
Top ▲

GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| class A G protein-coupled receptor | ||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 7 | 400 | 3q13.31 | DRD3 | dopamine receptor D3 | 51 |
| Mouse | 7 | 446 | 16 28.44 cM | Drd3 | dopamine receptor D3 | 43 |
| Rat | 7 | 446 | 11q21 | Drd3 | dopamine receptor D3 | 133 |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| D3 receptor | dopamine D3 receptor | dopaminergic receptor D3 | D3R |
Database Links  |
|
| Specialist databases | |
| GPCRdb | drd3_human (Hs), drd3_mouse (Mm), drd3_rat (Rn) |
| Other databases | |
| Alphafold | P35462 (Hs), P30728 (Mm), P19020 (Rn) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL234 (Hs), CHEMBL3441 (Mm), CHEMBL3138 (Rn) |
| DrugBank Target | P35462 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000151577 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000022705 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000060806 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 1814 (Hs), 13490 (Mm), 29238 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000151577 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:1814 (Hs), mmu:13490 (Mm), rno:29238 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 126451 (Hs) |
| Orphanet | ORPHA121179 (Hs) |
| Pharos | P35462 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_000796 (Hs), NM_007877 (Mm), NM_017140 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_000787 (Hs), NP_031903 (Mm), NP_058836 (Rn) |
| SynPHARM | 2633 (in complex with eticlopride) |
| UniProtKB | P35462 (Hs), P30728 (Mm), P19020 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | DRD3 (Hs) |
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
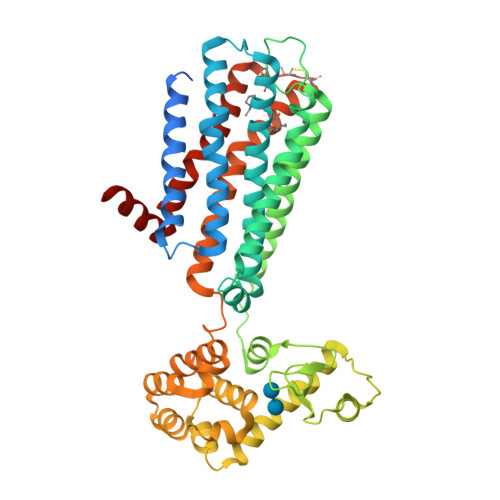
|
|
||||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| dopamine |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific agonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PF-592379 has no measurable binding to D1, D2 or D5 receptors [32]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific antagonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allosteric Modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immuno Process Associations | |||||||||
|
Primary Transduction Mechanisms 
|
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gi/Go family |
Adenylyl cyclase inhibition Potassium channel |
| References: 27,86,116-117,128 | |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Expression Datasets  |
|
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology 
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General Comments |
| Alternative splicing leads to a 425aa isoform in mouse [43] and several shorter presumably inactive isoforms in rat [52] and human [126]. Two polymorphic variants [Ser9] and [Gly9] in human [79]. The organization of the coding sequence of the human gene has been established [54]. Anti-psychotic drugs display closely similar or slightly lower antagonist affinity at D3 compared to D2 receptors. S(+)14297, initially reported as a D3 receptor antagonist [104] displays full agonist activity in two functional assays [114]. |
1. Accili D, Fishburn CS, Drago J, Steiner H, Lachowicz JE, Park BH, Gauda EB, Lee EJ, Cool MH, Sibley DR et al.. (1996) A targeted mutation of the D3 dopamine receptor gene is associated with hyperactivity in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 93 (5): 1945-9. [PMID:8700864]
2. Ahlenius S, Salmi P. (1994) Behavioral and biochemical effects of the dopamine D3 receptor-selective ligand, 7-OH-DPAT, in the normal and the reserpine-treated rat. Eur J Pharmacol, 260 (2-3): 177-81. [PMID:7988642]
3. Akunne HC, Towers P, Ellis GJ, Dijkstra D, Wikström H, Heffner TG, Wise LD, Pugsley TA. (1995) Characterization of binding of [3H]PD 128907, a selective dopamine D3 receptor agonist ligand, to CHO-K1 cells. Life Sci, 57 (15): 1401-10. [PMID:7674830]
4. Andreoli M, Tessari M, Pilla M, Valerio E, Hagan JJ, Heidbreder CA. (2003) Selective antagonism at dopamine D3 receptors prevents nicotine-triggered relapse to nicotine-seeking behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology, 28 (7): 1272-80. [PMID:12700694]
5. Aretha CW, Sinha A, Galloway MP. (1995) Dopamine D3-preferring ligands act at synthesis modulating autoreceptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 274 (2): 609-13. [PMID:7636720]
6. Arnt J, Skarsfeldt T. (1998) Do novel antipsychotics have similar pharmacological characteristics? A review of the evidence. Neuropsychopharmacology, 18 (2): 63-101. [PMID:9430133]
7. Ashby Jr CR, Paul M, Gardner EL, Heidbreder CA, Hagan JJ. (2003) Acute administration of the selective D3 receptor antagonist SB-277011A blocks the acquisition and expression of the conditioned place preference response to heroin in male rats. Synapse, 48 (3): 154-6. [PMID:12645041]
8. Asico LD, Ladines C, Fuchs S, Accili D, Carey RM, Semeraro C, Pocchiari F, Felder RA, Eisner GM, Jose PA. (1998) Disruption of the dopamine D3 receptor gene produces renin-dependent hypertension. J Clin Invest, 102 (3): 493-8. [PMID:9691085]
9. Auerbach SS, DrugMatrix® and ToxFX® Coordinator National Toxicology Program. National Toxicology Program: Dept of Health and Human Services. Accessed on 02/05/2014. Modified on 02/05/2014. DrugMatrix, https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/drugmatrix/index.html
10. Aujla H, Beninger RJ. (2005) The dopamine D(3) receptor-preferring partial agonist BP 897 dose-dependently attenuates the expression of amphetamine-conditioned place preference in rats. Behav Pharmacol, 16 (3): 181-6. [PMID:15864073]
