
Top ▲

GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
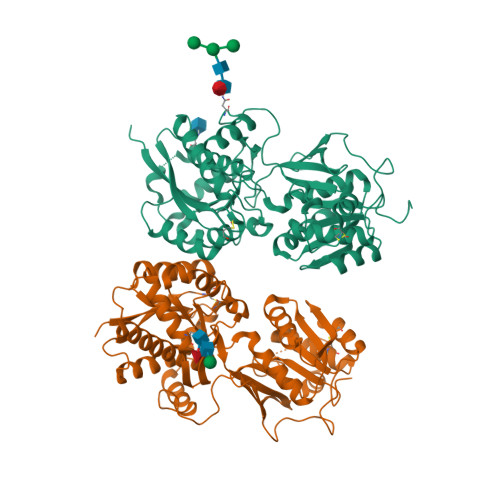
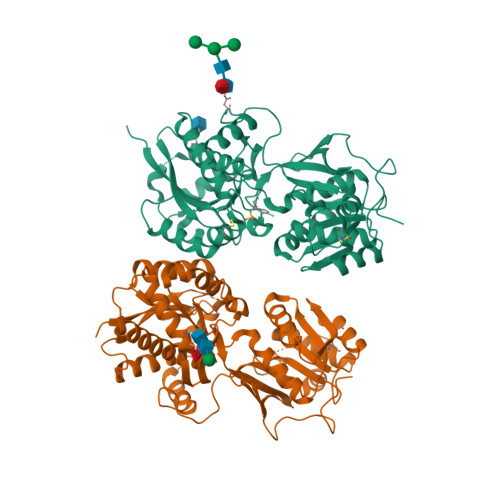
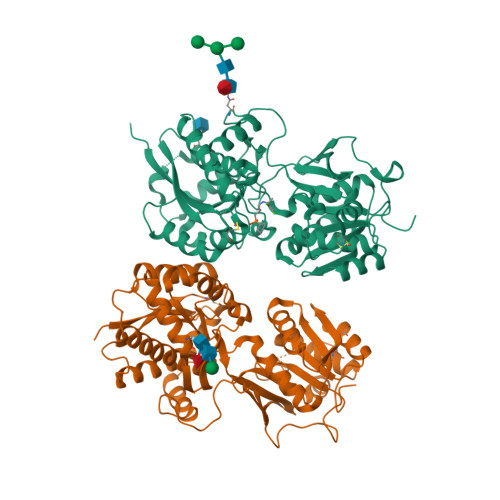
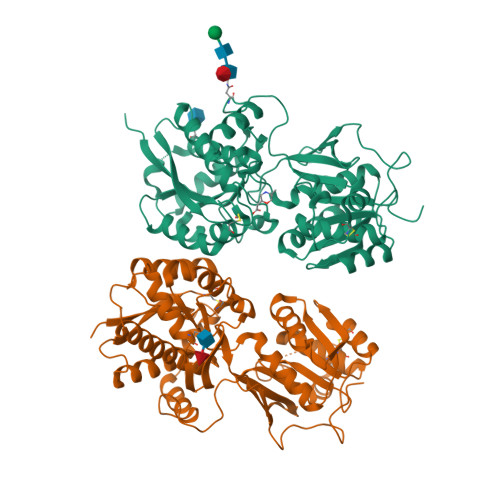
| Quaternary Structure: Subunits |
| KCTD8 (Accessory protein) |
| KCTD12 (Accessory protein) |
| kctd12b (Accessory protein) |
| KCTD16 (Accessory protein) |
| GABAB1 |
| GABAB2 |
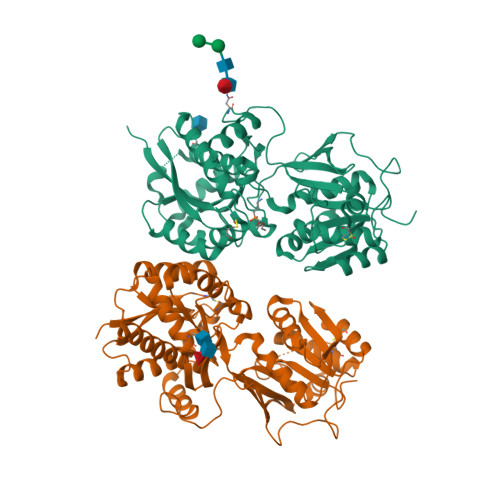
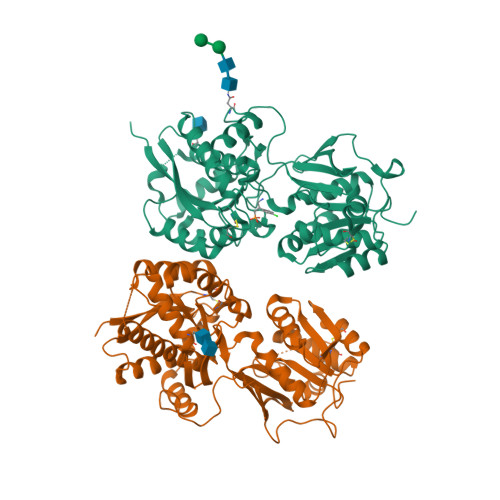
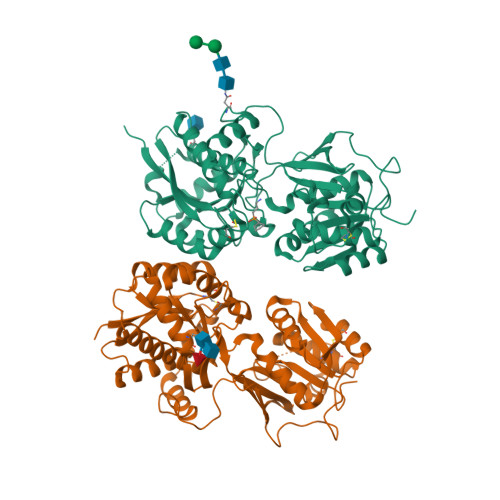
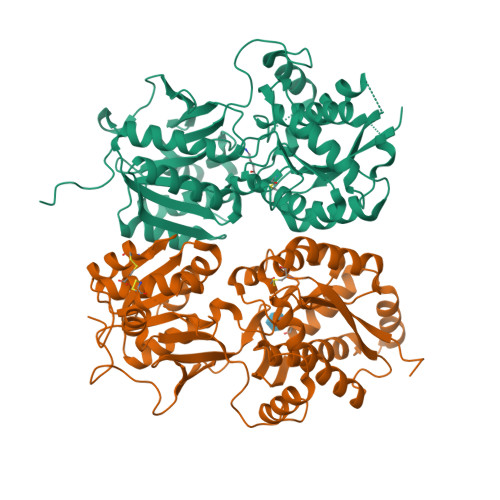
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| GABA |
| Comments: Functional GABA receptors contain both GABAB1 and GABAB2 subunits |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific agonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Values included are those determined on the native receptor in which GABAB1 is associated with GABAB2. Affinity for agonists are at least 10 time lower when measured on GABAB1 alone. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific antagonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allosteric Modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Primary Transduction Mechanisms 
|
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gi/Go family |
Adenylyl cyclase inhibition Potassium channel |
| References: 14,17,25 | |
Secondary Transduction Mechanisms  |
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Adenylyl cyclase stimulation | |
| Comments: Potentiation rather than stimulation. The GABAB1 subunit has been reported to interact with the transcription factor ATFx, and as such this receptor subunit has been proposed to generate signals that may be independent to G-protein. This however, requires further examination to be firmly established. | |
| References: 12 | |
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
1. Bolser DC, Blythin DJ, Chapman RW, Egan RW, Hey JA, Rizzo C, Kuo SC, Kreutner W. (1995) The pharmacology of SCH 50911: a novel, orally-active GABA-beta receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 274 (3): 1393-8. [PMID:7562513]
2. Bonanno G, Raiteri M. (1993) gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) autoreceptors in rat cerebral cortex and spinal cord represent pharmacologically distinct subtypes of the GABAB receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 265 (2): 765-70. [PMID:8388458]
3. Bowery NG, Bettler B, Froestl W, Gallagher JP, Marshall F, Raiteri M, Bonner TI, Enna SJ. (2002) International Union of Pharmacology. XXXIII. Mammalian gamma-aminobutyric acid(B) receptors: structure and function. Pharmacol Rev, 54 (2): 247-64. [PMID:12037141]
