescues TRPM4 channels from desensitization. J Biol Chem, 280 (47): 39185-92. [PMID:16186107]