11. Banala AK, Levy BA, Khatri SS, Furman CA, Roof RA, Mishra Y, Griffin SA, Sibley DR, Luedtke RR, Newman AH. (2011) N-(3-fluoro-4-(4-(2-methoxy or 2,3-dichlorophenyl)piperazine-1-yl)butyl)arylcarboxamides as selective dopamine D3 receptor ligands: critical role of the carboxamide linker for D3 receptor selectivity. J Med Chem, 54 (10): 3581-94. [PMID:21495689]
12. Booze RM, Wallace DR. (1995) Dopamine D2 and D3 receptors in the rat striatum and nucleus accumbens: use of 7-OH-DPAT and [125I]-iodosulpride. Synapse, 19 (1): 1-13. [PMID:7709338]
13. Boulay D, Depoortere R, Rostene W, Perrault G, Sanger DJ. (1999) Dopamine D3 receptor agonists produce similar decreases in body temperature and locomotor activity in D3 knock-out and wild-type mice. Neuropharmacology, 38 (4): 555-65. [PMID:10221759]
14. Bouthenet ML, Souil E, Martres MP, Sokoloff P, Giros B, Schwartz JC. (1991) Localization of dopamine D3 receptor mRNA in the rat brain using in situ hybridization histochemistry: comparison with dopamine D2 receptor mRNA. Brain Res, 564 (2): 203-19. [PMID:1839781]
15. Bowery B, Rothwell LA, Seabrook GR. (1994) Comparison between the pharmacology of dopamine receptors mediating the inhibition of cell firing in rat brain slices through the substantia nigra pars compacta and ventral tegmental area. Br J Pharmacol, 112 (3): 873-80. [PMID:7921615]
16. Boyce-Rustay JM, Risinger FO. (2003) Dopamine D3 receptor knockout mice and the motivational effects of ethanol. Pharmacol Biochem Behav, 75 (2): 373-9. [PMID:12873629]
17. Boyfield I, Winn F, Coldwell M. (1996) Comparison of agonist potencies at human dopamine D2 and D3 receptors, expressed in the same cell line, using the Cytosensor Microphysiometer. Biochem Soc Trans, 24: 57S-57S. [PMID:8674731]
18. Burris KD, Pacheco MA, Filtz TM, Kung MP, Kung HF, Molinoff PB. (1995) Lack of discrimination by agonists for D2 and D3 dopamine receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology, 12 (4): 335-45. [PMID:7576010]
19. Burstein ES, Ma J, Wong S, Gao Y, Pham E, Knapp AE, Nash NR, Olsson R, Davis RE, Hacksell U et al.. (2005) Intrinsic efficacy of antipsychotics at human D2, D3, and D4 dopamine receptors: identification of the clozapine metabolite N-desmethylclozapine as a D2/D3 partial agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 315 (3): 1278-87. [PMID:16135699]
20. Caine SB, Koob GF. (1993) Modulation of cocaine self-administration in the rat through D-3 dopamine receptors. Science, 260 (5115): 1814-6. [PMID:8099761]
21. CARLSSON A, LINDQVIST M, MAGNUSSON T. (1957) 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine and 5-hydroxytryptophan as reserpine antagonists. Nature, 180 (4596): 1200. [PMID:13483658]
22. Carta AR, Gerfen CR, Steiner H. (2000) Cocaine effects on gene regulation in the striatum and behavior: increased sensitivity in D3 dopamine receptor-deficient mice. Neuroreport, 11 (11): 2395-9. [PMID:10943692]
23. Cervo L, Burbassi S, Colovic M, Caccia S. (2005) Selective antagonist at D3 receptors, but not non-selective partial agonists, influences the expression of cocaine-induced conditioned place preference in free-feeding rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav, 82 (4): 727-34. [PMID:16405981]
24. Cervo L, Cocco A, Petrella C, Heidbreder CA. (2007) Selective antagonism at dopamine D3 receptors attenuates cocaine-seeking behaviour in the rat. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol, 10 (2): 167-81. [PMID:16426478]
25. Chaperon F, Thiébot MH. (1996) Effects of dopaminergic D3-receptor-preferring ligands on the acquisition of place conditioning in rats. Behav Pharmacol, 7 (1): 105-109. [PMID:11224401]
26. Chien EY, Liu W, Zhao Q, Katritch V, Han GW, Hanson MA, Shi L, Newman AH, Javitch JA, Cherezov V et al.. (2010) Structure of the human dopamine D3 receptor in complex with a D2/D3 selective antagonist. Science, 330 (6007): 1091-5. [PMID:21097933]
27. Chio CL, Lajiness ME, Huff RM. (1994) Activation of heterologously expressed D3 dopamine receptors: comparison with D2 dopamine receptors. Mol Pharmacol, 45 (1): 51-60. [PMID:8302280]
28. Choi JK, Mandeville JB, Chen YI, Grundt P, Sarkar SK, Newman AH, Jenkins BG. (2010) Imaging brain regional and cortical laminar effects of selective D3 agonists and antagonists. Psychopharmacology (Berl.), 212 (1): 59-72. [PMID:20628733]
29. Choi S, Haggart D, Toll L, Cuny GD. (2004) Synthesis, receptor binding and functional studies of mesoridazine stereoisomers. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 14 (17): 4379-82. [PMID:15357957]
30. Chumpradit S, Kung MP, Vessotskie J, Foulon C, Mu M, Kung HF. (1994) Iodinated 2-aminotetralins and 3-amino-1-benzopyrans: ligands for dopamine D2 and D3 receptors. J Med Chem, 37 (24): 4245-50. [PMID:7990123]
31. Clemens S, Sawchuk MA, Hochman S. (2005) Reversal of the circadian expression of tyrosine-hydroxylase but not nitric oxide synthase levels in the spinal cord of dopamine D3 receptor knockout mice. Neuroscience, 133 (2): 353-7. [PMID:15878801]
32. Collins GT, Butler P, Wayman C, Ratcliffe S, Gupta P, Oberhofer G, Caine SB. (2012) Lack of abuse potential in a highly selective dopamine D3 agonist, PF-592,379, in drug self-administration and drug discrimination in rats. Behav Pharmacol, 23 (3): 280-91. [PMID:22470105]
33. Cooper DC, Loeltzow TE, Xu M, Tonegawa S, White FJ, Wolf ME. (1996) Regulations of dopamine release and synthesis in dopamine D3R receptor knockout mice. (Abstract) Soc Neurosci Abst, 22: 1319-.