4. Chen LH, Sun B, Zhang Y, Xu TJ, Xia ZX, Liu JF, Nan FJ. (2014) Discovery of a Negative Allosteric Modulator of GABAB Receptors. ACS Med Chem Lett, 5 (7): 742-7. [PMID:25050158]
5. Crunelli V, Leresche N. (1991) A role for GABAB receptors in excitation and inhibition of thalamocortical cells. Trends Neurosci, 14 (1): 16-21. [PMID:1709527]
6. Dutar P, Nicoll RA. (1988) A physiological role for GABAB receptors in the central nervous system. Nature, 332 (6160): 156-8. [PMID:2831457]
7. Froestl W, Mickel SJ. (1997) Chemistry of GABAB modulators. In The GABA Receptors. Edited by Enna SJ, Bowery NG (Humana Press) 271-296. [ISBN:0896034585]
8. Galvez T, Urwyler S, Prézeau L, Mosbacher J, Joly C, Malitschek B, Heid J, Brabet I, Froestl W, Bettler B et al.. (2000) Ca(2+) requirement for high-affinity gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) binding at GABA(B) receptors: involvement of serine 269 of the GABA(B)R1 subunit. Mol Pharmacol, 57 (3): 419-26. [PMID:10692480]
9. Gemignani A, Paudice P, Bonanno G, Raiteri M. (1994) Pharmacological discrimination between gamma-aminobutyric acid type B receptors regulating cholecystokinin and somatostatin release from rat neocortex synaptosomes. Mol Pharmacol, 46 (3): 558-62. [PMID:7935338]
10. Geng Y, Bush M, Mosyak L, Wang F, Fan QR. (2013) Structural mechanism of ligand activation in human GABA(B) receptor. Nature, 504 (7479): 254-9. [PMID:24305054]
11. Hellyer SD, Albold S, Wang T, Chen ANY, May LT, Leach K, Gregory KJ. (2018) "Selective" Class C G Protein-Coupled Receptor Modulators Are Neutral or Biased mGlu5 Allosteric Ligands. Mol Pharmacol, 93 (5): 504-514. [PMID:29514854]
12. Hill DR. (1985) GABAB receptor modulation of adenylate cyclase activity in rat brain slices. Br J Pharmacol, 84 (1): 249-57. [PMID:2579700]
13. Hirst WD, Babbs AJ, Green A, Minton JA, Shaw TE, Wise A, Rice SQ, Pangalos MN, Price GW. (2003) Pharmacological characterisation of a cell line expressing GABA B1b and GABA B2 receptor subunits. Biochem Pharmacol, 65 (7): 1103-13. [PMID:12663046]
14. Jones KA, Borowsky B, Tamm JA, Craig DA, Durkin MM, Dai M, Yao WJ, Johnson M, Gunwaldsen C, Huang LY et al.. (1998) GABA(B) receptors function as a heteromeric assembly of the subunits GABA(B)R1 and GABA(B)R2. Nature, 396 (6712): 674-9. [PMID:9872315]
15. Kaupmann K, Huggel K, Heid J, Flor PJ, Bischoff S, Mickel SJ, McMaster G, Angst C, Bittiger H, Froestl W et al.. (1997) Expression cloning of GABA(B) receptors uncovers similarity to metabotropic glutamate receptors. Nature, 386 (6622): 239-46. [PMID:9069281]