34. Cox BA, Rosser MP, Kozlowski MR, Duwe KM, Neve RL, Neve KA. (1995) Regulation and functional characterization of a rat recombinant dopamine D3 receptor. Synapse, 21 (1): 1-9. [PMID:8525456]
35. Crocq MA, Mant R, Asherson P, Williams J, Hode Y, Mayerova A, Collier D, Lannfelt L, Sokoloff P, Schwartz JC et al.. (1992) Association between schizophrenia and homozygosity at the dopamine D3 receptor gene. J Med Genet, 29 (12): 858-60. [PMID:1362221]
36. Daly SA, Waddington JL. (1993) Behavioural effects of the putative D-3 dopamine receptor agonist 7-OH-DPAT in relation to other "D-2-like" agonists. Neuropharmacology, 32 (5): 509-10. [PMID:8321432]
37. Damsma G, Bottema T, Westerink BH, Tepper PG, Dijkstra D, Pugsley TA, MacKenzie RG, Heffner TG, Wikström H. (1993) Pharmacological aspects of R-(+)-7-OH-DPAT, a putative dopamine D3 receptor ligand. Eur J Pharmacol, 249 (3): R9-10. [PMID:8287911]
38. Depoortere R, Perrault G, Sanger DJ. (1996) Behavioural effects in the rat of the putative dopamine D3 receptor agonist 7-OH-DPAT: comparison with quinpirole and apomorphine. Psychopharmacology (Berl.), 124 (3): 231-40. [PMID:8740044]
39. Devoto P, Collu M, Muntoni AL, Pistis M, Serra G, Gessa GL, Diana M. (1995) Biochemical and electrophysiological effects of 7-OH-DPAT on the mesolimbic dopaminergic system. Synapse, 20 (2): 153-5. [PMID:7570345]
40. Diaz J, Lévesque D, Lammers CH, Griffon N, Martres MP, Schwartz JC, Sokoloff P. (1995) Phenotypical characterization of neurons expressing the dopamine D3 receptor in the rat brain. Neuroscience, 65 (3): 731-45. [PMID:7609872]
41. Diaz J, Pilon C, Le Foll B, Gros C, Triller A, Schwartz JC, Sokoloff P. (2000) Dopamine D3 receptors expressed by all mesencephalic dopamine neurons. J Neurosci, 20 (23): 8677-84. [PMID:11102473]
42. Dijkstra D, Rodenhuis N, Vermeulen ES, Pugsley TA, Wise LD, Wikström HV. (2002) Further characterization of structural requirements for ligands at the dopamine D(2) and D(3) receptor: exploring the thiophene moiety. J Med Chem, 45 (14): 3022-31. [PMID:12086487]
43. Fishburn CS, Belleli D, David C, Carmon S, Fuchs S. (1993) A novel short isoform of the D3 dopamine receptor generated by alternative splicing in the third cytoplasmic loop. J Biol Chem, 268 (8): 5872-8. [PMID:8449953]
44. Freedman SB, Patel S, Marwood R, Emms F, Seabrook GR, Knowles MR, McAllister G. (1994) Expression and pharmacological characterization of the human D3 dopamine receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 268 (1): 417-26. [PMID:8301582]
45. Furman CA, Roof RA, Moritz AE, Miller BN, Doyle TB, Free RB, Banala AK, Paul NM, Kumar V, Sibley CD et al.. (2015) Investigation of the binding and functional properties of extended length D3 dopamine receptor-selective antagonists. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol, 25 (9): 1448-61. [PMID:25583363]
46. Gainetdinov RR, Sotnikova TD, Grekhova TV, Rayevsky KS. (1996) In vivo evidence for preferential role of dopamine D3 receptor in the presynaptic regulation of dopamine release but not synthesis. Eur J Pharmacol, 308 (3): 261-9. [PMID:8858296]
47. Galaj E, Ananthan S, Saliba M, Ranaldi R. (2014) The effects of the novel DA D3 receptor antagonist SR 21502 on cocaine reward, cocaine seeking and cocaine-induced locomotor activity in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl.), 231 (3): 501-10. [PMID:24037509]
48. Gehlert DR, Gackenheimer SL, Seeman P, Schaus J. (1992) Autoradiographic localization of [3H]quinpirole binding to dopamine D2 and D3 receptors in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol, 211 (2): 189-94. [PMID:1351846]
49. Gilbert DB, Cooper SJ. (1995) 7-OH-DPAT injected into the accumbens reduces locomotion and sucrose ingestion: D3 autoreceptor-mediated effects?. Pharmacol Biochem Behav, 52 (2): 275-80. [PMID:8577791]
50. Gilbert JG, Newman AH, Gardner EL, Ashby Jr CR, Heidbreder CA, Pak AC, Peng XQ, Xi ZX. (2005) Acute administration of SB-277011A, NGB 2904, or BP 897 inhibits cocaine cue-induced reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior in rats: role of dopamine D3 receptors. Synapse, 57 (1): 17-28. [PMID:15858839]
51. Giros B, Martres M-P, Sokoloff P, Schwartz J-C. (1990) cDNA cloning of the human dopaminergic D3 receptor and chromosome identification. C R Acad Sci III, 311: 501-508. [PMID:2129115]
52. Giros B, Martres MP, Pilon C, Sokoloff P, Schwartz JC. (1991) Shorter variants of the D3 dopamine receptor produced through various patterns of alternative splicing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 176: 1584-1592. [PMID:2039532]
53. Gobert A, Rivet JM, Audinot V, Cistarelli L, Spedding M, Vian J, Peglion JL, Millan MJ. (1995) Functional correlates of dopamine D3 receptor activation in the rat in vivo and their modulation by the selective antagonist, (+)-S 14297: II. Both D2 and "silent" D3 autoreceptors control synthesis and release in mesolimbic, mesocortical and nigrostriatal pathways. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 275 (2): 899-913. [PMID:7473181]
54. Griffon N, Crocq MA, Pilon C, Martres MP, Mayerova A, Uyanik G, Burgert E, Duval F, Macher JP, Javoy-Agid F et al.. (1996) Dopamine D3 receptor gene: organization, transcript variants, and polymorphism associated with schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet, 67 (1): 63-70. [PMID:8678117]
55. Grundt P, Prevatt KM, Cao J, Taylor M, Floresca CZ, Choi JK, Jenkins BG, Luedtke RR, Newman AH. (2007) Heterocyclic analogues of N-(4-(4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl)butyl)arylcarboxamides with functionalized linking chains as novel dopamine D3 receptor ligands: potential substance abuse therapeutic agents. J Med Chem, 50 (17): 4135-46. [PMID:17672446]
56. Hachimine P, Seepersad N, Ananthan S, Ranaldi R. (2014) The novel dopamine D3 receptor antagonist, SR 21502, reduces cocaine conditioned place preference in rats. Neurosci Lett, 569: 137-41. [PMID:24704326]
57. Heier RF, Dolak LA, Duncan JN, Hyslop DK, Lipton MF, Martin IJ, Mauragis MA, Piercey MF, Nichols NF, Schreur PJ et al.. (1997) Synthesis and biological activities of (R)-5,6-dihydro-N,N-dimethyl-4H-imidazo[4,5,1-ij]quinolin-5-amine and its metabolites. J Med Chem, 40 (5): 639-46. [PMID:9057850]
58. Heinrich T, Böttcher H, Gericke R, Bartoszyk GD, Anzali S, Seyfried CA, Greiner HE, Van Amsterdam C. (2004) Synthesis and structure--activity relationship in a class of indolebutylpiperazines as dual 5-HT(1A) receptor agonists and serotonin reuptake inhibitors. J Med Chem, 47 (19): 4684-92. [PMID:15341484]
59. Herroelen L, De Backer JP, Wilczak N, Flamez A, Vauquelin G, De Keyser J. (1994) Autoradiographic distribution of D3-type dopamine receptors in human brain using [3H]7-hydroxy-N,N-di-n-propyl-2-aminotetralin. Brain Res, 648 (2): 222-8. [PMID:7922537]
60. Hoare SR, Coldwell MC, Armstrong D, Strange PG. (2000) Regulation of human D(1), d(2(long)), d(2(short)), D(3) and D(4) dopamine receptors by amiloride and amiloride analogues. Br J Pharmacol, 130 (5): 1045-59. [PMID:10882389]
61. Hu R, Song R, Yang R, Su R, Li J. (2013) The dopamine D3 receptor antagonist YQA14 that inhibits the expression and drug-primed reactivation of morphine-induced conditioned place preference in rats. Eur J Pharmacol, (1-3). [PMID:24513519]
62. Jeanneteau F, Funalot B, Jankovic J, Deng H, Lagarde JP, Lucotte G, Sokoloff P. (2006) A functional variant of the dopamine D3 receptor is associated with risk and age-at-onset of essential tremor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 103 (28): 10753-8. [PMID:16809426]
63. Jordan CJ, Humburg B, Rice M, Bi GH, You ZB, Shaik AB, Cao J, Bonifazi A, Gadiano A, Rais R et al.. (2019) The highly selective dopamine D3R antagonist, R-VK4-40 attenuates oxycodone reward and augments analgesia in rodents. Neuropharmacology, 158: 107597. [PMID:30974107]
64. Joseph JD, Wang YM, Miles PR, Budygin EA, Picetti R, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG, Wightman RM. (2002) Dopamine autoreceptor regulation of release and uptake in mouse brain slices in the absence of D(3) receptors. Neuroscience, 112 (1): 39-49. [PMID:12044470]
65. Kagaya T, Yonaga M, Furuya Y, Hashimoto T, Kuroki J, Nishizawa Y. (1996) Dopamine D3 agonists disrupt social behavior in rats. Brain Res, 721 (1-2): 229-32. [PMID:8793104]
66. Kennedy JL, Billett EA, Macciardi FM, Verga M, Parsons TJ, Meltzer HY, Lieberman J, Buchanan JA. (1995) Association study of dopamine D3 receptor gene and schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet, 60 (6): 558-62. [PMID:8825896]
67. Khroyan TV, Baker DA, Neisewander JL. (1995) Dose-dependent effects of the D3-preferring agonist 7-OH-DPAT on motor behaviors and place conditioning. Psychopharmacology (Berl.), 122 (4): 351-7. [PMID:8657832]
68. Kiss B, Horváth A, Némethy Z, Schmidt E, Laszlovszky I, Bugovics G, Fazekas K, Hornok K, Orosz S, Gyertyán I et al.. (2010) Cariprazine (RGH-188), a dopamine D(3) receptor-preferring, D(3)/D(2) dopamine receptor antagonist-partial agonist antipsychotic candidate: in vitro and neurochemical profile. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 333 (1): 328-40. [PMID:20093397]
69. Kling-Petersen T, Ljung E, Svensson K. (1994) The preferential dopamine autoreceptor antagonist (+)-UH232 antagonizes the positive reinforcing effects of cocaine and d-amphetamine in the ICSS paradigm. Pharmacol Biochem Behav, 49 (2): 345-51. [PMID:7824548]
70. Kling-Petersen T, Ljung E, Svensson K. (1995) Effects on locomotor activity after local application of D3 preferring compounds in discrete areas of the rat brain. J Neural Transm Gen Sect, 102 (3): 209-20. [PMID:8788069]
71. Koeltzow T, Cooper DC, Hu X-T, Xu M, Tonegawa S, White FJ. (1995) In vivo effects of dopaminergic ligands on dopamine D3 receptor deficient mice. (Abstract) Soc Neurosci Abst, 21: 364-.