16. Keir MJ, Barakat MJ, Dev KK, Bittiger H, Bettler B, Henley JM. (1999) Characterisation and partial purification of the GABA(B) receptor from the rat cerebellum using the novel antagonist [3H]CGP 62349. Brain Res Mol Brain Res, 71 (2): 279-89. [PMID:10521582]
17. Knight AR, Bowery NG. (1996) The pharmacology of adenylyl cyclase modulation by GABAB receptors in rat brain slices. Neuropharmacology, 35 (6): 703-12. [PMID:8887979]
18. Malherbe P, Masciadri R, Norcross RD, Knoflach F, Kratzeisen C, Zenner MT, Kolb Y, Marcuz A, Huwyler J, Nakagawa T et al.. (2008) Characterization of (R,S)-5,7-di-tert-butyl-3-hydroxy-3-trifluoromethyl-3H-benzofuran-2-one as a positive allosteric modulator of GABAB receptors. Br J Pharmacol, 154 (4): 797-811. [PMID:18536733]
19. Newberry NR, Nicoll RA. (1984) Direct hyperpolarizing action of baclofen on hippocampal pyramidal cells. Nature, 308 (5958): 450-2. [PMID:6709051]
20. Patel S, Naeem S, Kesingland A, Froestl W, Capogna M, Urban L, Fox A. (2001) The effects of GABA(B) agonists and gabapentin on mechanical hyperalgesia in models of neuropathic and inflammatory pain in the rat. Pain, 90 (3): 217-26. [PMID:11207393]
21. Urwyler S, Mosbacher J, Lingenhoehl K, Heid J, Hofstetter K, Froestl W, Bettler B, Kaupmann K. (2001) Positive allosteric modulation of native and recombinant gamma-aminobutyric acid(B) receptors by 2,6-Di-tert-butyl-4-(3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-propyl)-phenol (CGP7930) and its aldehyde analog CGP13501. Mol Pharmacol, 60 (5): 963-71. [PMID:11641424]
22. Urwyler S, Pozza MF, Lingenhoehl K, Mosbacher J, Lampert C, Froestl W, Koller M, Kaupmann K. (2003) N,N'-Dicyclopentyl-2-methylsulfanyl-5-nitro-pyrimidine-4,6-diamine (GS39783) and structurally related compounds: novel allosteric enhancers of gamma-aminobutyric acidB receptor function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 307 (1): 322-30. [PMID:12954816]
23. Voisin DL, Nagy F. (2001) Sustained L-type calcium currents in dissociated deep dorsal horn neurons of the rat: characteristics and modulation. Neuroscience, 102 (2): 461-72. [PMID:11166132]
24. Wood MD, Murkitt KL, Rice SQ, Testa T, Punia PK, Stammers M, Jenkins O, Elshourbagy NA, Shabon U, Taylor SJ et al.. (2000) The human GABA(B1b) and GABA(B2) heterodimeric recombinant receptor shows low sensitivity to phaclofen and saclofen. Br J Pharmacol, 131 (6): 1050-4. [PMID:11082110]
25. Xu J, Wojcik WJ. (1986) Gamma aminobutyric acid B receptor-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase in cultured cerebellar granule cells: blockade by islet-activating protein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 239 (2): 568-73. [PMID:2430096]