72. Kreiss DS, Bergstrom DA, Gonzalez AM, Huang KX, Sibley DR, Walters JR. (1995) Dopamine receptor agonist potencies for inhibition of cell firing correlate with dopamine D3 receptor binding affinities. Eur J Pharmacol, 277: 209-214. [PMID:7493610]
73. Kurashima M, Yamada K, Nagashima M, Shirakawa K, Furukawa T. (1995) Effects of putative dopamine D3 receptor agonists, 7-OH-DPAT, and quinpirole, on yawning, stereotypy, and body temperature in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav, 52 (3): 503-8. [PMID:8545466]
74. Lacroix LP, Ceolin L, Zocchi A, Varnier G, Garzotti M, Curcuruto O, Heidbreder CA. (2006) Selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonists enhance cortical acetylcholine levels measured with high-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry without anti-cholinesterases. J Neurosci Methods, 157 (1): 25-31. [PMID:16697046]
75. Lacroix LP, Hows ME, Shah AJ, Hagan JJ, Heidbreder CA. (2003) Selective antagonism at dopamine D3 receptors enhances monoaminergic and cholinergic neurotransmission in the rat anterior cingulate cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology, 28 (5): 839-49. [PMID:12637956]
76. Lahti RA, Roberts RC, Tamminga CA. (1995) D2-family receptor distribution in human postmortem tissue: an autoradiographic study. Neuroreport, 6 (18): 2505-12. [PMID:8741751]
77. Landwehrmeyer B, Mengod G, Palacios JM. (1993) Differential visualization of dopamine D2 and D3 receptor sites in rat brain. A comparative study using in situ hybridization histochemistry and ligand binding autoradiography. Eur J Neurosci, 5 (2): 145-53. [PMID:8261096]
78. Landwehrmeyer B, Mengod G, Palacios JM. (1993) Dopamine D3 receptor mRNA and binding sites in human brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res, 18 (1-2): 187-92. [PMID:8097550]
79. Lannfelt L, Sokoloff P, Martres MP, Pilon C, Giros B, Jonsson E, Sedvall G, Schwartz JC. (1992) Amino acid substitution in the dopamine D3 receptor as a useful polymorphism for investigating psychiatric disorders. Psychiatr Genet, 2: 249-256.
80. Le Foll B, Diaz J, Sokoloff P. (2005) Neuroadaptations to hyperdopaminergia in dopamine D3 receptor-deficient mice. Life Sci, 76: 1281-1296. [PMID:15642598]
81. Lejeune F, Millan MJ. (1995) Activation of dopamine D3 autoreceptors inhibits firing of ventral tegmental dopaminergic neurones in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol, 275 (3): R7-9. [PMID:7768288]
82. Leriche L, Schwartz JC, Sokoloff P. (2003) The dopamine D3 receptor mediates locomotor hyperactivity induced by NMDA receptor blockade. Neuropharmacology, 45 (2): 174-81. [PMID:12842123]
83. Levant B, Grigoriadis DE, DeSouza EB. (1992) Characterization of [3H]quinpirole binding to D2-like dopamine receptors in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 262 (3): 929-35. [PMID:1356154]
84. Levant B, Vansell NR. (1997) In vivo occupancy of D2 dopamine receptors by nafadotride. Neuropsychopharmacology, 17 (2): 67-71. [PMID:9252981]
85. Liu JC, Cox RF, Greif GJ, Freedman JE, Waszczak BL. (1994) The putative dopamine D3 receptor agonist 7-OH-DPAT: lack of mesolimbic selectivity. Eur J Pharmacol, 264: 269-278. [PMID:7698165]
86. Liu LX, Monsma Jr FJ, Sibley DR, Chiodo LA. (1996) D2L, D2S, and D3 dopamine receptors stably transfected into NG108-15 cells couple to a voltage-dependent potassium current via distinct G protein mechanisms. Synapse, 24 (2): 156-64. [PMID:8890457]
87. Liu XY, Mao LM, Zhang GC, Papasian CJ, Fibuch EE, Lan HX, Zhou HF, Xu M, Wang JQ. (2009) Activity-dependent modulation of limbic dopamine D3 receptors by CaMKII. Neuron, 61 (3): 425-38. [PMID:19217379]
88. Luippold G, Beilharz M, Wehrmann M, Unger L, Gross G, Mühlbauer B. (2005) Effect of dopamine D3 receptor blockade on renal function and glomerular size in diabetic rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol, 371 (5): 420-7. [PMID:15887004]
89. Lévesque D, Diaz J, Pilon C, Martres MP, Giros B, Souil E, Schott D, Morgat JL, Schwartz JC, Sokoloff P. (1992) Identification, characterization, and localization of the dopamine D3 receptor in rat brain using 7-[3H]hydroxy-N,N-di-n-propyl-2-aminotetralin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 89 (17): 8155-9. [PMID:1518841]
90. MacKenzie RG, VanLeeuwen D, Pugsley TA, Shih YH, Demattos S, Tang L, Todd RD, O'Malley KL. (1994) Characterization of the human dopamine D3 receptor expressed in transfected cell lines. Eur J Pharmacol, 266 (1): 79-85. [PMID:7907989]
91. Maggio R, Scarselli M, Novi F, Millan MJ, Corsini GU. (2003) Potent activation of dopamine D3/D2 heterodimers by the antiparkinsonian agents, S32504, pramipexole and ropinirole. J Neurochem, 87 (3): 631-41. [PMID:14535946]
92. Malmberg A, Jackson DM, Eriksson A, Mohell N. (1993) Unique binding characteristics of antipsychotic agents interacting with human dopamine D2A, D2B, and D3 receptors. Mol Pharmacol, 43 (5): 749-54. [PMID:8099194]
93. Mant R, Williams J, Asherson P, Parfitt E, McGuffin P, Owen MJ. (1994) Relationship between homozygosity at the dopamine D3 receptor gene and schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet, 54 (1): 21-6. [PMID:7909989]
94. McAllister G, Knowles MR, Ward-Booth SM, Sinclair HA, Patel S, Marwood R, Emms F, Patel S, Smith A, Seabrook GR et al.. (1995) Functional coupling of human D2, D3, and D4 dopamine receptors in HEK293 cells. J Recept Signal Transduct Res, 15 (1-4): 267-81. [PMID:8903944]
95. McElroy J, Zeller KL, Amy KA, Ward KA, Cawley JF, Mazzola AL, Keim W, Rohrbach K. (1993) In vivo agonist properties of 7-hydroxy-N,N-Di-N-propyl-2-aminotetralin, a dopamine D3-selective receptor ligand. Drug Development Research, 30: 257-259.
96. McQuade JA, Benoit SC, Xu M, Woods SC, Seeley RJ. (2004) High-fat diet induced adiposity in mice with targeted disruption of the dopamine-3 receptor gene. Behav Brain Res, 151 (1-2): 313-9. [PMID:15084447]
97. Meade JA, Free RB, Miller NR, Chun LS, Doyle TB, Moritz AE, Conroy JL, Watts VJ, Sibley DR. (2015) (-)-Stepholidine is a potent pan-dopamine receptor antagonist of both G protein- and β-arrestin-mediated signaling. Psychopharmacology (Berl.), 232 (5): 917-30. [PMID:25231919]
98. Mierau J, Schneider FJ, Ensinger HA, Chio CL, Lajiness ME, Huff RM. (1995) Pramipexole binding and activation of cloned and expressed dopamine D2, D3 and D4 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol, 290 (1): 29-36. [PMID:7664822]
99. Millan MJ, Audinot V, Melon C, Newman-Tancredi A. (1995) Evidence that dopamine D3 receptors participate in clozapine-induced hypothermia. Eur J Pharmacol, 280 (2): 225-9. [PMID:7589191]
100. Millan MJ, Audinot V, Rivet JM, Gobert A, Vian J, Prost JF, Spedding M, Peglion JL. (1994) S 14297, a novel selective ligand at cloned human dopamine D3 receptors, blocks 7-OH-DPAT-induced hypothermia in rats. Eur J Pharmacol, 260 (2-3): R3-5. [PMID:7988633]
101. Millan MJ, Di Cara B, Dekeyne A, Panayi F, De Groote L, Sicard D, Cistarelli L, Billiras R, Gobert A. (2007) Selective blockade of dopamine D(3) versus D(2) receptors enhances frontocortical cholinergic transmission and social memory in rats: a parallel neurochemical and behavioural analysis. J Neurochem, 100 (4): 1047-61. [PMID:17266737]
102. Millan MJ, Gobert A, Newman-Tancredi A, Lejeune F, Cussac D, Rivet JM, Audinot V, Dubuffet T, Lavielle G. (2000) S33084, a novel, potent, selective, and competitive antagonist at dopamine D(3)-receptors: I. Receptorial, electrophysiological and neurochemical profile compared with GR218,231 and L741,626. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 293 (3): 1048-62. [PMID:10869410]
103. Millan MJ, Maiofiss L, Cussac D, Audinot V, Boutin JA, Newman-Tancredi A. (2002) Differential actions of antiparkinson agents at multiple classes of monoaminergic receptor. I. A multivariate analysis of the binding profiles of 14 drugs at 21 native and cloned human receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 303 (2): 791-804. [PMID:12388666]
104. Millan MJ, Peglion JL, Vian J, Rivet JM, Brocco M, Gobert A, Newman-Tancredi A, Dacquet C, Bervoets K, Girardon S. (1995) Functional correlates of dopamine D3 receptor activation in the rat in vivo and their modulation by the selective antagonist, (+)-S 14297: 1. Activation of postsynaptic D3 receptors mediates hypothermia, whereas blockade of D2 receptors elicits prolactin secretion and catalepsy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 275: 885-898. [PMID:7473180]
105. Mizuo K, Narita M, Miyatake M, Suzuki T. (2004) Enhancement of dopamine-induced signaling responses in the forebrain of mice lacking dopamine D3 receptor. Neurosci Lett, 358 (1): 13-6. [PMID:15016423]
106. Narita M, Mizuo K, Mizoguchi H, Sakata M, Narita M, Tseng LF, Suzuki T. (2003) Molecular evidence for the functional role of dopamine D3 receptor in the morphine-induced rewarding effect and hyperlocomotion. J Neurosci, 23 (3): 1006-12. [PMID:12574430]
107. Narita M, Soma M, Tamaki H, Narita M, Suzuki T. (2002) Intensification of the development of ethanol dependence in mice lacking dopamine D(3) receptor. Neurosci Lett, 324 (2): 129-32. [PMID:11988344]
108. Nürnberger A, Räbiger M, Mack A, Diaz J, Sokoloff P, Mühlbauer B, Luippold G. (2004) Subapical localization of the dopamine D3 receptor in proximal tubules of the rat kidney. J Histochem Cytochem, 52 (12): 1647-55. [PMID:15557219]
109. O'Hara CM, Uhland-Smith A, O'Malley KL, Todd RD. (1996) Inhibition of dopamine synthesis by dopamine D2 and D3 but not D4 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 277 (1): 186-92. [PMID:8613917]
110. Parsian A, Chakraverty S, Todd RD. (1995) Possible association between the dopamine D3 receptor gene and bipolar affective disorder. Am J Med Genet, 60 (3): 234-7. [PMID:7573178]
111. Parsons B, Stanley M, Javitch J. (1993) Differential visualization of dopamine D2 and D3 receptors in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol, 234 (2-3): 269-72. [PMID:8097723]
112. Patel S, Patel S, Marwood R, Emms F, Marston D, Leeson PD, Curtis NR, Kulagowski JJ, Freedman SB. (1996) Identification and pharmacological characterization of [125I]L-750,667, a novel radioligand for the dopamine D4 receptor. Mol Pharmacol, 50 (6): 1658-64. [PMID:8967990]
113. Peng XQ, Ashby Jr CR, Spiller K, Li X, Li J, Thomasson N, Millan MJ, Mocaër E, Muńoz C, Gardner EL et al.. (2009) The preferential dopamine D3 receptor antagonist S33138 inhibits cocaine reward and cocaine-triggered relapse to drug-seeking behavior in rats. Neuropharmacology, 56 (4): 752-60. [PMID:19136017]
114. Perachon S, Betancur C, Pilon C, Rostène W, Schwartz JC, Sokoloff P. (2000) Role of dopamine D3 receptors in thermoregulation: a reappraisal. Neuroreport, 11 (1): 221-5. [PMID:10683862]
115. Pilla M, Perachon S, Sautel F, Garrido F, Mann A, Wermuth CG, Schwartz JC, Everitt BJ, Sokoloff P. (1999) Selective inhibition of cocaine-seeking behaviour by a partial dopamine D3 receptor agonist. Nature, 400 (6742): 371-5. [PMID:10432116]
116. Pilon C, Lévesque D, Dimitriadou V, Griffon N, Martres MP, Schwartz JC, Sokoloff P. (1994) Functional coupling of the human dopamine D3 receptor in a transfected NG 108-15 neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cell line. Eur J Pharmacol, 268 (2): 129-39. [PMID:7957635]
117. Potenza MN, Graminski GF, Schmauss C, Lerner MR. (1994) Functional expression and characterization of human D2 and D3 dopamine receptors. J Neurosci, 14 (3 Pt 2): 1463-76. [PMID:7907363]
118. Pugsley TA, Davis MD, Akunne HC, MacKenzie RG, Shih YH, Damsma G, Wikstrom H, Whetzel SZ, Georgic LM, Cooke LW et al.. (1995) Neurochemical and functional characterization of the preferentially selective dopamine D3 agonist PD 128907. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 275 (3): 1355-66. [PMID:8531103]
119. Reavill C, Taylor SG, Wood MD, Ashmeade T, Austin NE, Avenell KY, Boyfield I, Branch CL, Cilia J, Coldwell MC et al.. (2000) Pharmacological actions of a novel, high-affinity, and selective human dopamine D(3) receptor antagonist, SB-277011-A. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 294 (3): 1154-65. [PMID:10945872]
120. Ricci A, Vega JA, Mammola CL, Amenta F. (1995) Localisation of dopamine D3 receptor in the rat cerebellar cortex: a light microscope autoradiographic study. Neurosci Lett, 190 (3): 163-6. [PMID:7637884]
121. Ricci A, Veglio F, Amenta F. (1995) Radioligand binding characterization of putative dopamine D3 receptor in human peripheral blood lymphocytes with [3H]7-OH-DPAT. J Neuroimmunol, 58 (2): 139-44. [PMID:7759603]
122. Rivet JM, Audinot V, Gobert A, Peglion JL, Millan MJ. (1994) Modulation of mesolimbic dopamine release by the selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonist, (+)-S 14297. Eur J Pharmacol, 265 (3): 175-7. [PMID:7875234]
123. Sanger DJ, Depoortere R, Perrault G. (1996) Evidence for a role for dopamine D3 receptors in the effects of dopamine agonists on operant behaviour in rats. Behav Pharmacol, 7 (5): 477-482. [PMID:11224444]
124. Sautel F, Griffon N, Lévesque D, Pilon C, Schwartz JC, Sokoloff P. (1995) A functional test identifies dopamine agonists selective for D3versus D2receptors. Neuroreport, 6: 329-332. [PMID:7756621]
125. Sautel F, Griffon N, Sokoloff P, Schwartz JC, Launay C, Simon P, Costentin J, Schoenfelder A, Garrido F, Mann A et al.. (1995) Nafadotride, a potent preferential dopamine D3 receptor antagonist, activates locomotion in rodents. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 275 (3): 1239-46. [PMID:8531087]
126. Schmauss C, Haroutunian V, Davis KL, Davidson M. (1993) Selective loss of dopamine D3-type receptor mRNA expression in parietal and motor cortices of patients with chronic schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 90 (19): 8942-6. [PMID:8415635]
127. Schotte A, Janssen PF, Gommeren W, Luyten WH, Van Gompel P, Lesage AS, De Loore K, Leysen JE. (1996) Risperidone compared with new and reference antipsychotic drugs: in vitro and in vivo receptor binding. Psychopharmacology (Berl.), 124 (1-2): 57-73. [PMID:8935801]
128. Seabrook GR, Patel S, Marwood R, Emms F, Knowles MR, Freedman SB, McAllister G. (1992) Stable expression of human D3 dopamine receptors in GH4C1 pituitary cells. FEBS Lett, 312 (2-3): 123-6. [PMID:1330688]
129. Seeman P. (2001) Antipsychotic drugs, dopamine receptors, and schizophrenia. Clinical Neuroscience Research, 1 (1-2): 53-60. DOI: 10.1016/S1566-2772(00)00007-4
130. Shahid M, Walker GB, Zorn SH, Wong EH. (2009) Asenapine: a novel psychopharmacologic agent with a unique human receptor signature. J Psychopharmacol (Oxford), 23 (1): 65-73. [PMID:18308814]
131. Skaaning Jensen B, Levavi-Sivan B, Fishburn CS, Fuchs S. (1997) Functional expression of the murine D2, D3, and D4 dopamine receptors in Xenopus laevis oocytes. FEBS Lett, 420: 191-195. [PMID:9459308]
132. Sokoloff P, Andrieux M, Besançon R, Pilon C, Martres MP, Giros B, Schwartz JC. (1992) Pharmacology of human dopamine D3 receptor expressed in a mammalian cell line: comparison with D2 receptor. Eur J Pharmacol, 225 (4): 331-7. [PMID:1354163]
133. Sokoloff P, Giros B, Martres MP, Bouthenet ML, Schwartz JC. (1990) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dopamine receptor (D3) as a target for neuroleptics. Nature, 347 (6289): 146-51. [PMID:1975644]
134. Sokoloff P, Leriche L, Diaz J, Louvel J, Pumain R. (2013) Direct and indirect interactions of the dopamine D₃ receptor with glutamate pathways: implications for the treatment of schizophrenia. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol, 386 (2): 107-24. [PMID:23001156]
135. Song R, Zhang HY, Li X, Bi GH, Gardner EL, Xi ZX. (2012) Increased vulnerability to cocaine in mice lacking dopamine D3 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 109 (43): 17675-80. [PMID:23045656]
136. Spetea M, Berzetei-Gurske IP, Guerrieri E, Schmidhammer H. (2012) Discovery and pharmacological evaluation of a diphenethylamine derivative (HS665), a highly potent and selective κ opioid receptor agonist. J Med Chem, 55 (22): 10302-6. [PMID:23134120]
137. Starr MS, Starr BS. (1995) Motor actions of 7-OH-DPAT in normal and reserpine-treated mice suggest involvement of both dopamine D2 and D3 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol, 277 (2-3): 151-8. [PMID:7493603]
138. Steiner H, Fuchs S, Accili D. (1997) D3 dopamine receptor-deficient mouse: evidence for reduced anxiety. Physiol Behav, 63 (1): 137-41. [PMID:9402626]
139. Svensson K, Carlsson A, Huff RM, Kling-Petersen T, Waters N. (1994) Behavioral and neurochemical data suggest functional differences between dopamine D2 and D3 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol, 263 (3): 235-43. [PMID:7843260]
140. Svensson K, Carlsson A, Waters N. (1994) Locomotor inhibition by the D3 ligand R-(+)-7-OH-DPAT is independent of changes in dopamine release. J Neural Transm Gen Sect, 95 (1): 71-4. [PMID:7857588]
141. Tang L, Todd RD, Heller A, O'Malley KL. (1994) Pharmacological and functional characterization of D2, D3 and D4 dopamine receptors in fibroblast and dopaminergic cell lines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 268 (1): 495-502. [PMID:8301592]
142. Tang L, Todd RD, O'Malley KL. (1994) Dopamine D2 and D3 receptors inhibit dopamine release. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 270 (2): 475-9. [PMID:8071839]
143. Tice MA, Hashemi T, Taylor LA, Duffy RA, McQuade RD. (1994) Characterization of the binding of SCH 39166 to the five cloned dopamine receptor subtypes. Pharmacol Biochem Behav, 49 (3): 567-71. [PMID:7862709]
144. Van Tol HH, Bunzow JR, Guan HC, Sunahara RK, Seeman P, Niznik HB, Civelli O. (1991) Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D4 receptor with high affinity for the antipsychotic clozapine. Nature, 350 (6319): 610-4. [PMID:1840645]
145. von Coburg Y, Kottke T, Weizel L, Ligneau X, Stark H. (2009) Potential utility of histamine H3 receptor antagonist pharmacophore in antipsychotics. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 19 (2): 538-42. [PMID:19091563]
146. Waters N, Löfberg L, Haadsma-Svensson S, Svensson K, Sonesson C, Carlsson A. (1994) Differential effects of dopamine D2 and D3 receptor antagonists in regard to dopamine release, in vivo receptor displacement and behaviour. J Neural Transm Gen Sect, 98 (1): 39-55. [PMID:7710738]
147. Waters N, Svensson K, Haadsma-Svensson SR, Smith MW, Carlsson A. (1993) The dopamine D3-receptor: a postsynaptic receptor inhibitory on rat locomotor activity. J Neural Transm Gen Sect, 94 (1): 11-9. [PMID:8129881]
148. Werner P, Hussy N, Buell G, Jones KA, North RA. (1996) D2, D3, and D4 dopamine receptors couple to G protein-regulated potassium channels in Xenopus oocytes. Mol Pharmacol, 49 (4): 656-61. [PMID:8609893]
149. Xi ZX, Gardner EL. (2007) Pharmacological actions of NGB 2904, a selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonist, in animal models of drug addiction. CNS Drug Rev, 13 (2): 240-59. [PMID:17627675]
150. Xi ZX, Gilbert J, Campos AC, Kline N, Ashby Jr CR, Hagan JJ, Heidbreder CA, Gardner EL. (2004) Blockade of mesolimbic dopamine D3 receptors inhibits stress-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl.), 176 (1): 57-65. [PMID:15083257]
151. Xiao J, Free RB, Barnaeva E, Conroy JL, Doyle T, Miller B, Bryant-Genevier M, Taylor MK, Hu X, Dulcey AE et al.. (2014) Discovery, optimization, and characterization of novel D2 dopamine receptor selective antagonists. J Med Chem, 57 (8): 3450-63. [PMID:24666157]
152. Xu M, Caine SB, Cooper DC, Gold LH, Graybiel AM, Hu XT, Loeltzow T, Koob GF, Moratalla R, White FJ, Tonegawa S. (1995) Analysis of dopamine D3 and D1 receptor mutant mice. (Abstract) Soc Neurosci Abst, 21: 363-.
153. Xu M, Koeltzow TE, Santiago GT, Moratalla R, Cooper DC, Hu XT, White NM, Graybiel AM, White FJ, Tonegawa S. (1997) Dopamine D3 receptor mutant mice exhibit increased behavioral sensitivity to concurrent stimulation of D1 and D2 receptors. Neuron, 19 (4): 837-48. [PMID:9354330]
154. Yamada S, Yokoo H, Nishi S. (1994) Differential effects of dopamine agonists on evoked dopamine release from slices of striatum and nucleus accumbens in rats. Brain Res, 648 (1): 176-9. [PMID:7922522]
155. Yu C, Yang Z, Ren H, Zhang Y, Han Y, He D, Lu Q, Wang X, Wang X, Yang C et al.. (2009) D3 dopamine receptor regulation of ETB receptors in renal proximal tubule cells from WKY and SHRs. Am J Hypertens, 22 (8): 877-83. [PMID:19390510]
156. Zhang Y, Fu C, Asico LD, Villar VA, Ren H, He D, Wang Z, Yang J, Jose PA, Zeng C. (2011) Role of Gα(12)- and Gα(13)-protein subunit linkage of D(3) dopamine receptors in the natriuretic effect of D(3) dopamine receptor in kidney. Hypertens Res, 34 (9): 1011-6. [PMID:21633357]
157. Zhen J, Antonio T, Dutta AK, Reith ME. (2010) Concentration of receptor and ligand revisited in a modified receptor binding protocol for high-affinity radioligands: [3H]Spiperone binding to D2 and D3 dopamine receptors. J Neurosci Methods, 188 (1): 32-8. [PMID:20122961]